| title | tags | categories | keywords | description | cover | abbrlink | date | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Spring源码系列-第9章-SpringMVC请求处理源码和HandlerMapping原理 |
|
|
Spring,框架,spring源码 |
SpringMVC请求处理源码和HandlerMapping原理 |
6f2cef28 |
2022-06-21 05:01:02 -0700 |
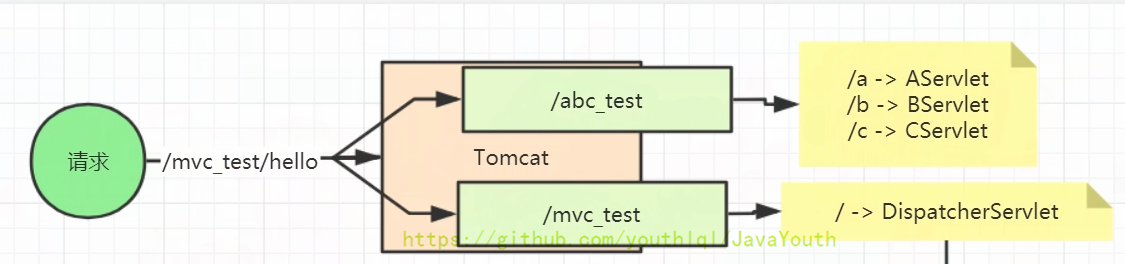
- tomcat里面可以部署多个项目应用。/abc_test和mvc_test这种就是项目路径,用于区分多个项目
- 在以前的Servlet开发中,每一个路径都需要有一个Servlet来处理。比如上图所画
- 有了SpringMVC,整个Tomcat下面就不会有很多Servlet了,只会有一个DispatcherServlet来统一处理
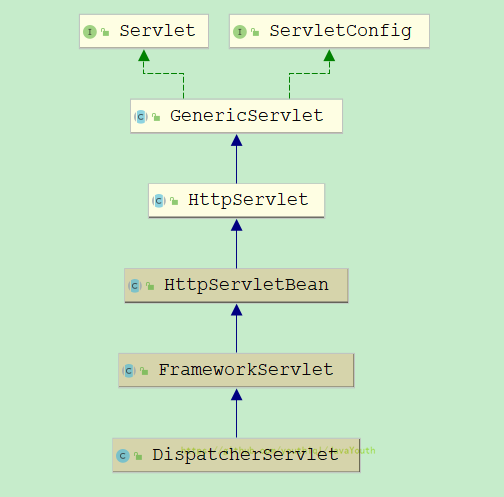
- Servlet里是Service()方法处理请求
- GenericServlet也是Service()方法处理请求
- HttpServlet开始根据请求类型将处理方法分为doGet,doPost,doPut,doDelete等等
- HttpServletBean没有处理方法
- FrameworkServlet也是有处理方法分别为doGet,doPost,doPut,doDelete等等,但是这些方法最终调用的都是
processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) - DispatcherServlet处理方法是doService()
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; //把request域的所有属性提前保存
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); //快照所有属性
}
}
}
//基本的东西保存到request域中方便处理 Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); //国际化解析器
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); //主题解析器
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) { //闪存管理器(重定向携带数据)
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
RequestPath previousRequestPath = null;
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
previousRequestPath = (RequestPath) request.getAttribute(ServletRequestPathUtils.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);
}
try {
doDispatch(request, response); //处理派发功能
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
ServletRequestPathUtils.setParsedRequestPath(previousRequestPath, request);
}
} //SpringMVC处理请求的核心流程
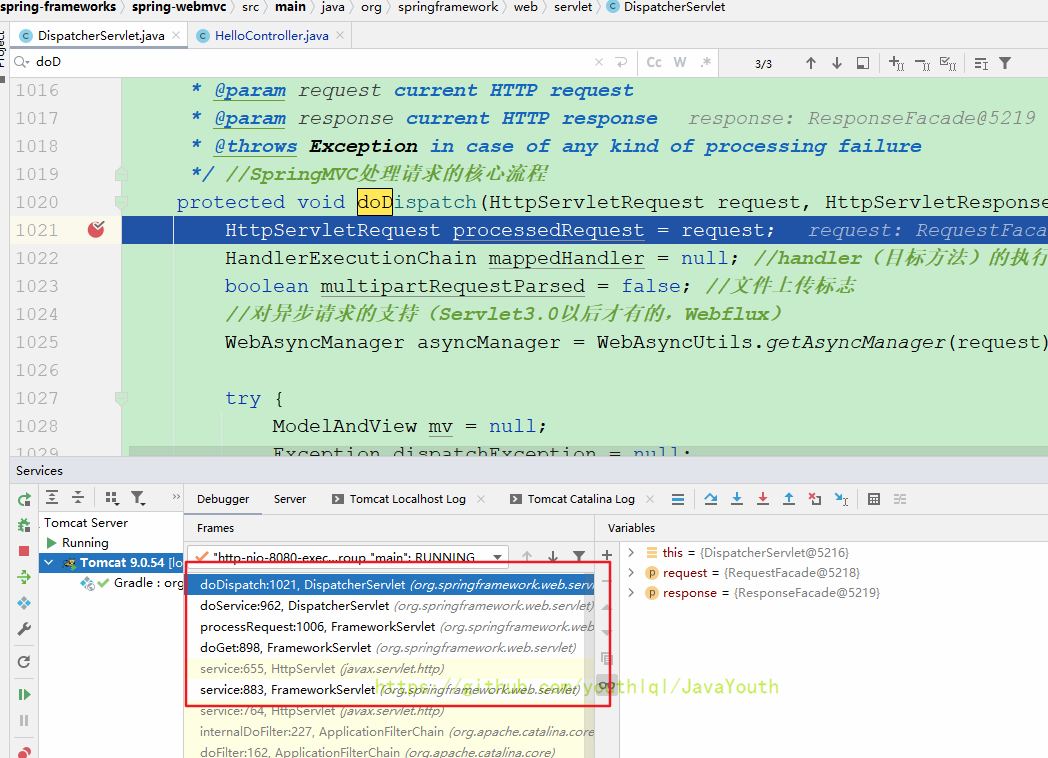
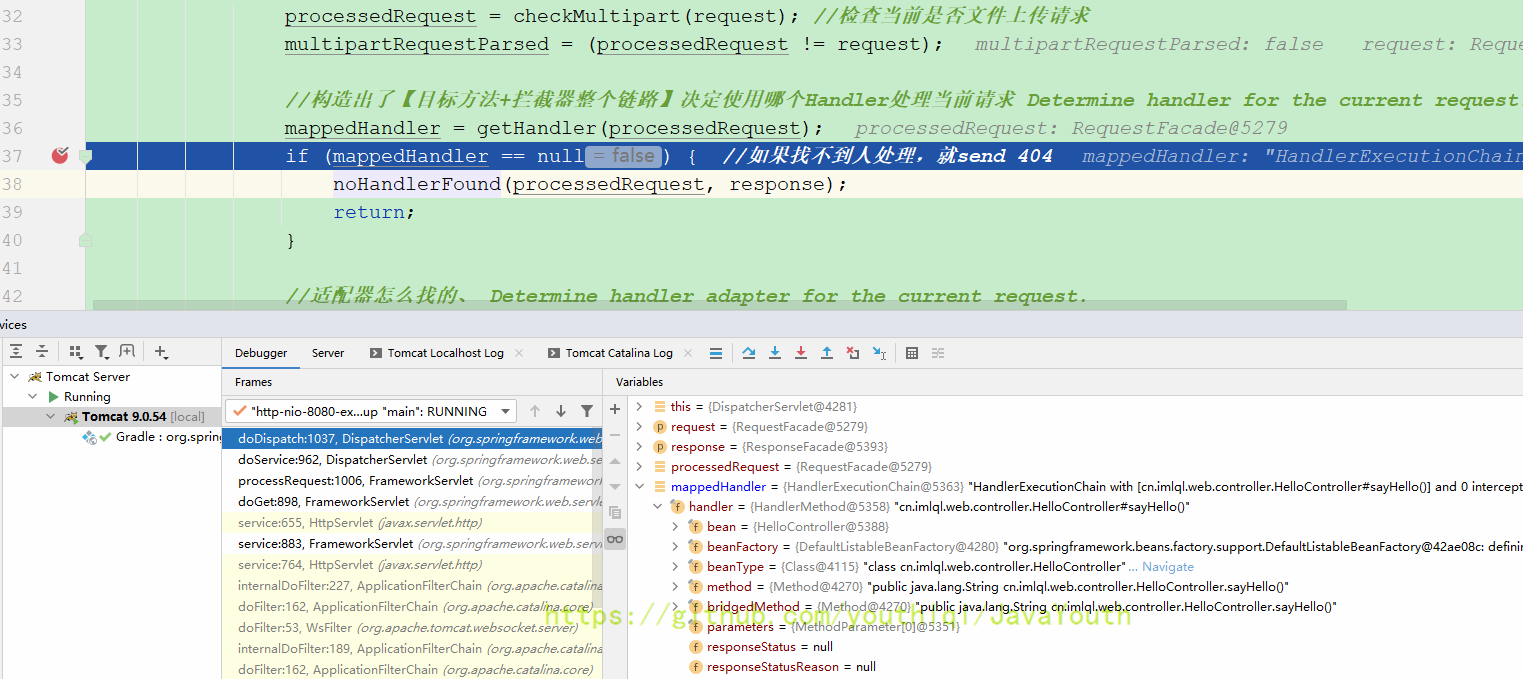
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; //handler(目标方法)的执行链
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; //文件上传标志
