- What is Elasticsearch?
- Elastic Stack
- Elasticsearch Basic Concept
- What is Lucene?
- Inverted Index
- Index Modules
- Document Operations
- Query DSL
Elasticsearch 是一個非常強大的 real-time distributed serach engine, 基於 Lucene 實現
其主要被應用於 full-text search, structural search 及 analytics
除了 search, 結合 Kibana, Logstash, Beats 等 open source 產品, Elastic Stack(ELK) 還被廣泛運用在大數據實時分析領域, 包括 log analysis, metrics monitor, infomation security 等
ELK 可以完成海量結構化/非結構化資料搜尋, 創建可視化報表, 對監控資料設定報警閾值, 或通過 mechina learning 來自動識別異常狀況
Elasticsearch 是基於 Restful API, 使用 Java 開發的 search engine, 並作為 Apache Lisence release
根據 DB Engine 排名顯示, Elasticsearch 為最受歡迎的企業級搜尋引擎
- 在當前軟體產業中, 搜尋為一個軟體系統或平台最基本的功能, 使用 Elasticsearch 可以創造出良好的搜尋體驗
- Elasticsearch 具備非常強大的大數據分析能力
- Elasticsearch 方便易用, 且可進行水平擴展
- Development community 活躍, 使用者基數龐大
- 擁有接近 real-time 的搜尋及分析能力
Lucene 可以算是當前最先進, 高性能且全功能的 search engine
但是 Lucene 僅為一個 library, 需要使用 Java 將 Lucene 集成到 application 中, 另外 Lucene 的工作原理十分的複雜
Elasticsearch 內部使用 Lucene 實現索引及搜尋, 透過 RESTful API 來封裝 Lucene 的複雜性, 使 full-text search 變得簡單易用
然而 Elasticsearch 不僅僅為 Lucene, 且也不僅僅為一個 full-text search engine, 其可以被以下三點精準定位:
- distributed real-time documents storage, 每個 field 都可以被索引及搜尋
- distributed real-time analytic search engine
- 能支撐上百個節點擴充, 並支持 PB 級結構化或非結構化資料儲存
Beats + Logstash + Elasticsearch + Kibana
Beats 是一個輕量型採集器平台, 這些採集器可以從 edge mechine 向 Logstash 或 Elasticsearch 發送資料, 期由 Go 進行開發, 運行效率較高, 不同的 beats 套件針對不同的 data source
Logstash 是動態資料收集管道, 擁有可擴充的 plugin 生態, 支持從不同來源收集資料並轉換, 最後將資料發送到不同的資料庫中, 能與 Elasticsearch 產生強大的協同作用, 在 2013 年被 Elastic 公司收購
其具有以下特性:
- 實時解析與轉化資料
- 可擴展性
- 可用性, 會通過持久話隊列來保證至少將運行中的事件送達一次
- 安全性, 可對資料進行傳輸加密
- 可監控
Elasticsearch 可對資料進行搜尋, 分析和儲存, 其是基於 JSON 的分散式搜尋和分析引擎, 專門為了實現水平擴展性, 高可用性及管理便攜性而設計
其實現原理主要分為以下幾個步驟:
- 將資料提交到 Elasticsearch 中
- 通過分詞器將對應語句分詞
- 將分詞結果及權重一並存入, 在搜尋資料時根據權重將結果排名並返回
Kibana 實現資料可視化, 其作用為將 Elasticsearch 中的資料以圖表的形式呈現, 且具有可擴展的使用者介面, 可以配置並管理 Elasticsearch
Kibana 最早是基於 Logstash 創建的工具, 後被 Elastic 公司於 2013 年收購
- Security
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Encryption
- Layerd security
- Alerting
- Monitoring
- Reporting
- Graph analytics
- dedicated APM UIs
- Machine Learning
- Near Realtime(NRT): 接近 real-time, 資料在 summit index 後馬上就可以搜尋到
- Cluster: 一個 cluster 有一個 unique identifier, default 為
elasticsearch, 具有相同 cluster name 的 nodes 才會組成一個 cluster - Node: 儲存 cluster data, 參與 cluster 索引和搜尋功能, node name default 為啟動時以一個隨機的 UUID 前七個字符, 通過 cluster name 在網絡中發現 member 並組成 cluster, single node 也可以為 cluster
