apimachinery 主要完成两个工作,多版本转换和序列化,今天我们来聊聊多版本转换,它跟一般应用的多版本还不太一样,有它自己的特色,因此搞懂它的相关概念和实现原理是相当有必要的。
Kubernetes 支持多个 API 版本,每个版本位于不同的 API 路径, 例如 /api/v1 或 /apis/rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1alpha1。
版本控制是在 API 级别而不是在资源或字段级别完成的,以确保 API 呈现出清晰、一致的系统资源和行为视图, 并能够控制对生命结束和/或实验性 API 的访问。
为了更容易演进和扩展其 API,Kubernetes 实现了 API 组, 这些 API 组可以被启用或禁用。
API 资源通过其 API 组、资源类型、名字空间(用于名字空间作用域的资源)和名称来区分。 API 服务器透明地处理 API 版本之间的转换:所有不同的版本实际上都是相同持久化数据的呈现,即底层数据是同一份数据。 API 服务器可以通过多个 API 版本提供相同的底层数据,但是根据调用 API 的版本不同,可以转换成对应版本的资源对象。
例如,假设针对相同的资源有两个 API 版本:v1 和 v1beta1。 如果你最初使用其 API 的 v1beta1 版本创建了一个对象, 你稍后可以使用 v1beta1 或 v1 API 版本来读取、更新或删除该对象, 直到 v1beta1 版本被废弃和移除为止。此后,你可以使用 v1 API 继续访问和修改该对象。其实这个特性完全是为了保持API的兼容而设计的,正常情况下,没有人会混着版本去用,它发挥作用的地方主要在升级迭代,要知道随着API的迭代开发,API 会逐渐 GA 进入到稳定版本,那 beta 版,以及 alpha 版则会在某一个阶段被移除,这时候,你用beta版API创建的资源对象,仍然能够用稳定版 API 来操作,这样就实现了无缝升级。
我们来举个例子体验下,在1.30 版本有一个用来做流控的 API,叫 FlowSchema,目前有四个版本,v1, v1beta1, v1beta2 和 v1beta3,我们以 v1beta2 创建一个FlowSchema 对象,然后使用 v1beta2 和 v1beta3分别将这个对象读出来:
1. 使用 v1beta2 创建该对象:
kubectl apply -f flowschema.ymlapiVersion: flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta2
kind: FlowSchema
metadata:
name: test
spec:
matchingPrecedence: 1000
priorityLevelConfiguration:
name: exempt
rules:
- nonResourceRules:
- nonResourceURLs:
- "/healthz"
- "/livez"
- "/readyz"
verbs:
- "*"
subjects:
- kind: Group
group:
name: "system:unauthenticated"2. 使用 v1beta2 读取:
kubectl get flowschema.v1beta2.flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io test -o yaml
或者
curl -H "Accept: application/yaml" http://127.0.0.1:8001/apis/flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta2/flowschemas/test输出:
Warning: flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta2 FlowSchema is deprecated in v1.26+, unavailable in v1.29+; use flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3 FlowSchema
apiVersion: flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta2
kind: FlowSchema
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta2","kind":"FlowSchema","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"test"},"spec":{"matchingPrecedence":1000,"priorityLevelConfiguration":{"name":"exempt"},"rules":[{"nonResourceRules":[{"nonResourceURLs":["/healthz","/livez","/readyz"],"verbs":["*"]}],"subjects":[{"group":{"name":"system:unauthenticated"},"kind":"Group"}]}]}}
creationTimestamp: "2023-11-05T02:17:34Z"
generation: 2
name: test
resourceVersion: "52473"
uid: d70bf2e9-3773-4cab-ae4d-b5e060009beb
spec:
matchingPrecedence: 1000
priorityLevelConfiguration:
name: exempt
rules:
- nonResourceRules:
- nonResourceURLs:
- /healthz
- /livez
- /readyz
verbs:
- '*'
subjects:
- group:
name: system:unauthenticated
kind: Group
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2023-11-05T02:25:45Z"
message: This FlowSchema references the PriorityLevelConfiguration object named
"exempt" and it exists
reason: Found
status: "False"
type: Dangling3. 使用 v1beta3 读取:
kubectl get flowschema.v1beta3.flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io test -o yaml
或者
curl -H "Accept: application/yaml" http://127.0.0.1:8001/apis/flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3/flowschemas/test输出:
Warning: flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3 FlowSchema is deprecated in v1.29+, unavailable in v1.32+
apiVersion: flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3
kind: FlowSchema
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta2","kind":"FlowSchema","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"test"},"spec":{"matchingPrecedence":1000,"priorityLevelConfiguration":{"name":"exempt"},"rules":[{"nonResourceRules":[{"nonResourceURLs":["/healthz","/livez","/readyz"],"verbs":["*"]}],"subjects":[{"group":{"name":"system:unauthenticated"},"kind":"Group"}]}]}}
creationTimestamp: "2023-11-05T02:17:34Z"
generation: 2
name: test
resourceVersion: "52473"
uid: d70bf2e9-3773-4cab-ae4d-b5e060009beb
spec:
matchingPrecedence: 1000
priorityLevelConfiguration:
name: exempt
rules:
- nonResourceRules:
- nonResourceURLs:
- /healthz
- /livez
- /readyz
verbs:
- '*'
subjects:
- group:
name: system:unauthenticated
kind: Group
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2023-11-05T02:25:45Z"
message: This FlowSchema references the PriorityLevelConfiguration object named
"exempt" and it exists
reason: Found
status: "False"
type: Dangling可以看到,使用两个版本读出来的对象,几乎完全一样,除了apiVersion字段有区别,metadata字段中的resourceVersion和uid字段都一样,说明他们其实是同一个对象,我们可以直接查看 etcd 来确认下:
# etcdctl --endpoints http://127.0.0.1:2379 get / --prefix --keys-only | grep test
/registry/flowschemas/test
# etcdctl --endpoints http://127.0.0.1:2379 get /registry/flowschemas/test
/registry/flowschemas/test
k8s
2
$flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3
FlowSchema
test"*$d70bf2e9-3773-4cab-ae4d-b5e060009beb2bB
0kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration{"apiVersion":"flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta2","kind":"FlowSchema","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"test"},"spec":{"matchingPrecedence":1000,"priorityLevelConfiguration":{"name":"exempt"},"rules":[{"nonResourceRules":[{"nonResourceURLs":["/healthz","/livez","/readyz"],"verbs":["*"]}],"subjects":[{"group":{"name":"system:unauthenticated"},"kind":"Group"}]}]}}
,api-priority-and-fairness-config-consumer-v1Apply$flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1betaFieldsV1:
{"f:status":{"f:conditions":{"k:{\"type\":\"Dangling\"}":{".":{},"f:lastTransitionTime":{},"f:message":{},"f:reason":{},"f:status":{},"f:type":{}}}}}Bstatus
kubectl-client-side-applyUpdate$flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1betaFieldsV1:
{"f:metadata":{"f:annotations":{".":{},"f:kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration":{}}},"f:spec":{"f:matchingPrecedence":{},"f:priorityLevelConfiguration":{"f:name":{}},"f:rules":{}}}BR
exempt"C
!
Group
system:unauthenticated
*/healthz2/livez2/readyz
DanglingFal"Found*]This FlowSchema references the PriorityLevelConfiguration object named "exempt" and it exists"可以看到存到数据库中实际上只有一条记录,但是却可以读出来两个不同的版本,说明在调用不同版本的API读取对象时,肯定是经历了某种转换。
这个例子其实还不太好,因为两个版本的 FlowSchema 对象的字段是完全一样的,如果两个版本之间有字段的差异,可能更能说明问题,但是由于现在 Kubernetes 发展的已经很成熟了,各个API都已经趋于成熟,都逐渐的把 beta 版的API给移除了,或者 beta 版跟 GA 版几乎没有差异,beta 的存在仅仅是为了能够兼容一下旧版本的应用。
通过上面的例子,我们大概感受了下 API 多版本的功能,此外,还有个多协议的功能点,即用户可以选择API返回的数据的格式,比如上例中,我们通过命令行的 -o 选项或者 api请求的Accept Header参数,来指定了希望返回 yaml 格式的数据,于是 apiserver 会将 API 资源给序列化成 yaml 格式返回给客户端,除了yaml 格式,apiserver 还支持序列化成 json 以及 protobuf 格式,例如:
curl -H "Accept: application/json" http://127.0.0.1:8001/apis/flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3/flowschemas/testcurl -H "Accept: application/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf" http://127.0.0.1:8001/apis/flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3/flowschemas/test
k8s
2
$flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3
FlowSchema
test"*$d70bf2e9-3773-4cab-ae4d-b5e060009beb252473bB
0kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration{"apiVersion":"flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta2","kind":"FlowSchema","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"test"},"spec":{"matchingPrecedence":1000,"priorityLevelConfiguration":{"name":"exempt"},"rules":[{"nonResourceRules":[{"nonResourceURLs":["/healthz","/livez","/readyz"],"verbs":["*"]}],"subjects":[{"group":{"name":"system:unauthenticated"},"kind":"Group"}]}]}}
,api-priority-and-fairness-config-consumer-v1Apply$flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1betaFieldsV1:
{"f:status":{"f:conditions":{"k:{\"type\":\"Dangling\"}":{".":{},"f:lastTransitionTime":{},"f:message":{},"f:reason":{},"f:status":{},"f:type":{}}}}}Bstatus
kubectl-client-side-applyUpdate$flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1betaFieldsV1:
{"f:metadata":{"f:annotations":{".":{},"f:kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration":{}}},"f:spec":{"f:matchingPrecedence":{},"f:priorityLevelConfiguration":{"f:name":{}},"f:rules":{}}}BR
exempt"C
!