//对异步请求的支持(Servlet3.0以后才有的,Webflux)
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); //检查当前是否文件上传请求
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
//构造出了【目标方法+拦截器整个链路】决定使用哪个Handler处理当前请求 Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) { //如果找不到人处理,就send 404
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
//适配器怎么找的、 Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
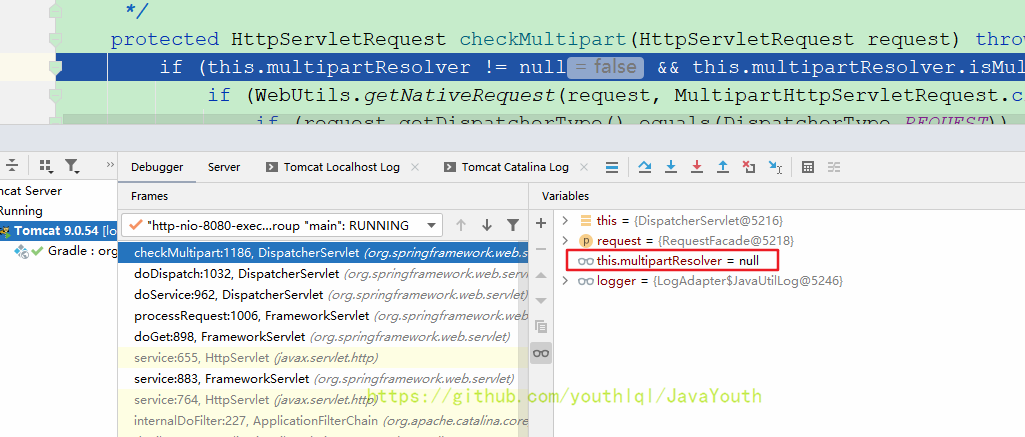
}protected HttpServletRequest checkMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException {
//使用文件上传解析器来判断是否文件上传请求
if (this.multipartResolver != null && this.multipartResolver.isMultipart(request)) {
// ......
}
// If not returned before: return original request.
return request;
}咱们这里目前连解析器都没有,所以就直接返回了
public boolean isMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) {
//所有文件上传请求头Content-Type都会有这个
return StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(request.getContentType(), "multipart/");
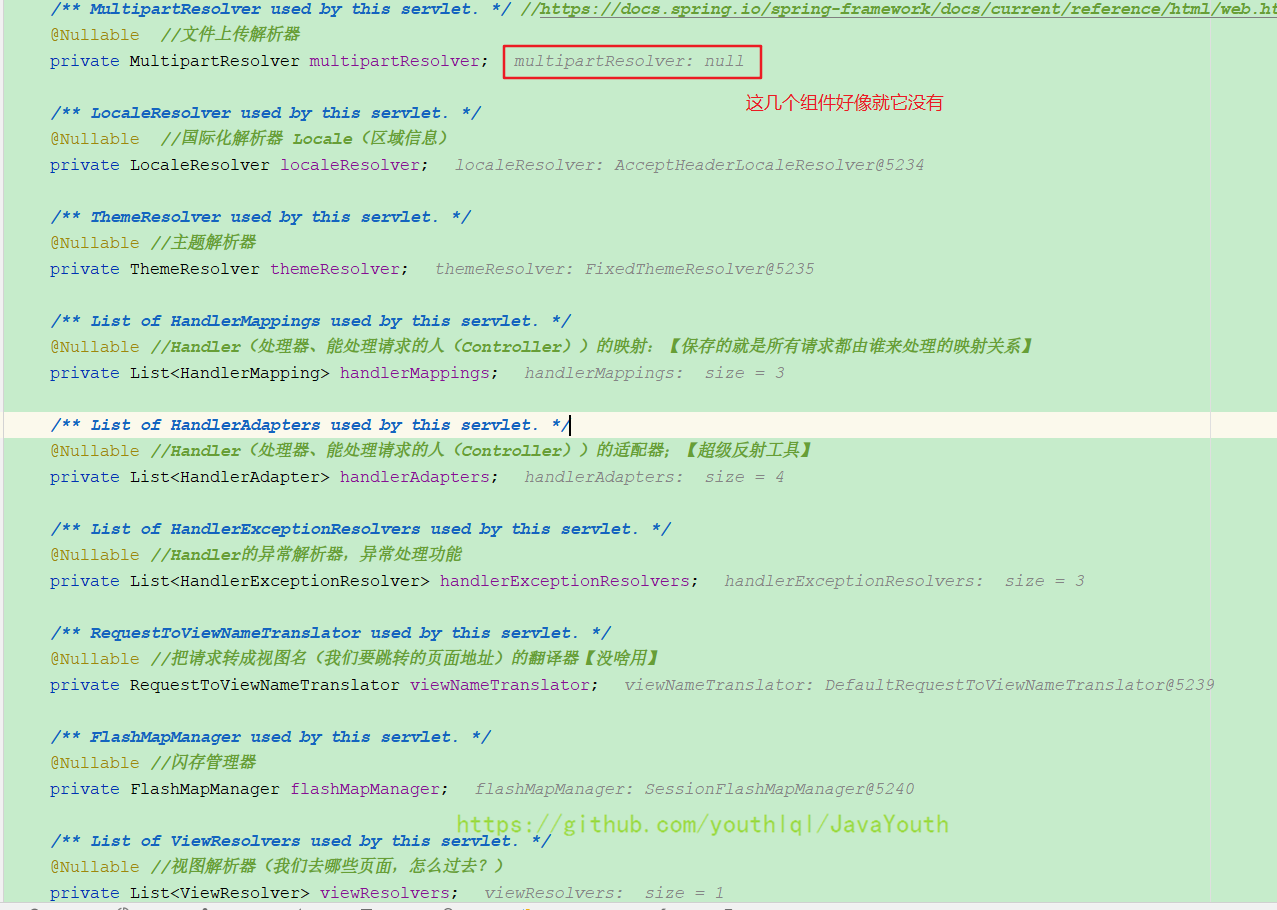
} //DispatcherServlet中的九大组件、全是接口,我们完全可以自定义实现。Spring默认也都准备好了这些组件的实现
/** MultipartResolver used by this servlet. */
@Nullable //文件上传解析器
private MultipartResolver multipartResolver;
/** LocaleResolver used by this servlet. */
@Nullable //国际化解析器 Locale(区域信息)
private LocaleResolver localeResolver;
/** ThemeResolver used by this servlet. */
@Nullable //主题解析器
private ThemeResolver themeResolver;
/** List of HandlerMappings used by this servlet. */
@Nullable //Handler(处理器、能处理请求的人(Controller))的映射:【保存的就是所有请求都由谁来处理的映射关系】
private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings;
/** List of HandlerAdapters used by this servlet. */
@Nullable //Handler处理器的适配器;是一个超级反射工具,帮我们解决参数呀,返回值这些,不需要我们很麻烦的写
private List<HandlerAdapter> handlerAdapters;
/** List of HandlerExceptionResolvers used by this servlet. */
@Nullable //Handler的异常解析器,异常处理功能
private List<HandlerExceptionResolver> handlerExceptionResolvers;