- Index: 一個 index 為一個 document 集合, 每個 index 有 unique name, 一個 cluster 中可以有任意多個 index
- Document: 被索引的一筆資料, 索引的基本資料單元, 以
JSON格式表示 - Shard: 在創建一個 index 時可以指定分成多少個 shard 來儲存, 每個 shard 本身也是一個功能完善且獨立的
"index", 可以被放置在 cluster 的任意 node 上
| RDBMS | Elasticserach |
|---|---|
| database | index |
| table | type(6.0.0 deprecated) |
| row | document |
| column | field |
| schema | mapping |
| index | reverse index |
| SQL | DSL |
| SELECT * FROM table | GET http://... |
| UPDATE table SET | PUT http://... |
| DELETE | DELETE http://... |
這邊先提出以下問題, 介紹完 ElasticSearch 底層工作原理再回來一一解答:
- 為什麼搜尋
*foo-bar*無法匹配foo-bar? - 為什麼增加更多的 document 會壓縮 index?
- 為什麼 ElasticSearch 需要佔用很大的記憶體空間?
Cluster in the cloud:
Cloud 中每個正方形都代表一個 es node:
在一個或多個 node 之間, 多個綠色方塊組合成一個 index:
在一個 index 中, 分布在多個 node 裡的綠色方塊稱為 shard:
一個 Elasticsearch Shard 本質上為一個 Lucene Index
Lucene為一個 search library, Elasticsearch 是基於 Lucene 建立的, 接下來的故事要說明 Elasticsearch 是如何基於 Lucene 工作
Lucene 中有許多小的 segment, 可以將其看成 Lucene 內部的 mini-index:
Segment 中有許多種類的資料結構: Inverted Index, Stored Fields, Document Values, Cache:
最重要的 Inverted Index:
Inverted Index 主要包含兩部分:
- 有序的
Dictionary(包含 term & frequency) - 與
Term對應的Postings(即存在這個 term 的文件)
搜尋時會先將搜尋的內容分解, 然後在 Dictionary 中找到對應的 Term, 進而查找到與搜尋內容相關的文件內容:
查詢 the fury:
AutoCompletion-Prefix: 若想查找以字母 c 開頭的 term, 可以簡單地通過 Binary Search 在 Inverted Index 中找到如 choice, coming 這樣的 term
昂貴搜尋: 若想要搜尋所有包含 our 的 term, 則需要 scan 整個 Inverted Index
這種情況若想優化, 可以思考如何生成合適的 term:
-
若想以
postfix作為查詢條件, 可以為 term 做反向處理:* suffix -> xiffus * -
可以將
GEO資訊轉換為GEO Hash:(60.6384, 6.5017) -> u4u8gyykk -
對於簡單數字可以為其生成多種形式的 term:
123 -> {1-hundreds, 12-tens, 123}
若想要搜尋包含某個特定內容的文件時, Inverted Index 就無法很好的解決問題, 因此 Lucene 另外提供了一種資料結構 Stored Fields 來解決這個問題
本質上 Stored Fields 是一個簡單的 key-value, 默認情況下 Elasticsearch 會儲存整個文件的 JSON source
上述兩種資料結構仍無法解決如排序, 聚合, facet 等問題, 因為可能會需要讀取大量不需要使用的資料
Document Values 主要被設計來解決以上問題, 其本質上是一個 Column-oriented Storage, 高度優化了具有相同型別資料的儲存結構
為了提升效率, Elasticsearch 可以將 index 中某個 document value 全部讀到記憶體中進行操作, 如此一來大大提升訪問速度, 但同時也會消耗大量記憶體空間
以上資料結構包括
Inverted Index,Stored Fields,Document Values及其 cache, 都在segment內部
搜尋時 Lucene 會搜尋所有的 segment, 並將每個 segment 的搜尋結果合併返回
Lucene 的一些特性使得這個過程非常重要:
- Segments are
immutable- 當刪除 documents 時, Lucene 只是將其標誌為刪除, 但檔案本身不會發生改變
- 當更新 documents 時, 本質上 Lucene 是先將 document 刪除, 再
Re-index
- Lucene 非常擅長資料壓縮
- Cache everything
當 Elasticsearch index 一個 document 時, 會為 document 建立對應的 cache, 並定期(s) 刷新資料:
segments 會隨著時間越來越多...
