-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 157
BESS Overview
Justine Sherry edited this page Feb 9, 2017
·
13 revisions
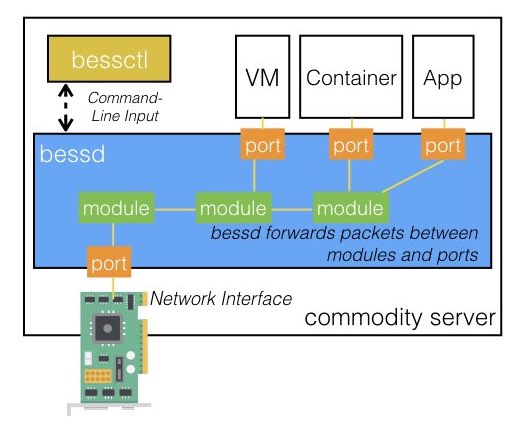
BESS is a software switch designed to be extensible and high performance. BESS is the first software switch designed specifically to support Network Functions Virtualization, in addition to traditional virtual networking tasks.
To get started with BESS, you should know about four key components of BESS:
- bessd: the "BESS daemon" is the core software switch. The daemon itself carries packets between ports and modules.
- ports: ports are places that packets may enter or exit bessd. A port can connect to a network interface, to a virtual machine, to a containerized app, or a normal process running in user space.
- modules: modules are chunks of code that allow bessd to inspect or modify packets. Modules receive and release packets via input and output gates. Some built-in modules include:
-
- A round-robin module, which receives packets on one input gate and releases packets in a round-robin fashion over multiple output gates.
-
- An ACL module, which receives packets on one input gate, and checks whether the packet header matches a blacklisted firewall rule. Packets which match a blacklisted rule are released on one gate, packets which do not match any blacklisted rule are released on another gate.
- bessctl: this is the controller for bessd. bessctl offers a command-line interface allowing an administrator to configure which ports are connected to which modules, inspect where traffic is flowing within bessd, and a variety of other useful administrative commands.