/** RequestToViewNameTranslator used by this servlet. */
@Nullable //把请求转成视图名(我们要跳转的页面地址)的翻译器【没啥用】
private RequestToViewNameTranslator viewNameTranslator;
/** FlashMapManager used by this servlet. */
@Nullable //闪存管理器
private FlashMapManager flashMapManager;
/** List of ViewResolvers used by this servlet. */
@Nullable //视图解析器(我们去哪些页面,怎么过去?)
private List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers;上面的图我们看到九大组件有八个已经有值了,我们现在看下他们是何时有值的。怎么找就很简单,你就找这些属性的setXXX方法,最后我找到了这里
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { //初始化所有策略,九大组件在这里进行了初始化
initMultipartResolver(context); //容器中有就用,没有就是null
initLocaleResolver(context); //从容器中获取,没有用默认
initThemeResolver(context); //从容器中获取,没有用默认
initHandlerMappings(context); //从容器中获取,没有用默认
initHandlerAdapters(context); //从容器中获取,没有用默认
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); //从容器中获取,没有用默认
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); //Spring没有浓重说他,//从容器中获取,没有用默认
initViewResolvers(context); //从容器中获取,没有用默认
initFlashMapManager(context); //从容器中获取,没有用默认
}代码几乎都是一样的逻辑,咱们就只看一个举个例子
private void initLocaleResolver(ApplicationContext context) {
try { //容器中先来获取
this.localeResolver = context.getBean(LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, LocaleResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Detected " + this.localeResolver);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Detected " + this.localeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// We need to use the default. 容器中没有,读取默认配置文件进行加载
this.localeResolver = getDefaultStrategy(context, LocaleResolver.class); //获取默认策略
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No LocaleResolver '" + LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.localeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}只要不满意九大组件的任何一个,自己可以实现指定的接口,这样就会放在容器中,SpringMVC
- Tomcat启动
- 触发DispatcherServlet的初始化
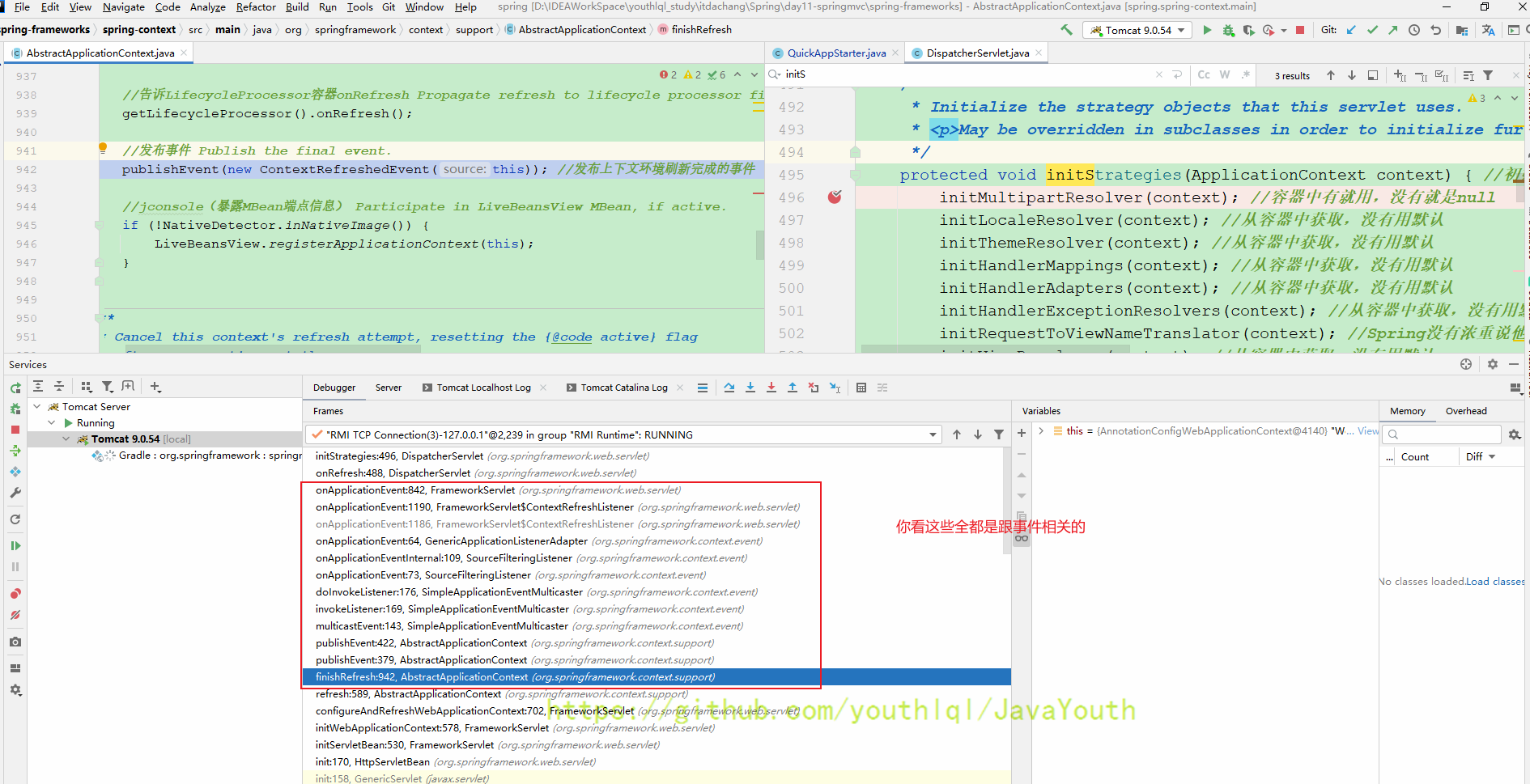
- DispatcherServlet初始化全部结束,容器会发送Spring的相关事件.
