Replies: 3 comments 1 reply
-
|
This is great! Could you submit a pull request? Thanks. |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
0 replies
-
|
A different version by gena https://code.earthengine.google.com/dd95c1b5f7f463dbdfebe5bede970586 |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
0 replies
-
|
Hi, I liked that example, this would be a modification of the going_timeseries function that can replicate the example. def goes_timeseries(
start_date="2021-10-24T14:00:00",
end_date="2021-10-25T01:00:00",
data="GOES-17",
scan="full_disk",
region=None,
show_night=[False, "a_mode"],
):
"""Create a time series of GOES data. The code is adapted from Justin Braaten's code: https://code.earthengine.google.com/57245f2d3d04233765c42fb5ef19c1f4.
Credits to Justin Braaten. See also https://jstnbraaten.medium.com/goes-in-earth-engine-53fbc8783c16
Args:
start_date (str, optional): The start date of the time series. Defaults to "2021-10-24T14:00:00".
end_date (str, optional): The end date of the time series. Defaults to "2021-10-25T01:00:00".
data (str, optional): The GOES satellite data to use. Defaults to "GOES-17".
scan (str, optional): The GOES scan to use. Defaults to "full_disk".
region (ee.Geometry, optional): The region of interest. Defaults to None.
show_night (list, optional): Show the clouds at night through [True, "a_mode"] o [True, "b_mode"]. Defaults to [False, "a_mode"]
Raises:
ValueError: The data must be either GOES-16 or GOES-17.
ValueError: The scan must be either full_disk, conus, or mesoscale.
Returns:
ee.ImageCollection: GOES timeseries.
"""
if data not in ["GOES-16", "GOES-17"]:
raise ValueError("The data must be either GOES-16 or GOES-17.")
if scan.lower() not in ["full_disk", "conus", "mesoscale"]:
raise ValueError("The scan must be either full_disk, conus, or mesoscale.")
scan_types = {
"full_disk": "MCMIPF",
"conus": "MCMIPC",
"mesoscale": "MCMIPM",
}
col = ee.ImageCollection(f"NOAA/GOES/{data[-2:]}/{scan_types[scan.lower()]}")
if region is None:
region = ee.Geometry.Polygon(
[
[
[-159.5954379282731, 60.40883060191719],
[-159.5954379282731, 24.517881970830725],
[-114.2438754282731, 24.517881970830725],
[-114.2438754282731, 60.40883060191719],
]
],
None,
False,
)
# Applies scaling factors.
def applyScaleAndOffset(img):
def getFactorImg(factorNames):
factorList = img.toDictionary().select(factorNames).values()
return ee.Image.constant(factorList)
scaleImg = getFactorImg(["CMI_C.._scale"])
offsetImg = getFactorImg(["CMI_C.._offset"])
scaled = img.select("CMI_C..").multiply(scaleImg).add(offsetImg)
return img.addBands(**{"srcImg": scaled, "overwrite": True})
# Adds a synthetic green band.
def addGreenBand(img):
green = img.expression(
"CMI_GREEN = 0.45 * red + 0.10 * nir + 0.45 * blue",
{
"blue": img.select("CMI_C01"),
"red": img.select("CMI_C02"),
"nir": img.select("CMI_C03"),
},
)
return img.addBands(green)
# Show at clouds at night (a-mode)
def showNighta(img):
# Make normalized infrared
IR_n = img.select('CMI_C13').unitScale(ee.Number(90), ee.Number(313))
IR_n = IR_n.expression(
"ir_p = (1 -IR_n)/1.4",
{
"IR_n": IR_n.select('CMI_C13'),
},
)
# Add infrared to rgb bands
R_ir = img.select('CMI_C02').max(IR_n)
G_ir = img.select('CMI_GREEN').max(IR_n)
B_ir = img.select('CMI_C01').max(IR_n)
return img.addBands([R_ir, G_ir, B_ir], overwrite=True)
# Show at clouds at night (b-mode)
def showNightb(img):
night = img.select('CMI_C03').unitScale(0, 0.016).subtract(1).multiply(-1)
cmi11 = img.select('CMI_C11').unitScale(100, 310)
cmi13 = img.select('CMI_C13').unitScale(100, 300)
cmi15 = img.select('CMI_C15').unitScale(100, 310)
iNight = cmi15.addBands([cmi13, cmi11]).clamp(0, 1).subtract(1).multiply(-1)
iRGBNight = iNight.visualize(**{"min": 0, "max": 1, "gamma": 1.4 }).updateMask(night)
iRGB = img.visualize(**{"bands": ['CMI_C02', 'CMI_C03', 'CMI_C01'], "min": 0.15, "max": 1, "gamma": 1.4 })
return iRGB.blend(iRGBNight).set("system:time_start", img.get("system:time_start"))