Group
system:unauthenticated
*/healthz2/livez2/readyz
DanglingFal"Found*]This FlowSchema references the PriorityLevelConfiguration object named "exempt" and it exists"从上面的功能介绍来看,k8s 社区将API 的兼容性看得很重要,能够做到这个程度的 API 兼容,真的是很良心的,难怪它会一统江湖,除了每个API都有一个进化迭代的过程之外,一旦API进入到GA稳定版阶段,后续对它的修改一定是不能破坏兼容性的,关于API兼容性的更多内容,可以阅读下社区的这个文档:Changing the API
OK,看了上面的功能介绍和示例,我们心里可能会有一些困惑:
- 不同版本之间是如何转换的?有两个版本还好说,那如果是有很多版本,难道要两两组合下吗,这会不会太傻了?
- 实际存储到etcd中的是什么版本的?上面的例子中,是通过v1beta2 API存进去的对象,可是通过etcdctl查看数据库中的数据,怎么好像是存储的v1beta3版本的?
- 实际存储到etcd中的数据是什么格式的?从上面的例子中,可以看到,使用etcdctl和curl protobuf格式查看到的数据,好像长的是一样的,难道直接是存储的protobuf格式的?
好,带着这些问题,我们进入下一个小节,来看看它的实现原理。
主要来说说版本是怎么转换的,为了方便各个版本之间互相转换,APIServer引入了一个内部版本的概念,每个API对象都有一个对应的内部版本,它是一个特殊的版本,是在APIServer内部对各个API对象进行处理时使用的数据结构(Struct),而不是使用的某个具体版本的数据结构(Struct),当该API对象跟外部交互时,则会从内部版本转换成对应的具体版本,我们称之为外部版本,这个“外部”其实包含两个地方:一个是通过HTTP协议跟客户端交互时,会将其转换成客户端请求的版本,一个是将该对象存储到数据库时,数据库会将其保存成某个版本的数据结构(Struct)。这个内部版本,有点类似于中间版本的概念,不论你请求的是哪个版本,都是那个版本跟内部版本之间互相转换,具体版本之间是不会直接进行转换的,这样就将一个网状的结构,转换成了星状的结构,减少了数据处理的维度,每个版本的API对象,只需要申明自己怎么跟内部版本进行转换就可以了。
还有就是将某个对象存储到数据库时,并不是存储的内部版本的数据结构,而是存储的某个具体版本的数据结构,一般是该API对象最稳定版本的数据结构,比如某个API对象同时有两个版本,v1和v1beta1,那么不论通过哪个版本请求过来的,最终存储到数据库中的,都是v1版本对应的数据结构,反过来,当你从数据库读出来对应的数据之后,APIServer则首先会将其从v1版本转换成内部版本,然后再进行其他的处理。当然,也有可能存储的不是最稳定的版本,而是某个中间版本,比如v1, v1beta1, v1beta2,可能它存的是 v1beta2 版本的数据结构,即次稳定版本,这种情况,一般都处在升级迭代的过程中,保证应用的兼容性,经历几个版本迭代之后,还是最终切到v1版本的数据结构上去。
OK,我们还是以上面的FlowSchema为例,来看看它不同版本之间转换的一个过程,先来看看FlowSchema各个版本的数据结构定义:
v1beta2 的数据结构:
# k8s.io/api/flowcontrol/v1beta2/types.go
type FlowSchema struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
// `metadata` is the standard object's metadata.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
// +optional
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=metadata"`
// `spec` is the specification of the desired behavior of a FlowSchema.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
// +optional
Spec FlowSchemaSpec `json:"spec,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=spec"`
// `status` is the current status of a FlowSchema.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
// +optional
Status FlowSchemaStatus `json:"status,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=status"`
}
// FlowSchemaSpec describes how the FlowSchema's specification looks like.