- 感知到容器准备好了的事件--初始化九大组件(底层是SourceFilteringListener, 把事件回调到DispatcherServlet的onRefresh方法)
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context); //初始化九大组件
} protected <T> T getDefaultStrategy(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) {
List<T> strategies = getDefaultStrategies(context, strategyInterface);
if (strategies.size() != 1) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"DispatcherServlet needs exactly 1 strategy for interface [" + strategyInterface.getName() + "]");
}
return strategies.get(0);
}
protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) {
if (defaultStrategies == null) {
try {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
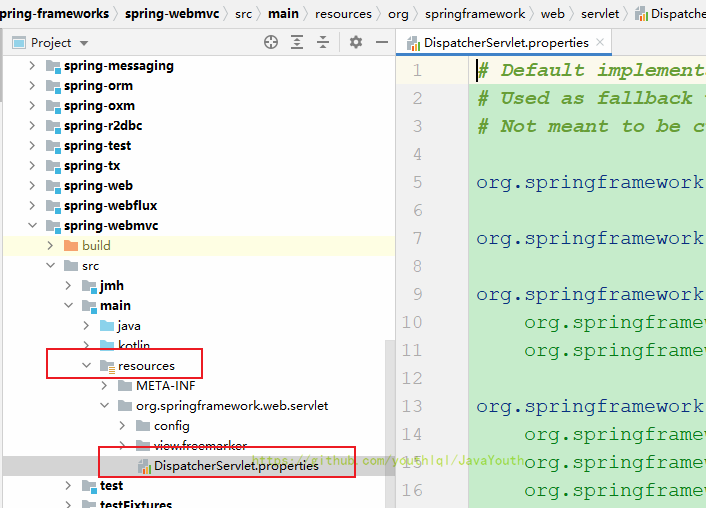
// by application developers. 去DispatcherServlet所在的类路径下找一个 DispatcherServlet.properties 资源
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, DispatcherServlet.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); //读取properties文件
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load '" + DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH + "': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
// ......
}
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "DispatcherServlet.properties";下面这些就是九大组件默认组件
# Default implementation classes for DispatcherServlet's strategy interfaces.
# Used as fallback when no matching beans are found in the DispatcherServlet context.
# Not meant to be customized by application developers.
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.RouterFunctionMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.HandlerFunctionAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager //SpringMVC处理请求的核心流程
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; //handler(目标方法)的执行链
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; //文件上传标志
