Given an array of integers heights representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, return the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram.
Example 1:
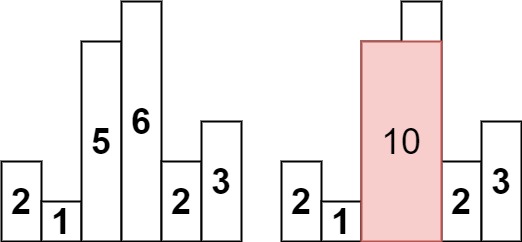
Input: heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3] Output: 10 Explanation: The above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1. The largest rectangle is shown in the red area, which has an area = 10 units.
Example 2:
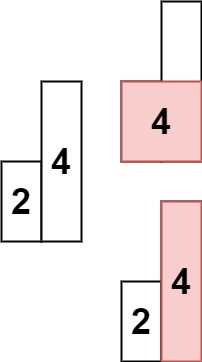
Input: heights = [2,4] Output: 4
1 <= heights.length <= 1050 <= heights[i] <= 104
class Solution:
def largestRectangleArea(self, heights: List[int]) -> int:
# Initialize the maximum area to 0
maxArea = 0
# Initialize the stack that will store tuples of (index, height)
stack = []
# Iterate through each bar in the histogram
for i, h in enumerate(heights):
# Initialize the start variable which denotes the start of a rectangle
start = i
# While the stack is not empty and the current height is less than the height at the top of the stack
while stack and stack[-1][1] > h:
# Pop the stack and calculate the area of the rectangle
# using the height of the popped bar and width as the current index minus the popped index
index, height = stack.pop()
maxArea = max(maxArea, height * (i - index))
# Update start to the index of the popped bar
start = index
# Append the current bar as the potential start of a new rectangle
stack.append((start, h))
# After we finish going through all the bars,
# we may have some bars left in the stack that could form rectangles extending to the end of the histogram
for i, h in stack:
# The width is the total width of the histogram minus the index where the bar started
maxArea = max(maxArea, h * (len(heights) - i))
# Return the maximum area found
return maxAreaThe solution has a time complexity of O(n), as each bar is pushed and popped from the stack exactly once. The space complexity is O(n) due to the stack used to store the indices and heights of the bars.