Task - Control Flow Statements - Looping Statements #88
Replies: 21 comments
-
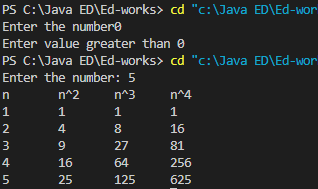
1Npowers.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class Npowers {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the number: ");
n=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
if(n>0)
{
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
int val=1;
for(int j=1;j<=4;j++)
{
if(i==0)
{
if(j==1)
{
System.out.print("n\t");
}
else
{
System.out.print("n^"+j);
System.out.print("\t");
}
}
else
{
val=val*i;
}
if(i>0)
System.out.print(String.format("%d\t",val));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("Enter value greater than 0");
}
sc.close();
}
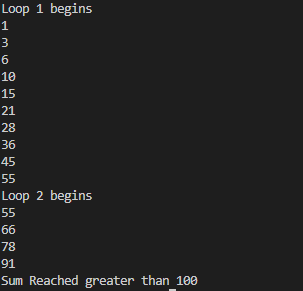
}Output2.twoloops.javapublic class twoloops {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i=1,sum=0;
System.out.println("Loop 1 begins");
while(i<=10)
{
sum=i+sum;
System.out.println(sum);
i++;
}
System.out.println("Loop 2 begins");
while(i<=100)
{
if(sum>100)
{
System.out.println("Sum Reached greater than 100");
break;
}
else if(sum<=100)
{
System.out.println(sum);
sum=sum+i;
i++;
}
}
}
}Output |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1import java.util.*;
public class PowerOfNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner obj = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the end number");
int endNumber = obj.nextInt();
if (endNumber > 0)
System.out.println("n^1 \t n^2 \t n^3 \t en^4");
else
System.out.println("Enter the number greater than zero");
for (int rowStart = 1; rowStart <= endNumber; rowStart++) {
int result = 1;
for (int columnStart = 1; columnStart <= 4; columnStart++) {
result *= rowStart;
System.out.print(result + "\t");
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
obj.close();
}
}2public class SumOfNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sumOfResult = 0;
int result = 0;
for (int iterate = 1; iterate <= 10; iterate++) {
sumOfResult += iterate;
System.out.print(sumOfResult + "\t");
}
for (int iterate = 1; iterate < 100; iterate++) {
result += iterate;
if (result >= 100) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("\nresult is : " + result);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
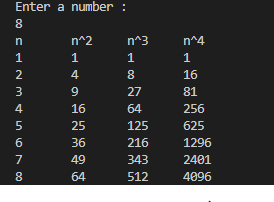
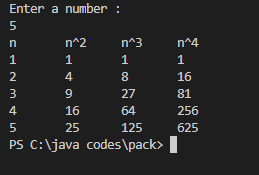
Task-Looping Statement1.LoopDemo.javapackage ControlFlowStatements;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LoopDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number : ");
int n=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("n\tn^2\tn^3\tn^4");
for (int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
System.out.print(i+"\t"+(int) Math.pow(i,2)+"\t"+(int) Math.pow(i,3)+"\t"+(int) Math.pow(i,4));
System.out.println();
}
}
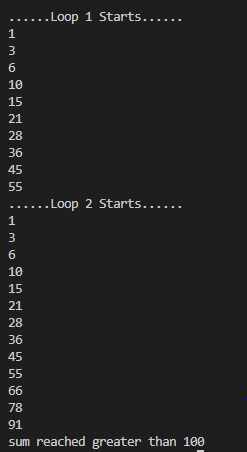
}Output2.SumDemo,javapackage ControlFlowStatements;
public class SumDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum=0;
System.out.println("......Loop 1 Starts......");
for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) {
sum+=i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
sum=0;
System.out.println("......Loop 2 Starts......");
for(int i=1;; i++) {
sum+=i;
if(sum>100){
System.out.println("sum reached greater than 100");
break;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
}Output |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1import java.util.Scanner;
public class Powers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number");
int n = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
System.out.println("n\tn^2\tn^3\tn^4");
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
System.out.print(i+"\t"+(int)Math.pow(i, 2)+"\t"+(int)Math.pow(i,3)+"\t"+(int)Math.pow(i, 4));
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}Output2public class TwoLoops {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum=0;
System.out.println("FIRST LOOP");
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
sum+=i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
sum=0;
System.out.println("\nSECOND LOOP");
for(int i=1; ;i++)
{
sum+=i;
if(sum>100)
{
System.out.println("Sum reached greater than 100");
break;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
}Output |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1import java.util.Scanner;
public class PowerSeries {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the number::");
int n=sc.nextInt();
if(n<0) System.out.println("Enter the number greater than zero");
else{
for(int i=0; i<=n;i++){
int res=1;
for(int j=1; j<=4;j++){