Elasticsearch 會將這些 segment 合併為新的 segment:
Elasticsearch 在 shard 中的搜尋過程與 Lucene Segment 搜尋過程類似:
與 Lucene Segment 搜尋不同在於, shard 可以分佈在不同的 node 上, 所以在搜尋並返回結果時所有的資料都需通過網絡傳輸
還有一點需要特別注意:
一次搜尋查照兩個 shard 等價於兩次分別搜尋 shard
Cluster 擴充時 shard 不會進行更近一步的拆分, 但是可能會被轉移到不同的 node 上:
可以為更重要的 index node 分配行能更佳的機器, 並確保每個 shard 都有 replication:
Query request 可能被分發到 cluster 中任意一個 node:
此時這個 node 就成為當前 request 的 coordinator:
Coordinator 會根據 index 資訊判斷 request routing 到哪個 node, 及判斷哪個 replication 為可用:
Elasticsearch 會將 Query 轉換成 Lucene Query:
並在所有的 segment 中執行計算:
Lucene 對於 filter 也會產生 cache(Filter PerSegment Cache):
查詢結束後, 結果會沿著下行路徑向上逐層返回:
Index structure in Lucene:
Index structure files:
| Name | Extension | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|
| Segments File | segments_N | Stores |
| Lock File | write.lock | The Write lock prevents multiple IndexWriters from writing to the same file. |
| Segment Info | .si | Stores metadata about a segment |
| Compound File | .cfs, .cfe | An optional "virtual" file consisting of all the other index files for systems that frequently run out of file handles. |
| Fields | .fnm | Stores information about the fields |
| Field Index | .fdx | Contains pointers to field data |
| Field Data | .fdt | The stored fields for documents |
| Term Dictionary | .tim | The term dictionary, stores term info |
| Term Index | .tip | The index into the Term Dictionary |
| Frequencies | .doc | Contains the list of docs which contain each term along with frequency |
| Positions | .pos | Stores position information about where a term occurs in the index |
| Payloads | .pay | Stores additional per-position metadata information such as character offsets and user payloads |
| Norms | .nvd, .nvm | Encodes length and boost factors for docs and fields |
| Per-Document Values | .dvd, .dvm | Encodes additional scoring factors or other per-document information. |
| Term Vector Index | .tvx | Stores offset into the document data file |
| Term Vector Data | .tvd | Contains term vector data. |
| Live Documents | .liv | Info about what documents are live |
| Point values | .dii, .dim | Holds indexed points, if any |
Index files relationship:
當一段文字導入到 Elasticsearch 中, 會需要經過一段 indexing 的過程
Inverted Index 類似於在書結尾處所看到的 index, 其主要負責將 document 中出現過的 term 映射到 document:
舉例來說, 可以從以下字符串來構建 Inverted Index:
Elasticsearch 會根據建立 index 的三個 documents 中來構建 Inverted Index:
| Term | Frequency | Document (postings) |
|---|---|---|
| choice | 1 | 3 |
| day | 1 | 2 |
| is | 3 | 1,2,3 |
| it | 1 | 1 |
| last | 1 | 2 |
| of | 1 | 2 |
| sunday | 2 | 1,2 |
| the | 3 | 2,3 |
| tomorrow | 1 | 1 |
| week | 1 | 2 |
| yours | 1 | 3 |
與常規的根據 document id 來查詢 term 相反, Inverted Index 是根據 term 來查詢對應的 document ids
需注意以下幾點:
- 刪除符號並小寫後, document 會按照 term 進行細分
- term 會以字母順序排序