type FlowSchemaSpec struct {
// `priorityLevelConfiguration` should reference a PriorityLevelConfiguration in the cluster. If the reference cannot
// be resolved, the FlowSchema will be ignored and marked as invalid in its status.
// Required.
PriorityLevelConfiguration PriorityLevelConfigurationReference `json:"priorityLevelConfiguration" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=priorityLevelConfiguration"`
// `matchingPrecedence` is used to choose among the FlowSchemas that match a given request. The chosen
// FlowSchema is among those with the numerically lowest (which we take to be logically highest)
// MatchingPrecedence. Each MatchingPrecedence value must be ranged in [1,10000].
// Note that if the precedence is not specified, it will be set to 1000 as default.
// +optional
MatchingPrecedence int32 `json:"matchingPrecedence" protobuf:"varint,2,opt,name=matchingPrecedence"`
// `distinguisherMethod` defines how to compute the flow distinguisher for requests that match this schema.
// `nil` specifies that the distinguisher is disabled and thus will always be the empty string.
// +optional
DistinguisherMethod *FlowDistinguisherMethod `json:"distinguisherMethod,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=distinguisherMethod"`
// `rules` describes which requests will match this flow schema. This FlowSchema matches a request if and only if
// at least one member of rules matches the request.
// if it is an empty slice, there will be no requests matching the FlowSchema.
// +listType=atomic
// +optional
Rules []PolicyRulesWithSubjects `json:"rules,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,4,rep,name=rules"`
}v1beta3的数据结构:
# k8s.io/api/flowcontrol/v1beta3/types.go
type FlowSchema struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
// `metadata` is the standard object's metadata.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
// +optional
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=metadata"`
// `spec` is the specification of the desired behavior of a FlowSchema.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
// +optional
Spec FlowSchemaSpec `json:"spec,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=spec"`
// `status` is the current status of a FlowSchema.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
// +optional
Status FlowSchemaStatus `json:"status,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=status"`
}
type FlowSchemaSpec struct {
// `priorityLevelConfiguration` should reference a PriorityLevelConfiguration in the cluster. If the reference cannot
// be resolved, the FlowSchema will be ignored and marked as invalid in its status.
// Required.
PriorityLevelConfiguration PriorityLevelConfigurationReference `json:"priorityLevelConfiguration" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=priorityLevelConfiguration"`
// `matchingPrecedence` is used to choose among the FlowSchemas that match a given request. The chosen
// FlowSchema is among those with the numerically lowest (which we take to be logically highest)
// MatchingPrecedence. Each MatchingPrecedence value must be ranged in [1,10000].
// Note that if the precedence is not specified, it will be set to 1000 as default.
// +optional
MatchingPrecedence int32 `json:"matchingPrecedence" protobuf:"varint,2,opt,name=matchingPrecedence"`
// `distinguisherMethod` defines how to compute the flow distinguisher for requests that match this schema.
// `nil` specifies that the distinguisher is disabled and thus will always be the empty string.
// +optional
DistinguisherMethod *FlowDistinguisherMethod `json:"distinguisherMethod,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=distinguisherMethod"`
// `rules` describes which requests will match this flow schema. This FlowSchema matches a request if and only if
// at least one member of rules matches the request.
// if it is an empty slice, there will be no requests matching the FlowSchema.
// +listType=atomic
// +optional
Rules []PolicyRulesWithSubjects `json:"rules,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,4,rep,name=rules"`
}内部结构
# kubernetes/pkg/apis/flowcontrol/types.go
type FlowSchema struct {
metav1.TypeMeta
// `metadata` is the standard object's metadata.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
// +optional
metav1.ObjectMeta
// `spec` is the specification of the desired behavior of a FlowSchema.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
// +optional
Spec FlowSchemaSpec
// `status` is the current status of a FlowSchema.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
// +optional
Status FlowSchemaStatus
}
type FlowSchemaSpec struct {
// `priorityLevelConfiguration` should reference a PriorityLevelConfiguration in the cluster. If the reference cannot
// be resolved, the FlowSchema will be ignored and marked as invalid in its status.