if(i==0){System.out.printf("n^%d \t",j); }
else{
res*=i;
System.out.printf("%d \t",res);
}
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
sc.close();
}
}2public class SumOfNumbers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum=0,i;
System.out.println("First Loop...");
for ( i = 1; i <=10;i++){
sum+=i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
System.out.println("Second Loop...");
i=1;
sum=0;
while(sum<100){
sum+=i;
if (sum<100){
System.out.println(sum);}
i++;
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1.import java.util.Scanner;
public class LoopProject {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the input: ");
int n=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
System.out.println("n\tn^2\tn^3\tn^4");
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\n",i,i*i,i*i*i,i*i*i*i);
}
sc.close();
}
}2.public class LoopProject1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum=0;
int i=1;
for( i=1;i<=10;i++){
sum=sum+i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
while(true){
sum=sum+i;
if(sum>100)
break;
System.out.println(sum);
i++;
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Looping Statements1.import java.util.Scanner;
public class LoopPower {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the input");
int n=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("n\t n^2\t n^3\t n^4");
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t",i,(int)Math.pow(i,2),(int)Math.pow(i,3),(int)Math.pow(i,4));
System.out.println("");
} }
}output2.package methods.menudriven;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SumLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter the number ");
int n=sc.nextInt();
int sum=0;
System.out.println("loop1:sum of the values from 1 to 10");
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
sum+=i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
sum=0;
System.out.println("loop2:greater than 100");
for(int i=1; ; i++) {
sum+=i;
if(sum>100)
break;
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
}output |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
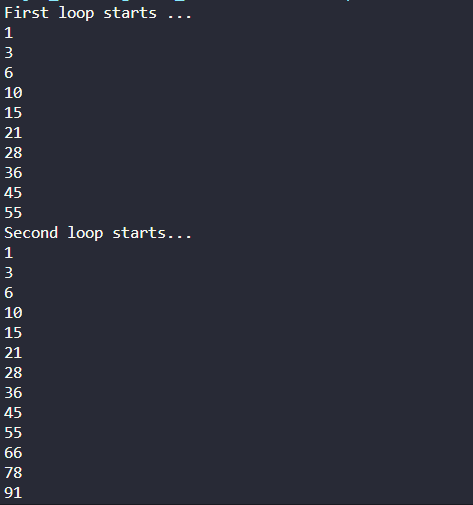
1import java.util.Scanner;
public class Loop1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the value of n");
int n = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
if(n>0){
System.out.println("n\tn^2\tn^3\tn^4");
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\n",i,i*i,i*i*i,i*i*i*i);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Enter the value of n greater than 0");
}
sc.close();
}
}2public class Loop2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum =0,i;
System.out.println("First loop starts ...");
for( i=1;i<=10;i++){
sum+=i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
sum=0;
System.out.println("Second loop starts... ");
i=1;
while(true){
if(sum>100){break;}
else{
sum+=i;
System.out.println(sum);
i++;
}
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
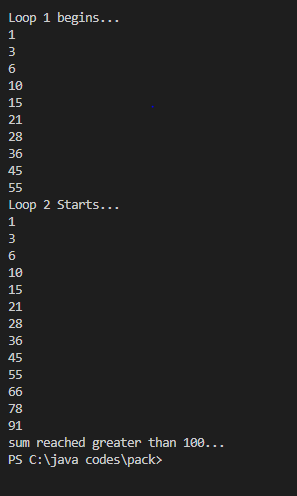
1 N Powerimport java.util.*;
public class NCap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number : ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("n\tn^2\tn^3\tn^4");
for (int i=1; i<=num; i++)
{
System.out.print(i+"\t"+(int) Math.pow(i,2)+"\t"+(int) Math.pow(i,3)+"\t"+(int) Math.pow(i,4));
System.out.println();
}
}
} Output:2 Two Loopspublic class TwoLoops {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum=0;
System.out.println("Loop 1 begins...");
for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) {
sum+=i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
sum=0;
System.out.println("Loop 2 Starts...");
for(int i=1;; i++) {
sum+=i;
if(sum>100){
System.out.println("sum reached greater than 100...");
break;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
}Output: |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1import java.util.Scanner;
public class Powers {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number");
int num=scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("n \t n^2 \t n^3 \t n^4");
for (int i=1; i<=num; i++){
System.out.println(i+"\t"+(int)Math.pow(i,2)+"\t"+(int)Math.pow(i,3)+"\t"+(int)Math.pow(i,4));
}
}
}2public class Loops {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum=0;
int i;
int num=10;
System.out.println("First loop:");
for (i = 1; i <=num; i++) {
sum=sum+i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
System.out.println("Second loop:");
sum=0;
for (i = 1 ; ; i++){
sum=sum+i;
if(sum>=100){
System.out.println("Sum Reached 100");