Frequency代表該 term 在整個 document set 中出現的次數Posting list主要紀錄該 term 的確切位置 (document offset)
默認情況下 Elasticsearch 會為 document 中所有的 field 構建 Inverted Index, 並指向該 field 所在的 document
Lucene 在資料寫入後會根據原始數據進行分詞, 並生成 posting list
查詢時會先通過 inverted index 找到資料位置(DocID) 再讀取原始資料(column/row based)
由於 Lucene 會為原始資料中每個 term 生成 inverted index, 資料量非常大, 所以 inverted index 對應的 posting list 則會存放在 disk 上
因此若每次查詢都直接讀取 disk 上的 posting list, 會產生大量的 disk I/O 嚴重影響查詢效能
為了解決 disk I/O 的問題, Lucene 引入了 secondary index FST(Finite State Transducer), 不但壓縮了儲存空間, 且大幅提升查詢效能
FST 在 Lucene 中扮演非常重要的角色, 主要用於在龐大的 term dictionary 中快速定位 term 的位置
FST 可以實現 key-value mapping, 相對於 hashmap 和 treemap 來說, FST 在查詢效率上稍遜於兩者, 但在空間效率上則是遠勝於兩者
FST達到了保證 term 查詢效率的前提下, 盡可能縮減儲存空間的目的
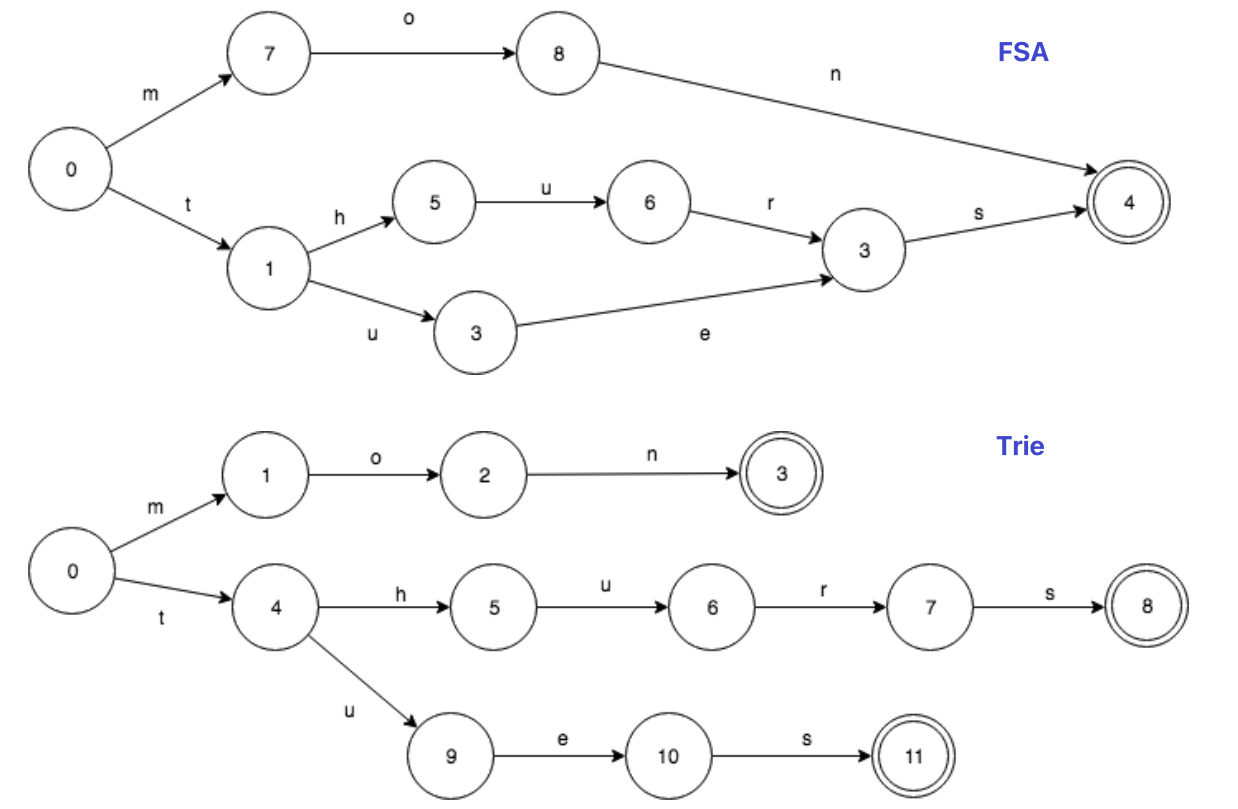
與 Trie Tree 不同點在於, FST 不僅共享前綴, 還共享後綴:
其在 Lucene 中實現原理如下:
- 將
term dictionary拆分成多個 block, 每個 block 包含 25~48 個 terms(Allen 和 After 組成一個 block) - 將每個 block 所有 terms 的公共前綴抽出來(Allen 和 After 公共前綴為 A)
- 為了加速查詢效能,
FST永駐heap, 無法被GC - 查詢時先通過 term 查詢 memory 中的 FST, 找到該 term 對應的 block address, 再讀取 disk 上的 term dictionary, 將 block 加載至 memory 遍歷(
O(logN)), 按照一定排序規則生成 DocID 的priority queue, 並按priority queue循序讀取 disk 中的 raw data(column/row based)
Index Modules are modules created per index and control all aspects related to an index.
在之前新增 document 時, 使用下面的方式會動態創建一個 customer 的 index:
curl -X POST "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/sh' -d'
{
"name": "John Doe"
}
'這個 index 實際上已經自動創建了一個 mapping:
{
"mappings": {
"_doc": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}如果需要對建立 index 的過程做更多的控制, 如想要確保這個 index 有數量適中的主分片, 且在新增任何資料之前分析器和 mapping 都已經被建立好, 就需要 import 兩點:
- 禁止自動創建 index
- 手動設定並創建 index
可以通過在 config/elasticsearch.yaml 的每個節點下添加下面的配置:
action.auto_create_index: false在 request body 中添加設置或是型別 mapping, 如下所示:
PUT /my_index
{
"settings": { ... any settings ... },
"mappings": {
"properties": { ... any properties ... }
}
}- settings: 設置 shards, replications 等配置資訊
- mappings: field mapping, type 等
- properties: object fields or nested fields
# create index test_index
PUT /test_index?pretty
{
# index settings
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": 1, # shard 數量為 1, default 5
"number_of_replicas": 1 # replication 數量 1, default 1
}
},
# index mapping
"mappings": {
"_doc": { # 型別, 建議設置為 _doc
"dynamic": false, # 動態映射配置
# field properties
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "integer" # 表示 field id 型別為 integer
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word", # 儲存時使用的分詞器
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart" # 查詢時使用的分詞器
},
"createAt": {
"type": "date"
}
}
}
}
}❗️NOTE:
dynamic為動態映射配置, 有三種狀態: true, 動態新增新的 field; false, 忽略新的 field, 不會新增 field mapping, 但會存在於_source中; strict, 若遇到新 field 會拋出 exception
output:
{
"acknowledged": true, # 是否在 cluster 中成功創建 index
"shards_acknowledged": true,