//对异步请求的支持(Servlet3.0以后才有的,Webflux)
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); //检查当前是否文件上传请求
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
//构造出了【目标方法+拦截器整个链路】决定使用哪个Handler处理当前请求 Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) { //如果找不到人处理,就send 404
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
//适配器怎么找的、 Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
// ......
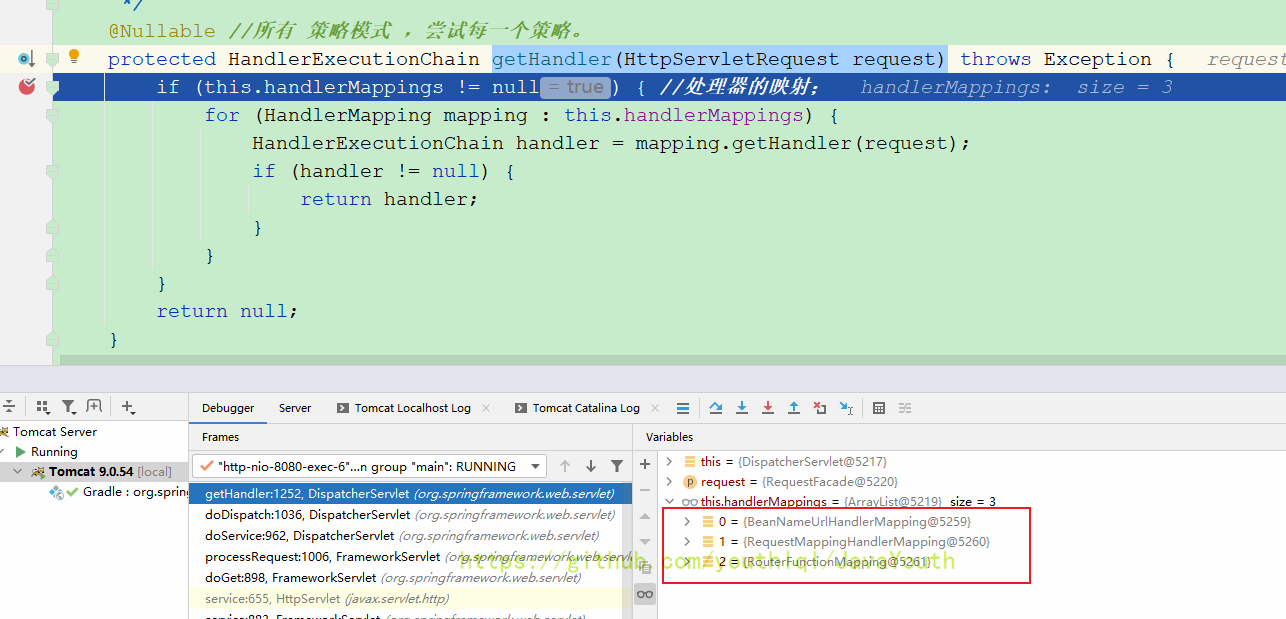
}这里会有三个默认的HandlerMapping,就是在DispatcherServlet.properties写的那三个,在之前说九大组件初始化的时候如果我们自己没有写,就获取默认的
- BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping:bean的名字作为URL路径,进行映射
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping:@RequestMapping注解作为URL地址进行映射
- 默认用它,而且它里面保存了所有请求映射信息
- RouterFunctionMapping: 支持函数式处理以及WebFlux相关功能,未来可能这个用的多
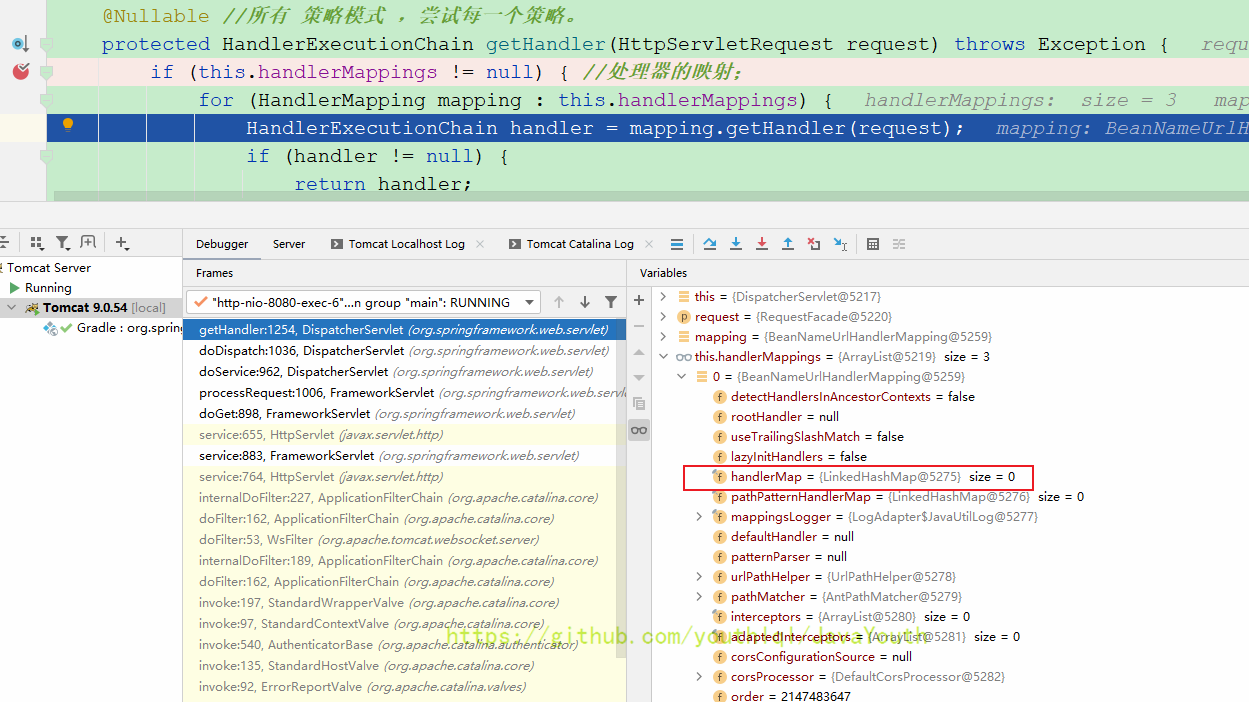
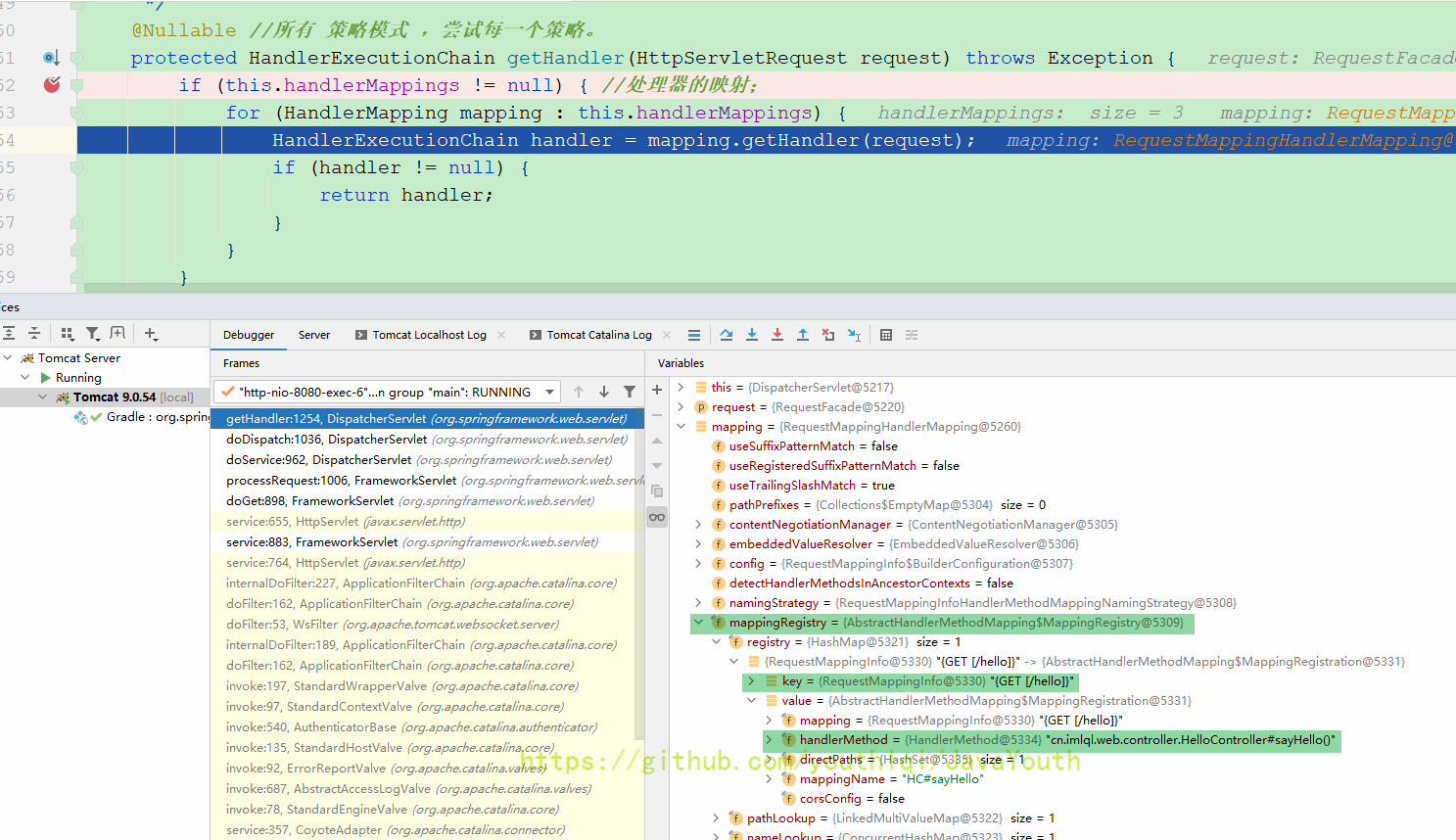
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping里找不到映射关系,就直接下一个循环了。咱们主要看RequestMappingHandlerMapping怎么处理的
RequestMappingHandlerMapping的父类有一个MappingRegistry属性保存了请求路径 ==> 请求Controller+方法的映射
F7进入mapping.getHandler(request)
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); //HandlerMapping的registry中找映射,返回HandlerMethod,真正执行当前请求的方法
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// Ensure presence of cached lookupPath for interceptors and others
if (!ServletRequestPathUtils.hasCachedPath(request)) {
initLookupPath(request);
}
//找到前面的目标方法以后,还要构造一个处理器链;
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
if (getCorsConfigurationSource() != null) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = getCorsConfigurationSource().getCorsConfiguration(request);
config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(config) : config);
}
if (config != null) {
config.validateAllowCredentials();