# Scales select bands for visualization.
def scaleForVis(img):
return (
img.select(["CMI_C01", "CMI_GREEN", "CMI_C02", "CMI_C03", "CMI_C05"])
.resample("bicubic")
.log10()
.interpolate([-1.6, 0.176], [0, 1], "clamp")
.unmask(0)
.set("system:time_start", img.get("system:time_start"))
)
# Wraps previous functions.
def processForVis(img):
if show_night[0]:
if show_night[1] == "a_mode":
return scaleForVis(showNighta(addGreenBand(applyScaleAndOffset(img))))
else:
return showNightb(applyScaleAndOffset(img))
else:
return scaleForVis(addGreenBand(applyScaleAndOffset(img)))
return col.filterDate(start_date, end_date).map(processForVis)The possible results of the function are:
# Ouput bands: ['CMI_C01', 'CMI_GREEN', 'CMI_C02', 'CMI_C03', 'CMI_C05']
col = goes_timeseries(start_date, end_date, data, scan, region, show_night=[False, "a_mode"])
# Ouput bands: ['CMI_C01', 'CMI_GREEN', 'CMI_C02', 'CMI_C03', 'CMI_C05']
col = goes_timeseries(start_date, end_date, data, scan, region, show_night=[True, "a_mode"])
# Ouput bands: ['vis-red', 'vis-green', 'vis-blue']
col = goes_timeseries(start_date, end_date, data, scan, region, show_night=[True, "b_mode"]) |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
1 reply
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.