"index": "test_index"
}# 查看 index
GET /test_index
# 可以同時查看多個 index
GET /test_index,other_index
# 查看所有 index
GET /_cat/indices?voutput:
{
"test_index": {
"aliases": {},
"mappings": {
"_doc": {
"dynamic": "false",
"properties": {
"createAt": {
"type": "date"
},
"id": {
"type": "integer"
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart"
}
}
}
},
"settings": {
"index": {
"creation_date": "1589271136921",
"number_of_shards": "1",
"number_of_replicas": "1",
"uuid": "xueDIxeUQnGBQTms65wA6Q",
"version": {
"created": "6050499"
},
"provided_name": "test_index"
}
}
}
}ES 提供了一系列針對 index 修改的語法, 包括 replication 數量, 新增 field, refresh_interval, index parser, aliases 等配置的修改
# 修改 replication
PUT /test_index/_settings
{
"index" : {
"number_of_replicas" : 2
}
}
# 修改 shard 刷新時間, default 為 1s
PUT /test_index/_settings
{
"index" : {
"refresh_interval" : "2s"
}
}
# 新增 field age
PUT /teset_index/_mapping/_doc
{
"properties": {
"age": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}修改完成後再次查看 index config:
GET /test_index
{
"test_index": {
"aliases": {},
"mappings": {
"_doc": {
"dynamic": "false",
"properties": {
"age": { #
"type": "integer"
},
"createAt": {
"type": "date"
},
"id": {
"type": "integer"
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart"
}
}
}
},
"settings": {
"index": {
"refresh_interval": "2s", #
"number_of_shards": "1", #
"provided_name": "test_index",
"creation_date": "1589271136921",
"number_of_replicas": "2",
"uuid": "xueDIxeUQnGBQTms65wA6Q",
"version": {
"created": "6050499"
}
}
}
}
}# 刪除 index
DELETE /test_index
# 驗證 index 是否存在
HEAD test_index
return: 404 - Not Found一旦 index 被關閉, 則此 index 只能顯示 metadata, 無法進行任何讀寫操作:
POST /test-index-users/_close關閉 index 後再插入資料:
POST /test-index-users/_doc
{
"name" : "test user2",
"age" : 18,
"remarks" : "hello user2"
}會報 index_closed_exception 錯誤
再打開 index:
POST /test-index-users/_openoutput:
{
"acknowledged" : true,
"shards_acknowledged" : true
}
此時又可以重新寫入資料:
```sh
POST /test-index-users/_doc
{
"name" : "test user2",
"age" : 18,
"remarks" : "hello user2"
}可以通過 RESTful API 的方式對 Elasticsearch document 進行操作
# 新增單筆資料並指定 document id 為 1
PUT /test_index/_doc/1?pretty
{
"name": "Regy"
}
# 新增單筆資料並自動生成 document id
POST /test_index/_doc?pretty
{
"name": "Regy2"
}
# 使用 op_type 属性,强制执行某种操作
PUT test_index/_doc/1?op_type=create
{
"name": "Regy3"
}❗️NOTE:
op_type=create強制執行時若 id 已存在, ES 會報version_conflict_engine_exception,op_type主要應用於同步資料場景
此時可以查詢資料:
GET /test_index/_doc/_search
{
"took": 1,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 2,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test_index",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"name": "Regy"
}
},
{
"_index": "test_index",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "P7-FCHIBJxE1TMY0WNGN",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"name": "Regy2"