break;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Problem_1package Project.PowerGeneration
import java.util.Scanner;
public class GeneratePower {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number to generate power: ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
System.out.println("n\tn^2\tn^3\tn^4");
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
System.out.print(i+"\t"+(int)Math.pow(i, 2)+"\t"+(int)Math.pow(i,3)+"\t"+(int)Math.pow(i, 4));
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}Problem_2package Project.PowerGeneration
public class GeneratePowerSum{
public static void main(String[] args){
int sum=0;
System.out.println("Loop 1: ");
for(int i=1; i<=10; i++){
sum+=i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
sum=0;
System.out.println("Loop 2: ");
for(int i=1;; i++) {
sum+=i;
if(sum>100){
System.out.println("Sum have reached 100");
break;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1 Task 2public class Task2Power {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter final limit number: ");
double power=scanner.nextDouble();
int limit=4;
if(power<=0)
{
System.out.println("number is less than zero");
}
else{
System.out.println("n\tn^2\tn^3\tn^4");
}
for(int i=1;i<=power;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=limit;j++)
{
System.out.printf("%d\t",(int)Math.pow(i,j));
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
scanner.close();
}
}2 sum public class Task2Loops {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=1;
int sum=0;
int temp=0;
System.out.println("Loop until sum upto 1 and 10");
for(int i=n;i<=10;i++) {
sum=sum+i;
System.out.printf("%d\n",sum);
}
System.out.println("Loop until sum greater than 100");
while(temp<=100);{
temp=temp+n;
System.out.printf("%d\n",temp);
n++;
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1import java.util.Scanner;
public class PowersOfNumbers {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number");
int n=sc.nextInt();
sc.close();
System.out.println("n \t n^2 \t n^3 \t n^4");
for (int i=1; i<=n; i++){
System.out.println(i+"\t"+(int)Math.pow(i,2)+"\t"+(int)Math.pow(i,3)+"\t"+(int)Math.pow(i,4));
}
}
}2public class TwoLoops {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum=0,i=1;
System.out.println("Loop 1");
sum=0;
while(sum<100){
sum+=i;
if (sum<100){
System.out.println(sum);}
i++;
}
System.out.println("Loop 2");
for ( i = 1; i <=10;i++){
sum+=i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1public class LoopPowers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number :: ");
int n = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("n \t n^2 \t n^3 \t n^4");
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
System.out.print(i + "\t" + (int) Math.pow(i, 2) + "\t" + (int) Math.pow(i,3) + "\t" + (int) Math.pow(i, 4));
System.out.println("\n");
}
}
}
## 2
```java
public class Loop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0,i = 1;
System.out.println("First Loop :: ");
for(;i<=10;i++){
sum += i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
System.out.println("Second Loop :: ");
while(true){
sum = 0; i =1;
sum += i;
if(sum <= 100){
System.out.println("Reached limit (100) !");
System.out.println(sum);
i++;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.*;
public class D88 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Loop1();
Loop2();
}
public static void Loop1() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number : ");
int n = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("n\tn^2\tn^3\tn^4");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out
.print(i + "\t" + (int) Math.pow(i, 2) + "\t" + (int) Math.pow(i, 3) + "\t" + (int) Math.pow(i, 4));
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void Loop2() {
int sum = 0;
System.out.println("Loop 1 ");
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sum += i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
sum = 0;
System.out.println("Loop 2 ");
for (int i = 1;; i++) {
sum += i;
if (sum > 100) {
System.out.println("Sum is greater than 100");
break;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.Scanner;
public class discussion88 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the number::");
int n = sc.nextInt();
if (n < 0)
System.out.println("Enter the number greater than zero");
else {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
int res = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= 4; j++) {
if (i == 0) {
System.out.printf("n^%d \t", j);
} else {
res *= i;
System.out.printf("%d \t", res);
