| Branch | Pipeline |
|---|---|
| master | |
| release | |
| milestone/1.0.0 |
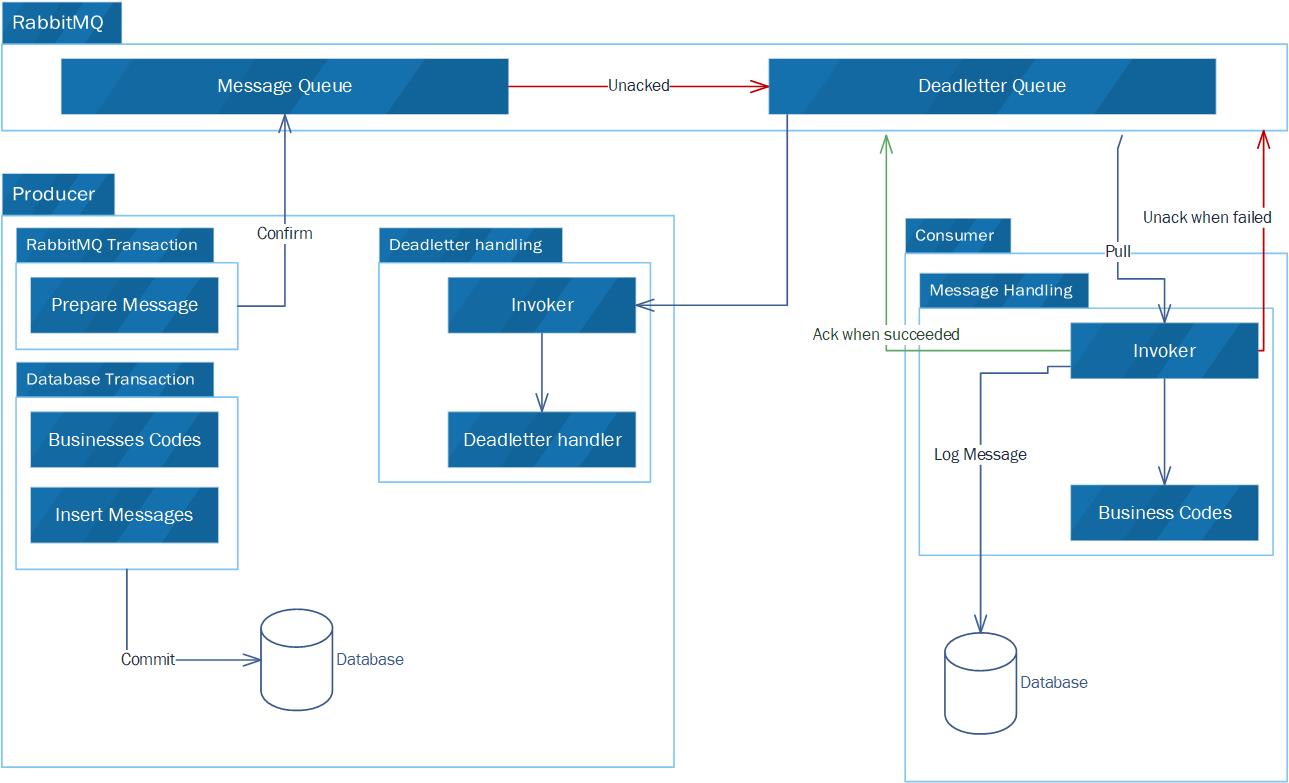
EventBus is a .Net Standard library to achieve eventually consistent in distributed architectures system like SOA,MicroService. It is lightweight,easy to use and efficiently.
*** Add following code after services.AddDbContext in StartUp.cs ***
services.AddEventBus(options =>
{
// using EntityFramework
options.UseEntityframework<**Your DbContext Type**>();
// OR using Ado.NET
options.UseMySQL(**Database connection string**)
// using RabbitMQ
options.UseRabbitMQ(rabbit =>
{
rabbit.HostName = "**Your hostname of RabbitMQ**";
rabbit.UserName = "**Your username if needed**";
rabbit.Password = "**Your password if needed**";
});
});*** Add following codes in Configure scope of StartUp.cs ***
app.UseEventBus();- Inject
IEventPublisherin constructor like.ctor(IEventPublisher eventPublisher) - Begin a transaction
- using EntityFramework
using(var transaction = dbContext.Database.BeginTransaction)
{
//TODO:Businesses codes
//Publish Event
await _eventPublisher.PrepareAsync(/*RouteKey*/, /*Content Object*/, /*MetaData Object*/);
//Commit transaction
transaction.Commit();
//Confirm Published Event.The event message won't publish untill invoked **IEventPublisher.ConfirmAsync()**
//And you can decide when the event message be confirmed all by your self.
await _eventPublisher.ConfirmAsync();
//Or you can just rollback these messages when exception was thrown.
await _eventPublisher.RollbackAsync();
}- using Ado.NET
IDbConnection dbConnection; /*Open your database connection.*/
IDbTransaction dbTransaction = dbConnection.BeginTransaction();
//TODO:Businesses codes
//Publish Event
await _eventPublisher.PrepareAsync(/*RouteKey*/, /*Content Object*/, /*MetaData Object*/,dbConnection,dbTransaction);
//Commit transaction
dbTransaction.Commit();
dbConnection.Close();
//Confirm Published Event.The event message won't publish untill invoked **IEventPublisher.ConfirmAsync()**
//And you can decide when the event message should be confirmed all by your self.
await _eventPublisher.ConfirmAsync();
//Or you can just rollback these messages when exception was thrown.
await _eventPublisher.RollbackAsync();- Declare a callback handler class implemented
IFailureHandler - Register callback handle in
AddEventBusscope
options.UseFailureHandle(failure =>
{
failure.RegisterFailureCallback(/*RouteKey*/, /*Type of your deadletter callback handler*/);
});- Declare a callback handler class implemented
ISubscribeCallbackHandler - Register callback handle in
StartUp.cs
services.AddSub(options =>
{
options.ConsumerClientCount = 1;
options.DefaultGroup = "/*Default Group Name*/";
// Use default group
options.RegisterCallback(/*RouteKey*/, /*Type of your callback handler*/);
// Use specialized group
options.RegisterCallback(/*RouteKey*/,/*Group Name*/ /*Type of your callback handler*/);
});