}
}
]
}
}# 根據 id 查詢單筆資料
GET /test_index/_doc/1
# output--->
{
"_index": "test_index",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 5,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"name": "Regy-update",
"age": 18
}
}
# 獲取 index 中所有資料
GET /test_index/_doc/_search
# output--->
{
"took": 1,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 3,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test_index",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "P7-FCHIBJxE1TMY0WNGN",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"name": "Regy2"
}
},
{
"_index": "test_index",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "_update",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"name": "Regy3"
}
},
{
"_index": "test_index",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"name": "Regy-update",
"age": 18
}
}
]
}
}
# 條件查詢
GET /test_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "2"
}
}
}
# output--->
{
"took": 1,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1,
"max_score": 0.9808292,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test_index",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "P7-FCHIBJxE1TMY0WNGN",
"_score": 0.9808292,
"_source": {
"name": "Regy2"
}
}
]
}
}# 根據 id 修改單筆資料
PUT /test_index/_doc/1?pretty
{
"name": "Regy-update-after"
}
# 根據查詢條件 id=10, 修改 name=after name
POST test_index/_update_by_query
{
"script": {
"source": "ctx._source.name = params.name",
"lang": "painless",
"params":{
"name":"after name"
}
},
"query": {
"term": {
"id": "10"
}
}
}❗️NOTE: 修改語法和新增語法相同, 可以理解為根據 ID, 資料存在則更新; 不存在則新增
# 根據 id 刪除單筆資料
DELETE /test_index/_doc/1
# delete by query
POST test_index/_delete_by_query
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "2"
}
}
}POST _bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "test_test1", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "1" } }
{ "this_is_field1" : "this_is_index_value" }
{ "delete" : { "_index" : "test_test1", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "2" } }
{ "create" : { "_index" : "test_test1", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "3" } }
{ "this_is_field3" : "this_is_create_value" }
{ "update" : {"_id" : "1", "_type" : "_doc", "_index" : "test_test1"} }
{ "doc" : {"this_is_field2" : "this_is_update_value"} }
# 查詢所有資料
GET /test_test1/_doc/_search
# output--->
{
"took": 33,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 2,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test_test1",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"this_is_field1": "this_is_index_value",
"this_is_field2": "this_is_update_value"
}
},
{
"_index": "test_test1",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"this_is_field3": "this_is_create_value"
}
}
]
}
}💡 POST _bulk 做了哪些操作?