// Required.
PriorityLevelConfiguration PriorityLevelConfigurationReference
// `matchingPrecedence` is used to choose among the FlowSchemas that match a given request. The chosen
// FlowSchema is among those with the numerically lowest (which we take to be logically highest)
// MatchingPrecedence. Each MatchingPrecedence value must be ranged in [1,10000].
// Note that if the precedence is not specified, it will be set to 1000 as default.
// +optional
MatchingPrecedence int32
// `distinguisherMethod` defines how to compute the flow distinguisher for requests that match this schema.
// `nil` specifies that the distinguisher is disabled and thus will always be the empty string.
// +optional
DistinguisherMethod *FlowDistinguisherMethod
// `rules` describes which requests will match this flow schema. This FlowSchema matches a request if and only if
// at least one member of rules matches the request.
// if it is an empty slice, there will be no requests matching the FlowSchema.
// +listType=set
// +optional
Rules []PolicyRulesWithSubjects
}从上面的代码可以看到,v1beta2 和v1beta3 目前的数据结构是一模一样的,并且都位于k8s.io/api这个第三方库中,只是所在的目录不同而已,而内部版本的数据结构的字段跟他们也是一样的,只是没有带用来做序列化的 tag,并且内部结构是位于 kubernetes 本身的代码目录树中的,并没有以第三方库的形式暴露出去。
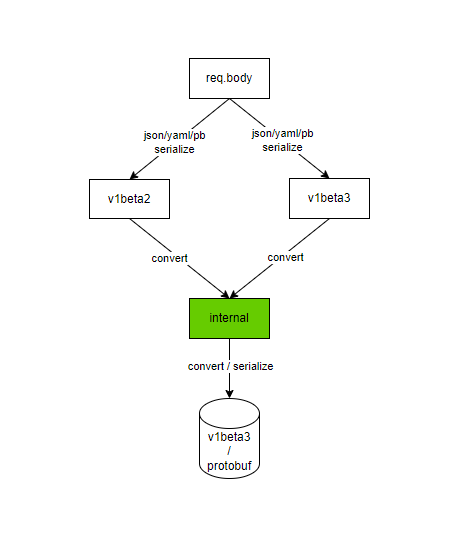
OK,我们先来看下创建过程中的版本转换以及序列化过程,如下图:
HTTP请求到了APIServer,会由该资源API对应的Handler来处理,第一步就是根据HTTP请求的Content-Type Header中标记的数据类型,比如是 json还 是 protobuf,来将字节类型的 req.body 反序列化为对应版本的数据结构的对象实例,第二步,又会将具体版本的对象转换成内部版本的对象,第三步,在存数据库的时候,又将内部版本的对象转换成了稳定版本的数据结构的对象实例,并且将其序列化为protobuf格式的数据,将其存到数据库中。在存数据库的时候,默认是使用protobuf格式,可以通过配置项 --storage-media-type 来更改存储的格式,支持 json/yaml/protobuf 三种格式。
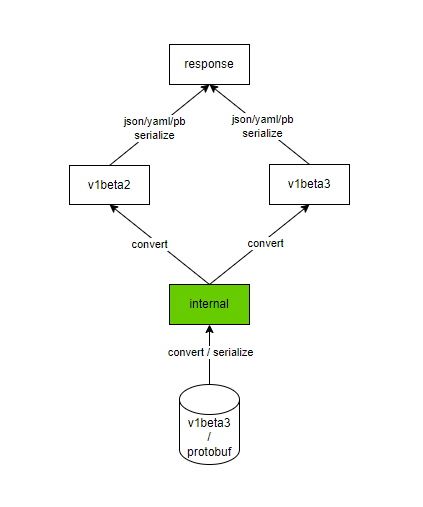
再来看看读取的过程,如下图:
读的过程,其实正好跟写的过程相反,当请求某一个版本的API对象时,首先会从数据库中读出字节类型的数据,然后将其反序列化为内部数据结构的对象实例,然后再转换成对应的版本,然后再根据请求中的Accept Header来决定将其序列化为哪种数据格式,返回给客户端。