}
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
int sum = 0, i;
System.out.println("First Loop...");
for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sum += i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
System.out.println("Second Loop...");
i = 1;
sum = 0;
while (sum < 100) {
sum += i;
if (sum < 100) {
System.out.println(sum);
}
i++;
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
12import java.util.Scanner;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
System.out.println("......Loop 1 Starts......");
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sum += i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
sum = 0;
System.out.println("......Loop 2 Starts......");
for (int i = 1;; i++) {
sum += i;
if (sum > 100) {
System.out.println("sum reached greater than 100");
break;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
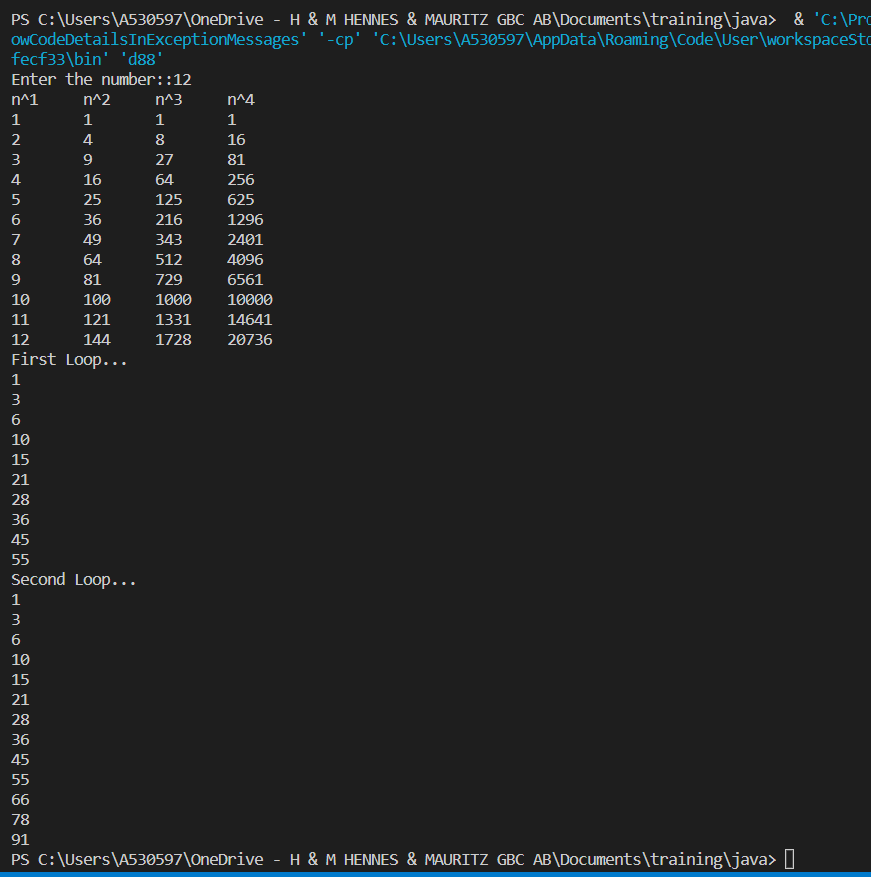
import java.util.Scanner;
public class d88 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the number::");
int n = sc.nextInt();
if (n < 0)
System.out.println("Enter the number greater than zero");
else {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
int res = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= 4; j++) {
if (i == 0) {
System.out.printf("n^%d \t", j);
} else {
res *= i;
System.out.printf("%d \t", res);
}
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
int sum = 0, i;
System.out.println("First Loop...");
for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sum += i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
System.out.println("Second Loop...");
i = 1;
sum = 0;
while (sum < 100) {
sum += i;
if (sum < 100) {
System.out.println(sum);
}
i++;
}
}
}screenshot |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
public class Ques1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int n;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the number: ");
n=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
if(n>0)
{
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
int val=1;
for(int j=1;j<=4;j++)
{
if(i==0)
{
if(j==1)
{
System.out.print("n\t");
}
else
{
System.out.print("n^"+j);
System.out.print("\t");
}
}
else
{
val=val*i;
}
if(i>0)
System.out.print(String.format("%d\t",val));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("Enter value greater than 0");
}
sc.close();
}
}
public class Ques2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int sumOfResult = 0;
int result = 0;
for (int iterate = 1; iterate <= 10; iterate++) {
sumOfResult += iterate;
System.out.print(sumOfResult + "\t");
}
for (int iterate = 1; iterate < 100; iterate++) {
result += iterate;
if (result >= 100) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("\nresult is : " + result);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.*;
public class task88 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
p1();
p2();
}
public static void p1() {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter a number");
int n = scn.nextInt();
if (n > 0) {
System.out.println("n^1 \t n^2 \t n^3 \t n^4");
} else {
System.out.println("enter a positive integer");
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int res = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= 4; j++) {
res = res * i;
System.out.print(res + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void p2() {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
int sum = 0;
System.out.println("loop 1");
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sum = sum + i;
System.out.println(sum + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("loop 2");
int j = 1;
sum = 0;
while (sum < 100) {
sum = sum + j;
if (sum < 100) {
System.out.println(sum);
}
++j;
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.*;
public class ControlFlow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 1st problem
System.out.println("Enter the number");
int n = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("n\tn^2\t n^3\tn^4");
if (n != 0 && n != -1) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out
.print(i + "\t" + (int) Math.pow(i, 2) + "\t" + (int) Math.pow(i, 3) + "\t" +
(int) Math.pow(i, 4));
System.out.println();
}
// 2nd Program
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sum += i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
int n1 = 1;
int s = 0;
while (n1 <= 100) {
if (s <= 100) {
System.out.println(s);
s = s + n1;
n++;
} else {
System.out.println("Sum has reached greater than 100");
break;
}
}
}
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.

Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.
-
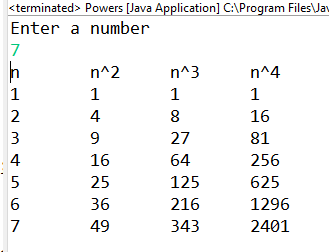
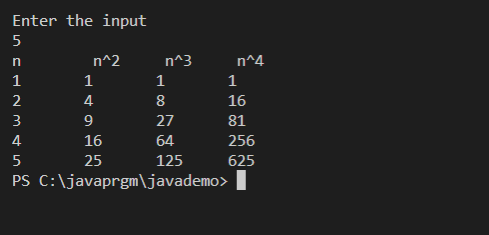
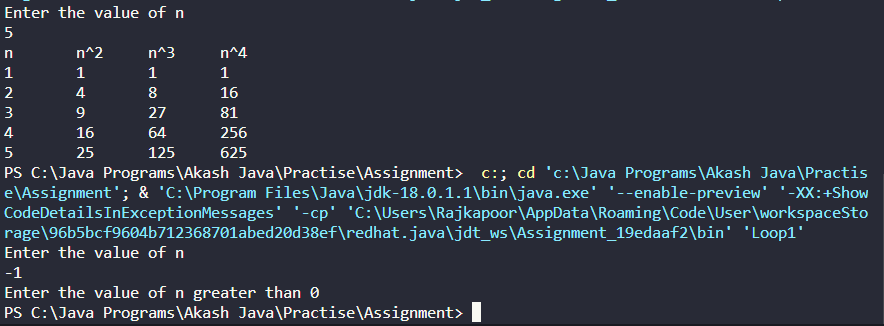
You are to write a program that generates the second, third, and fourth powers of a list of
whole numbers from 1 to n where n is input by the user. Write a Java program to do this.
First, ask the user for the largest of the whole numbers to use (n). Second, output column
headers (see below, n, n^2, n^3, n^4). Then, use a for loop to iterate from 1 to n, computing
each of that loop variable to the second power, third power and fourth power. Assuming
your loop variable is called i, you can do this either as i*i or Math.pow(i,2). To output the
values in nice columns as shown below, separate each output with a tab (“\t”). This is
similar to using \n for a new line.
Test your program with different input values such as 5, 10, 1, 0 and -1. For 0 and -1, you
should get no output at all. If you wrote your loop correctly, that will be the case.
Debugging tip: If you get incorrect results when running code that contains a loop, place
some print statements inside the loop to print the values of any variables that you think
might be involved in the errors. This helps you check what your loop is actually doing.
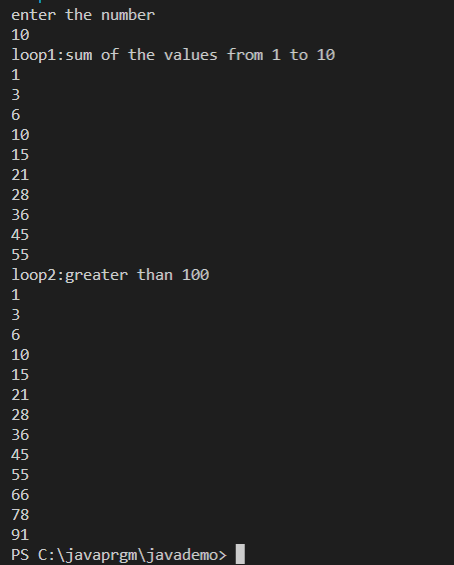
Write one additional program which itself contains two loops. You will have to decide
which loop type to use and how to write each one. Both loops will have a loop body that
consists of a computation and an output.
instance, it will output 1, 3 (1+2), 6 (1+2+3), 10 (1+2+3+4), etc (on separate lines).
than 100, again outputting results as you go.
You will have to decide what type of loops to use and how to write each, and what other
variables and instructions are needed in your program.
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
All reactions