Essentially you precompile the entire app into static javascript, html and css, which is just fetched by the client. No server required, although needs to be hosted somewhere.
Advantages
- Quick to get going
- Can quickly show a prototype
- Can deliver and test simple functionality, UX
- Very agile as we can strap on a lot of the frontend to a backend later if need be
- Technology agnostic
Disadvantages
- Doesn't allow for extended functionality
- No application state
- Too simple

Advantages
- Simple overall architecture
- Familiar to most
- Fulfills full brief. Can do everything required through this structure
- Technology agnostic, (Django, Rust, node.js all options..)
Disadvantages
- Slightly poorer UX, because requires full rerender for updates to application state.
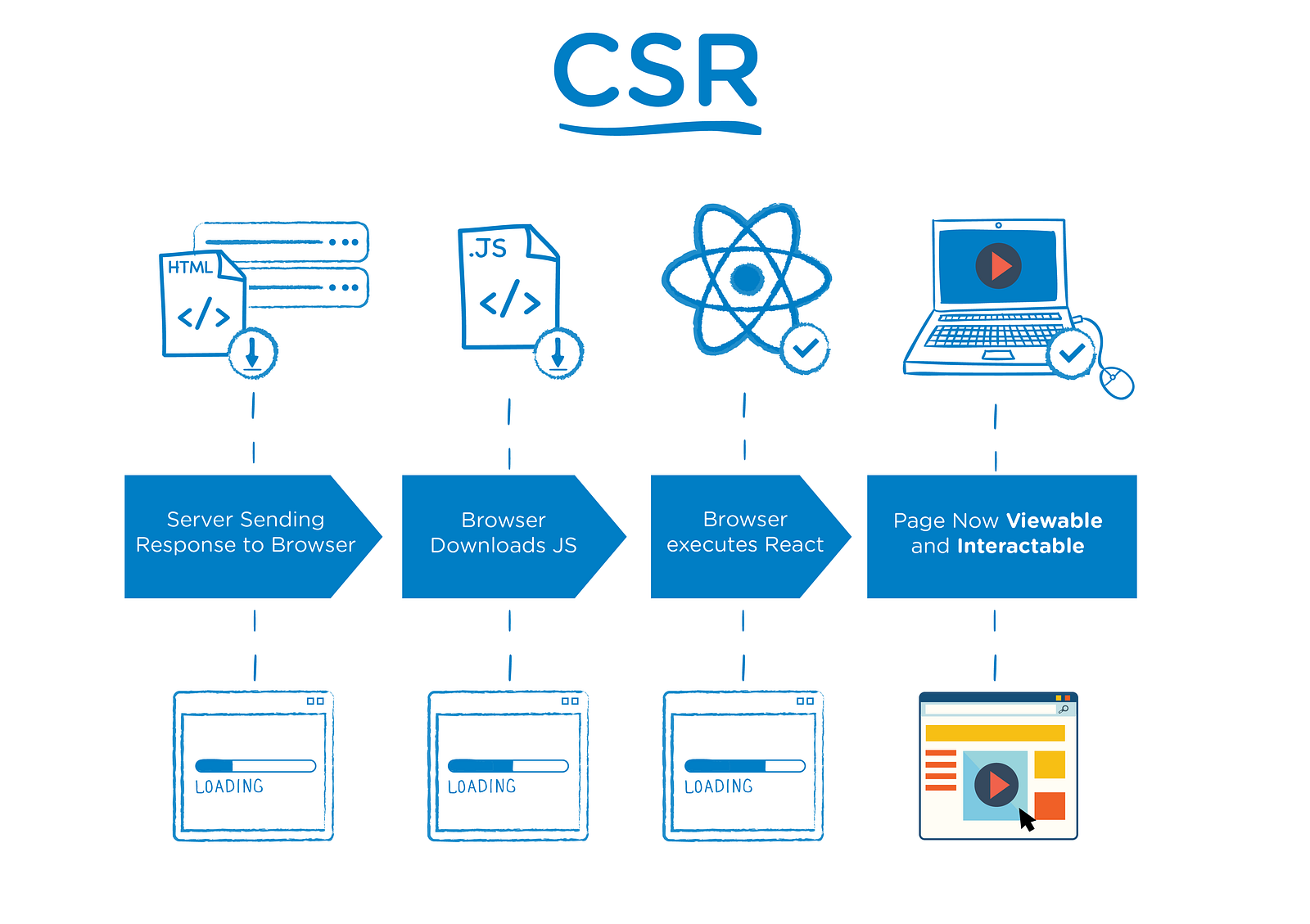
Advantages
- Simple overall architecture
- Mixed technology stack, better UX, sort of jack of all trades approach
- Still fairly technology agnostic although does require a more involved frontend architecture (ie a js framework).
Disadvantages
- Have to wire up API to frontend which adds complexity.
- Have to manage frontend state which adds complexity.
- Slightly slower first render as application must load assets on client.
Modern server side rendering (with integration of a dynamic frontend framework) works like each of the below:
Highest order of application complexity but also closest to real world scenario. This is quite opinionated about technology, you basically need a node server OR a server able to spawn a node process to run the server side render, then send what's called 'hydrating' data to the client.
One thing about all of these is there is plenty of decent boiler-plate out there so initial setup and what not isn't that complex, necessarily. That said mindful of everyone feeling comfortable and able to contribute.