}
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}F7进入getHandlerInternal(request)
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
request.removeAttribute(PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
try {
return super.getHandlerInternal(request);
}
finally {
ProducesRequestCondition.clearMediaTypesAttribute(request);
}
}继续F7进super.getHandlerInternal(request)
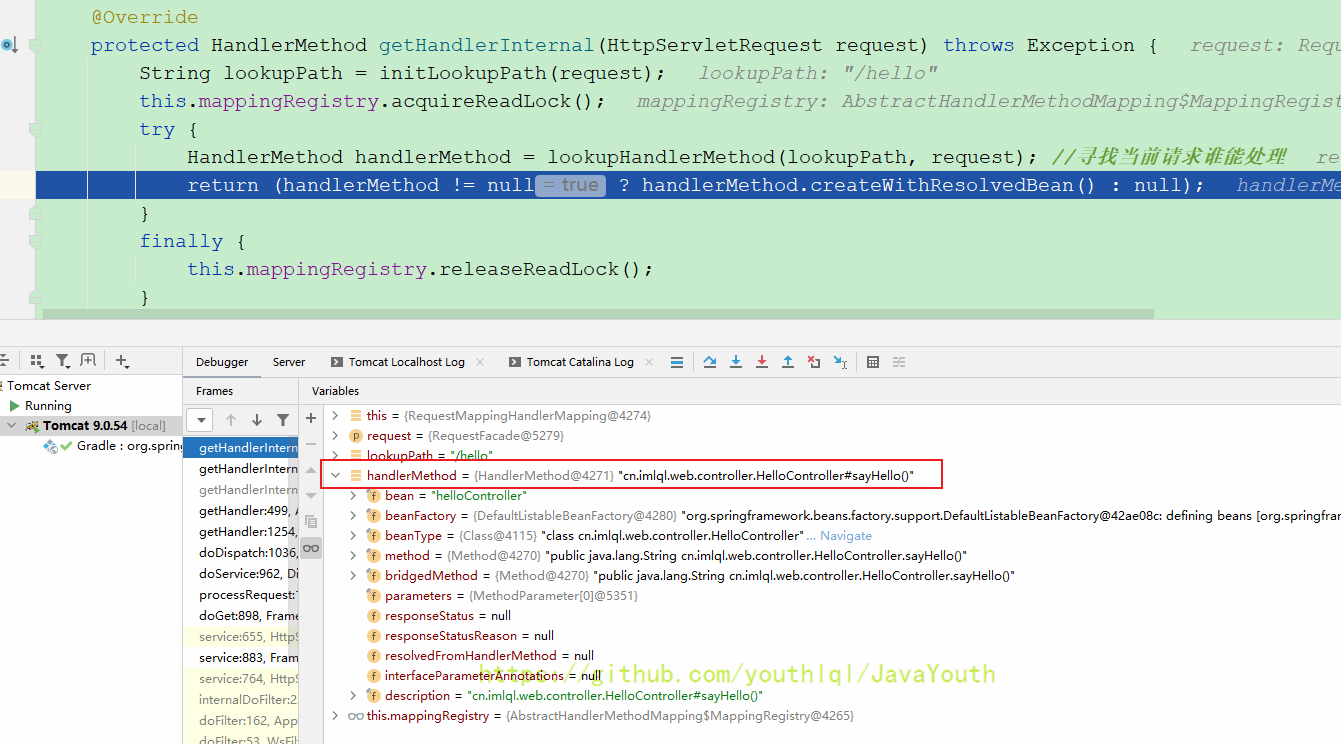
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); //寻找当前请求谁能处理
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}F7进入lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request)
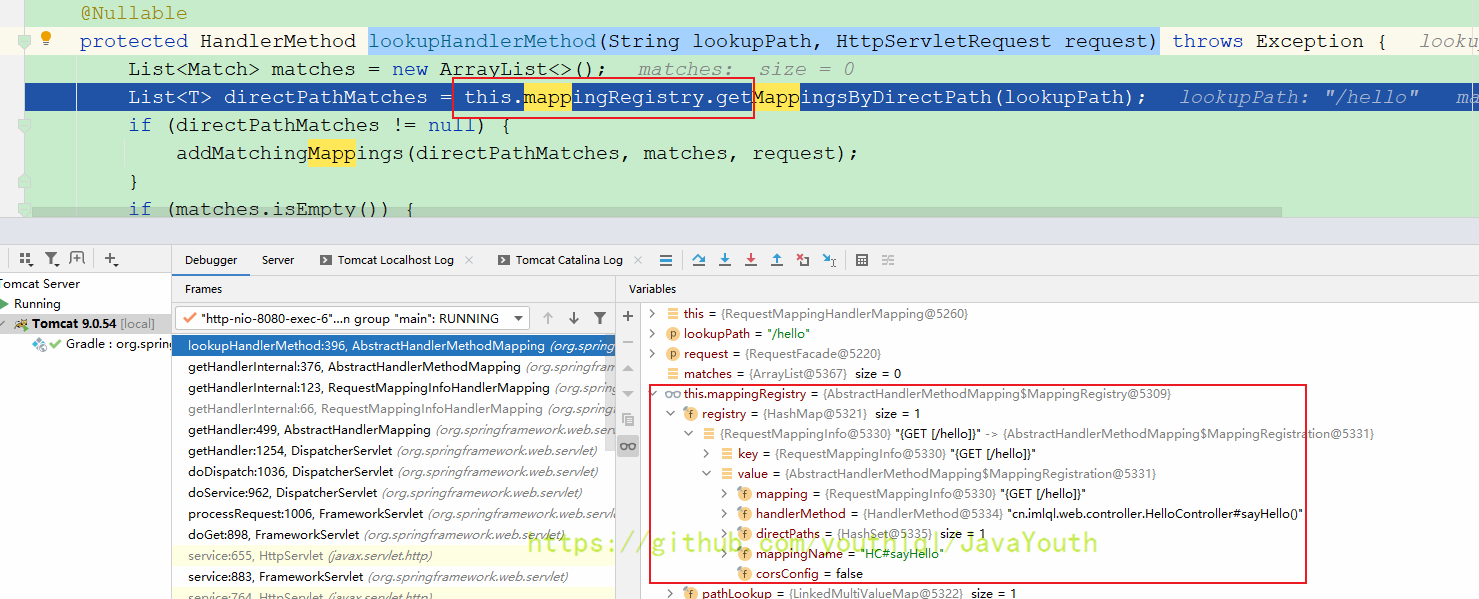
可以看到还是从mappingRegistry里获取。我们后面再看mappingRegistry是什么时候被放入东西的,这里我们接着返回
这个时候是已经找到了由哪个处理器处理,接着返回
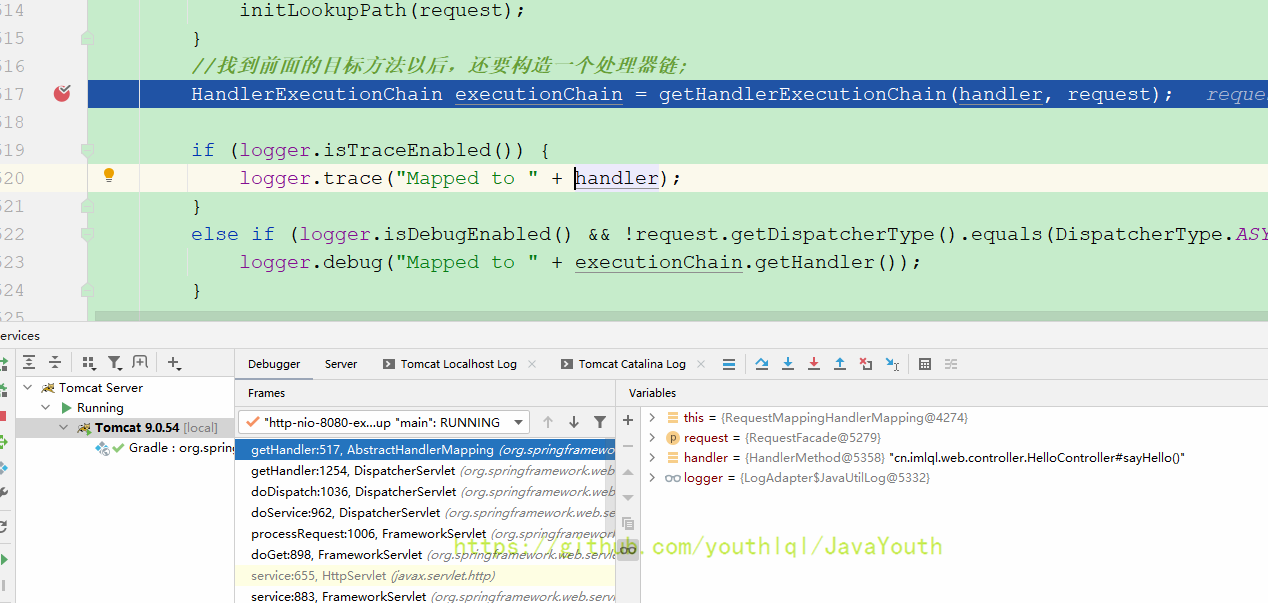
返回到这一步,准备执行getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request)
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
//把系统中所有的拦截器拿过来
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(request)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor); //所有拦截器加进去
}
}
return chain;
}- 咱们没写拦截器,就没有。
- 继续往回返
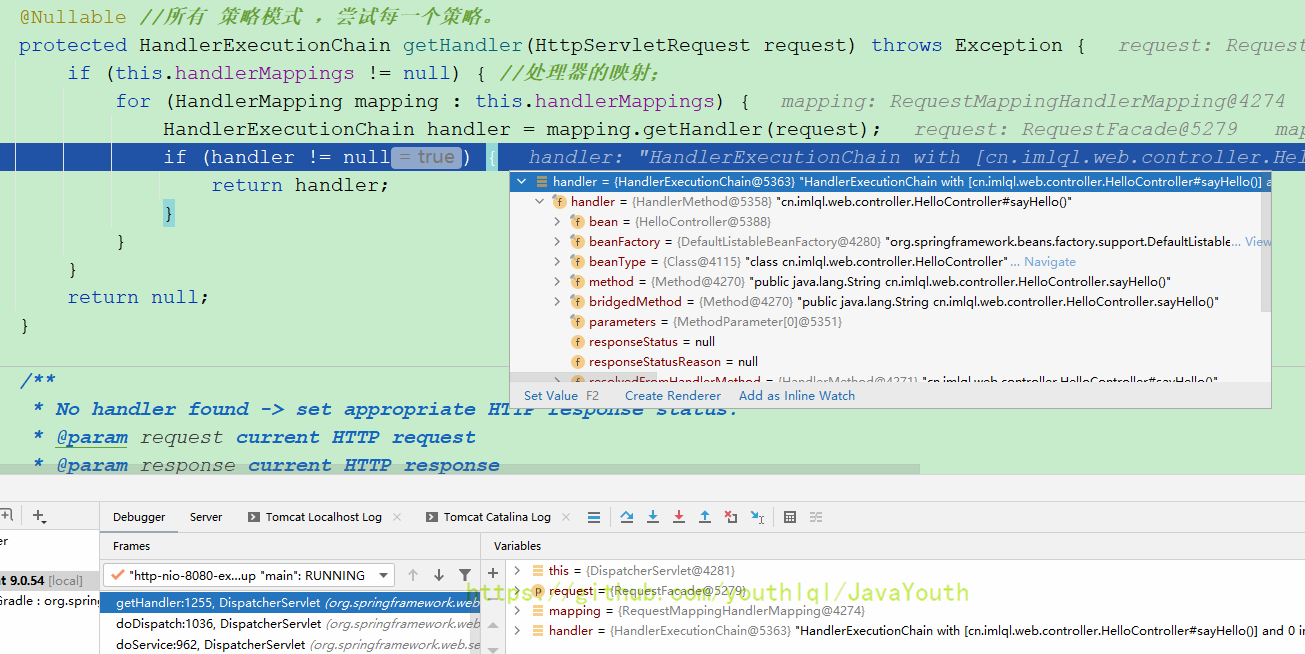
这里就是责任链模式,有能处理的handler就直接返回
自此RequestMappingHandlerMapping处理结束
上面我们看到了实际上是从MappingRegistry里拿到URL-->XXXController的映射关系的,那么下面就来演讲MappingRegistry是何时保存的这映射关系,又是怎样保存的
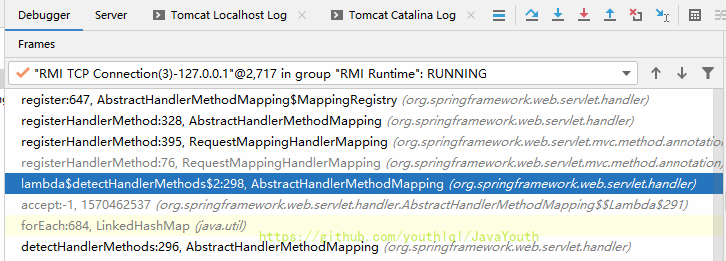
我们这里还是靠猜测,猜它调用哪个方法。找到了如下方法,给第一行打断点,重启。
//分析所有的Controller;里面的每一个@RequestMapping 注解才能知道这个事情
public void registerMapping(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) { //哪个请求由哪个方法处理会通过这个进行注册
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Register \"" + mapping + "\" to " + method.toGenericString());
}
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}重启的时候没有发现没跑到这里,然后我就看了下这个MappingRegistry,发现它是个AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的内部类