- 若 index
test_test1不存在則創建, 同時若 id=1 document 存在則更新 - 刪除 id=2 document
- 新增 id=3 document; 若 document 存在則報 exception
- 更新 id=1 document
實際環境中 bulk operation 使用較多, 其可大幅縮減 IO 以提升效率
Term-level queries 即根據結構化資料中的精確值來查找 document, 與 Full text queries 的不同之處在於, Term-level queries 不會對查詢值進行分詞, 直接於 Inverted Index 中進行精準查詢
而 Full text queries 則會先對查詢的詞進行分詞, 並對分詞結果一一於 Inverted Index 進行模糊查詢
以下設計一個測試資料集以範例說明:
PUT /test-dsl-term-level
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"programming_languages": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"required_matches": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
}
POST /test-dsl-term-level/_bulk
{ "index": { "_id": 1 }}
{"name": "Jane Smith", "programming_languages": [ "c++", "java" ], "required_matches": 2}
{ "index": { "_id": 2 }}
{"name": "Jason Response", "programming_languages": [ "java", "php" ], "required_matches": 2}
{ "index": { "_id": 3 }}
{"name": "Dave Pdai", "programming_languages": [ "java", "c++", "php" ], "required_matches": 3, "remarks": "hello world"}由於種種原因, document field 的值可能不存在:
- 原 sh 中 field 為
null或[] - 該 field 在 mapping 中被設置為
"index": false - field length 超出 mapping 中
ignore_above設置長度 - field 格式錯誤, 且 mapping 中定義
ignore_malformed
可使用 exist 來查詢 field 是否存在:
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"exists": {
"field": "remarks"
}
}
}ids 即為 search id:
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": [3, 1]
}
}
}通過 prefix 查找某個 field:
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"name": {
"value": "Jan"
}
}
}
}term 根據 Postings lists 進行精準查詢:
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"programming_languages": "php"
}
}
}依照每個查詢值進行 term query, 每個查詢值之間為 OR 關係:
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"terms": {
"programming_languages": ["php","c++"]
}
}
}The terms_set query is the same as the terms query, except you can define the number of matching terms required to return a document.
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"terms_set": {
"programming_languages": {
"terms": [ "java", "php" ],
"minimum_should_match_field": "required_matches"
}
}
}
}Returns documents that contain terms matching a wildcard pattern.
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"name": {
"value": "D*ai",
"boost": 1.0,
"rewrite": "constant_score"
}
}
}
}Returns documents that contain terms within a provided range.
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"required_matches": {
"gte": 3,
"lte": 4
}
}
}
}Returns documents that contain terms matching a regular expression.
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"regexp": {
"name": {
"value": "Ja.*",
"case_insensitive": true
}
}
}
}Returns documents that contain terms similar to the search term, as measured by a Levenshtein edit distance.
GET /test-dsl-term-level/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"remarks": {
"value": "hell"
}
}
}
}