class MappingRegistry {
private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>();
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> pathLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
private final Map<String, List<HandlerMethod>> nameLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Map<HandlerMethod, CorsConfiguration> corsLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
Set<String> directPaths = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.getDirectPaths(mapping);
for (String path : directPaths) {
this.pathLookup.add(path, mapping);
}
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
corsConfig.validateAllowCredentials();
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
// 在这里put的
this.registry.put(mapping,
new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directPaths, name, corsConfig != null));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
}我发现上面有一个registry是个Map类型,很容易想到这应该就是保存映射的,然后我就在它的put方法那里打断点,只找到了这一个put。重启应用
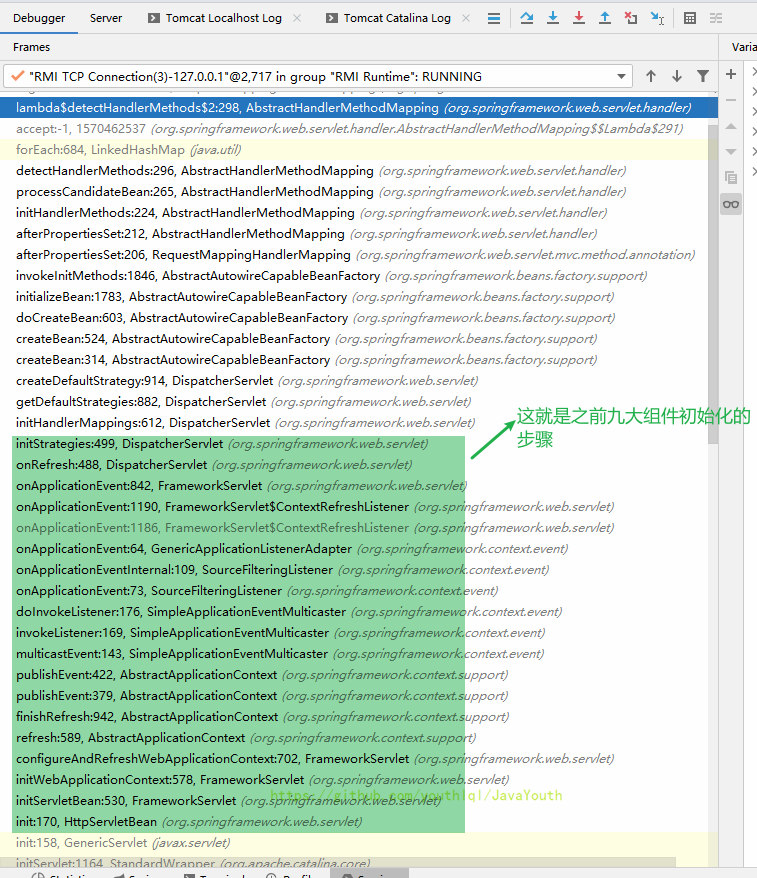
意料之中,启动应用的时候从init初始化那里调用过来了
DispatcherServlet#onRefresh()开始初始化九大组件,就会开始初始化HandlerMapping- 首先是创建
DispatcherServlet.properties里指定的三个HandlerMapping实现类的对象。还是用createBean来创建HandlerMapping的 - 其中RequestMappingHandlerMapping创建完对象后,因为它实现了InitializingBean,所以会调用RequestMappingHandlerMapping#afterPropertiesSet()
- 接着就是拿到Web子容器的所有组件,for循环处理。看是不是有@Controller注解或者@RequestMapping注解
- 最后把分析到的RequestMapping信息放到HandlerMapping的registry中
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(useTrailingSlashMatch());
this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager());
if (getPatternParser() != null) {
this.config.setPatternParser(getPatternParser());
Assert.isTrue(!this.useSuffixPatternMatch && !this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch,
"Suffix pattern matching not supported with PathPatternParser.");
}
else {
this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(useSuffixPatternMatch());
this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch());
this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher());
}
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}public void afterPropertiesSet() {
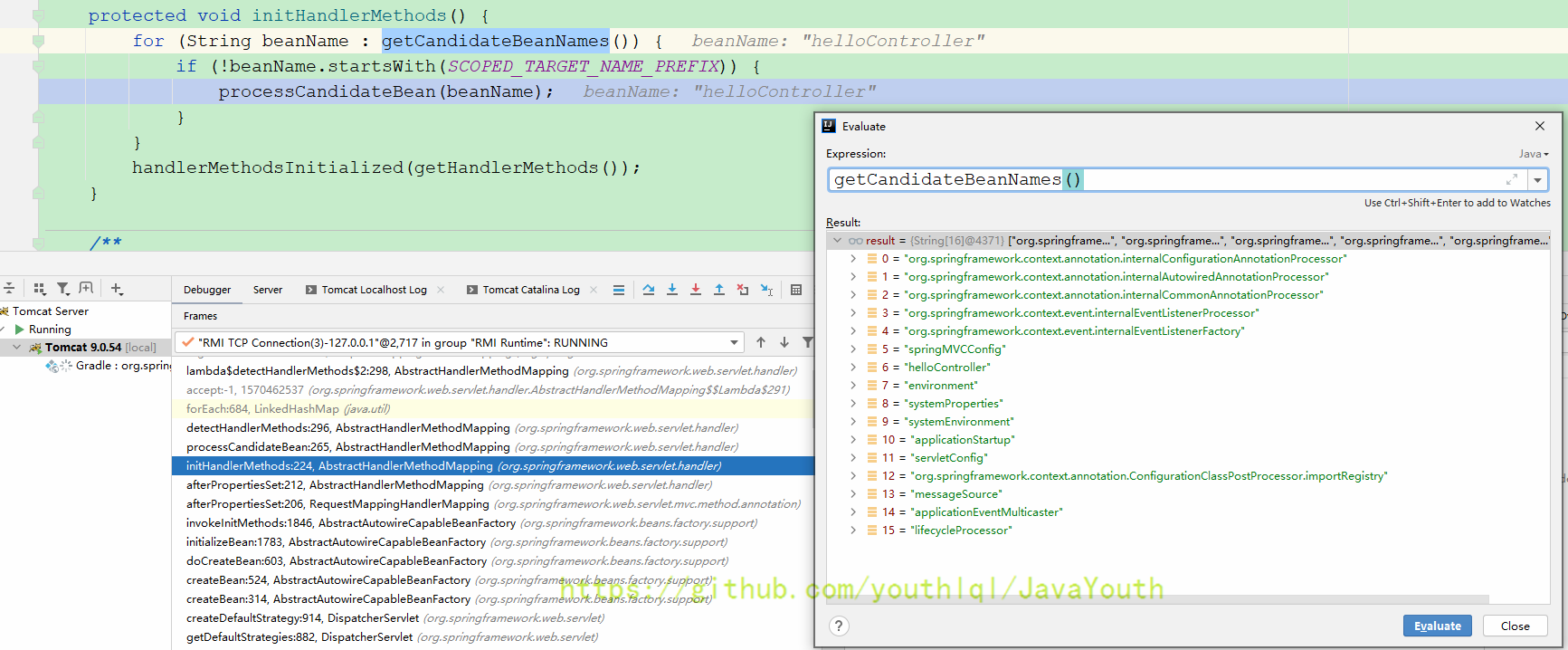
initHandlerMethods(); //初始化HandlerMethods。
}可以看到这里只拿了Web子容器的所有组件进行for循环
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName); //分析当前bean的HandlerMethods
}
} protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}- 这里首先会过滤Bean,只有你Bean也就是类上标注了@Controller注解或者@RequestMapping注解,才会给这个类走下面的流程
- 那这个是什么意思呢?
- 平常我们写XXXController就是写一个@Controller注解就完事了【注意@RestController值是@Controller的复合注解,包含了@Controller】
- 实际上我们可以不写@Controller注解,直接@Component+@RequestMapping也是一样的效果
- 然后那个detectHandlerMethods就是探查容器里满足条件的方法
- 下面看下怎么探索的
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType); //探索当前类里面所有满足的方法,所有标注了 RequestMapping
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
else if (mappingsLogger.isDebugEnabled()) {
mappingsLogger.debug(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
} protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method); //为每一个方法尝试创建 RequestMappingInfo
if (info != null) {
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
} @Nullable
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
// 找每一个标有@RequestMapping注解的方法
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}自此一切就明了了,原理就是上面写的流程概述。for循环组件,找@RequestMapping注解
Q:功能增强的时候什么时候用后置处理器BeanPostProcessor,什么时候用生命周期InitializingBean呢?
A:
- 如果是所有组件都可能会用到的增强功能,那就实现后置处理器BeanPostProcessor来增强
- 如果是单组件增强,最好用InitializingBean。可以看到mvc的RequestMappingHandlerMapping这里用的就是InitializingBean