-
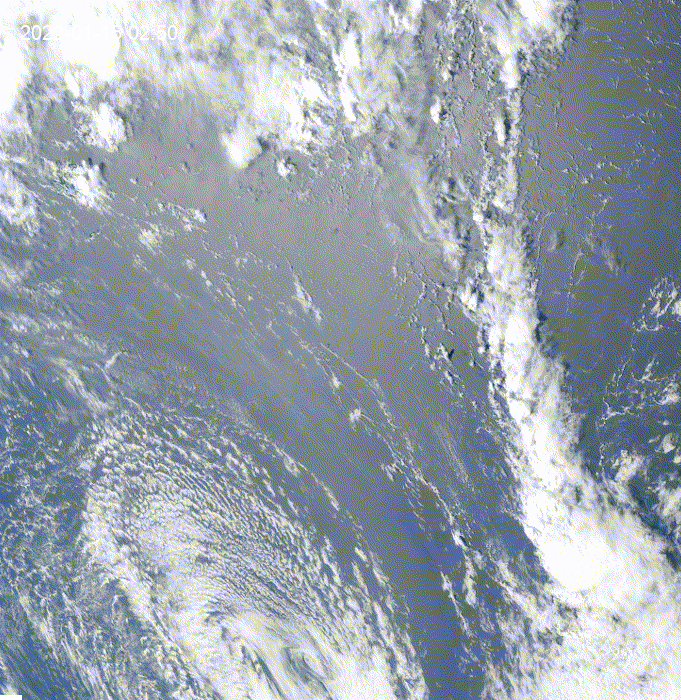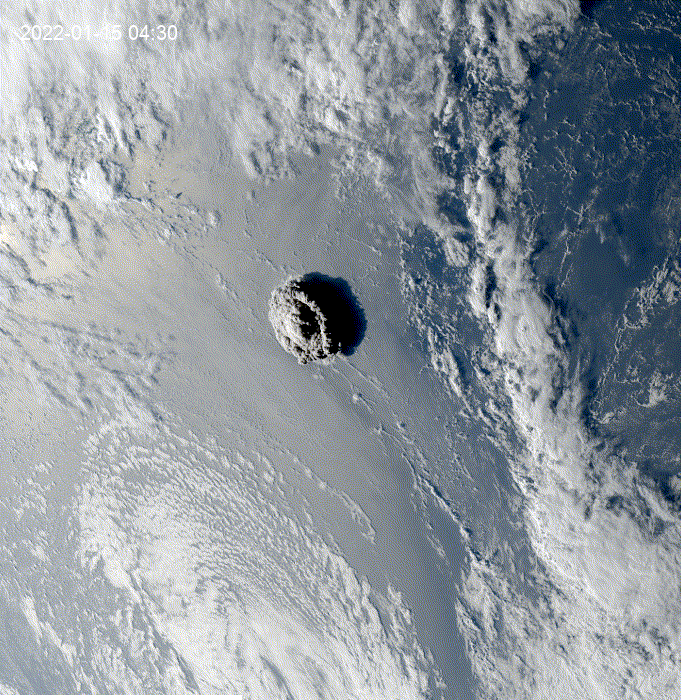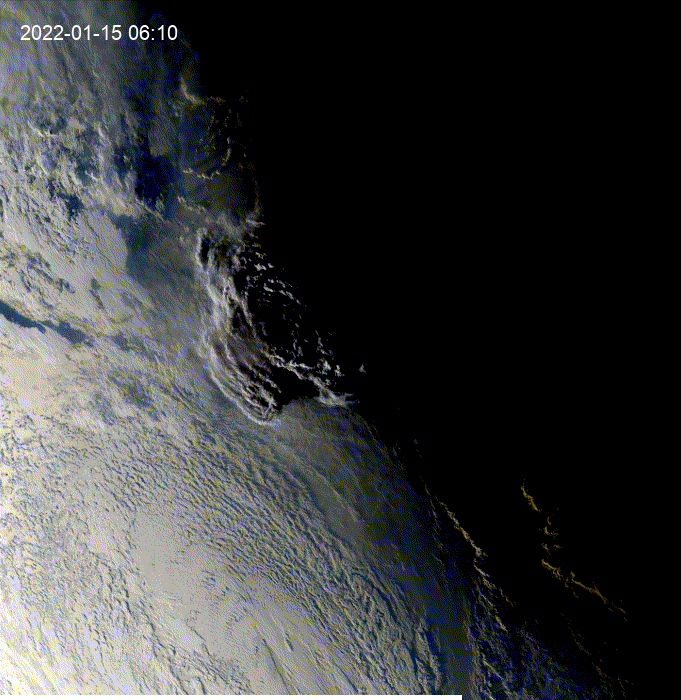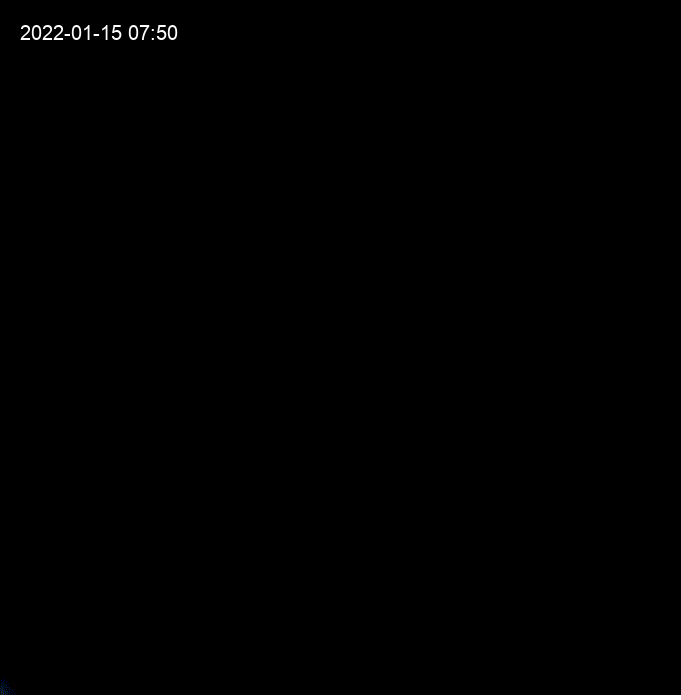
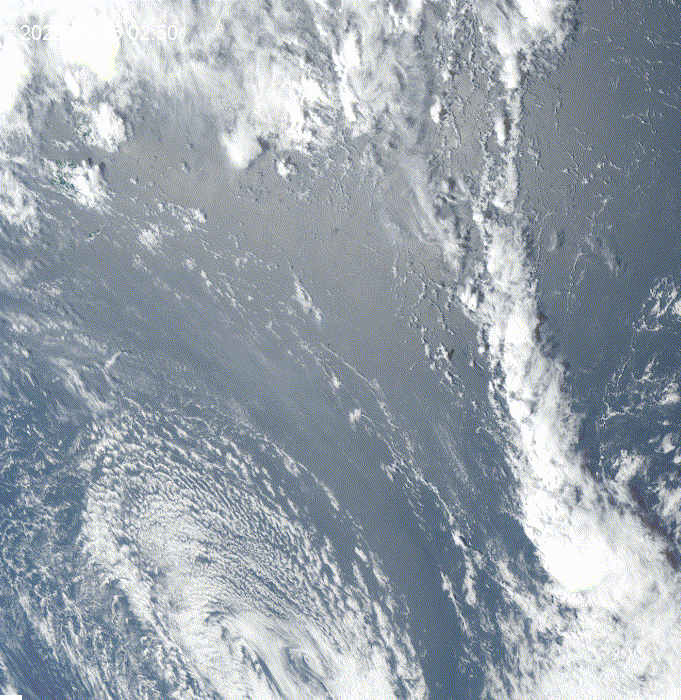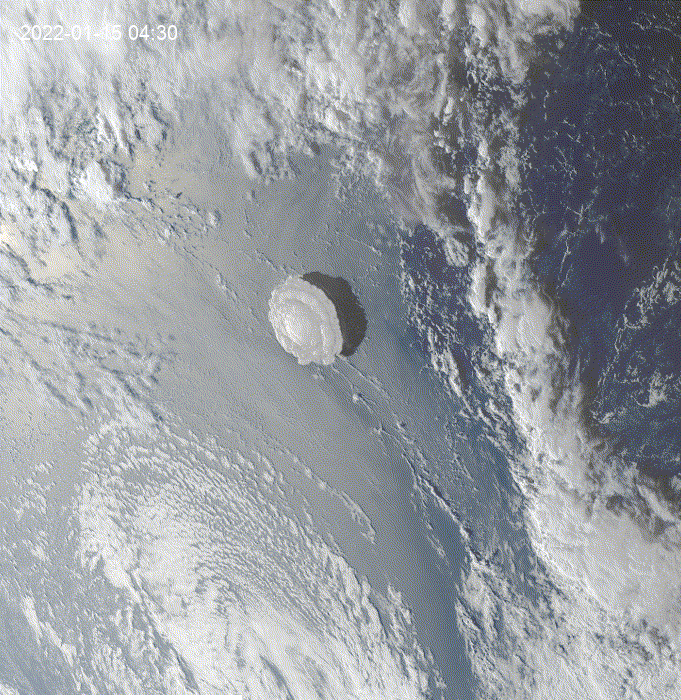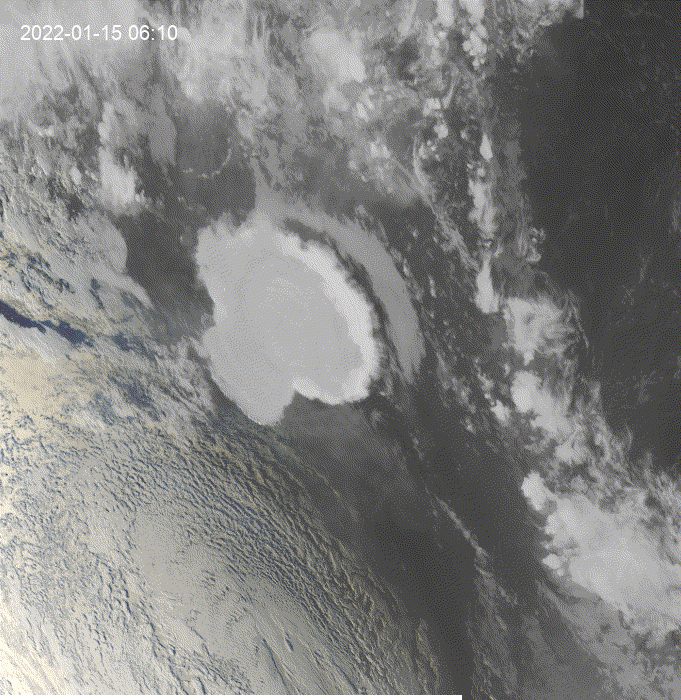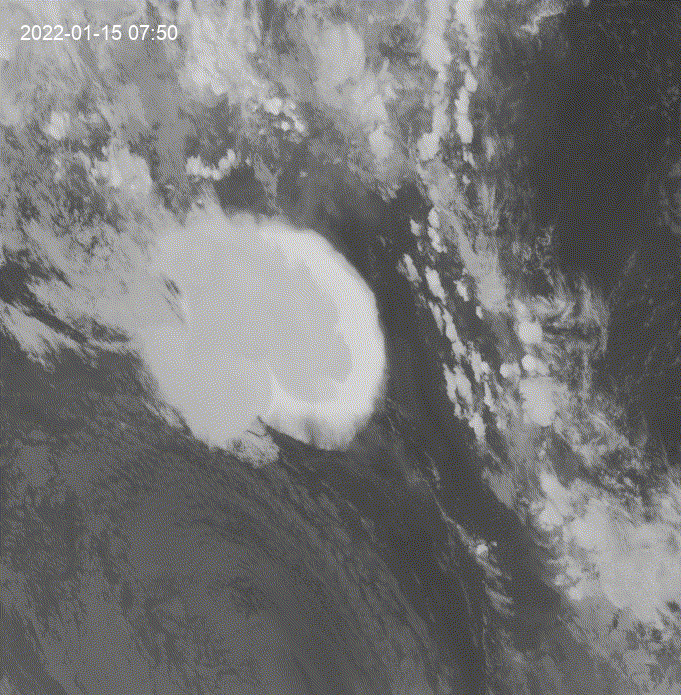
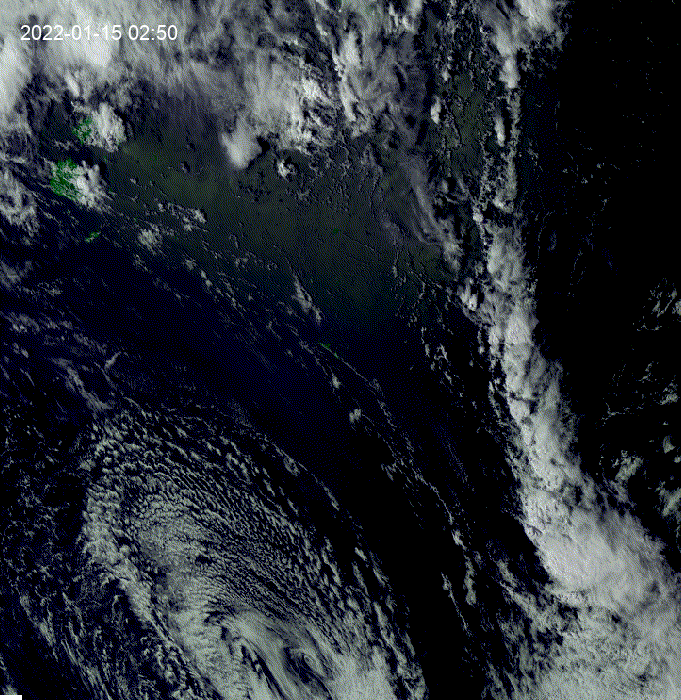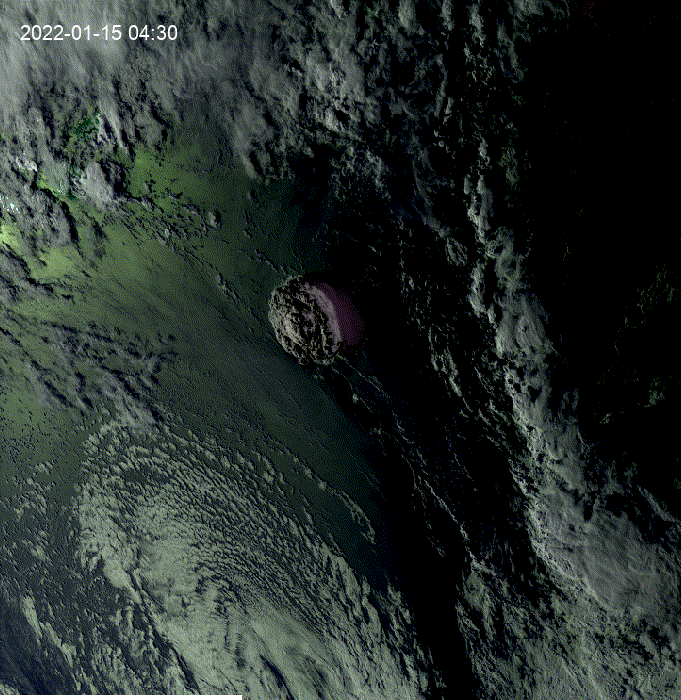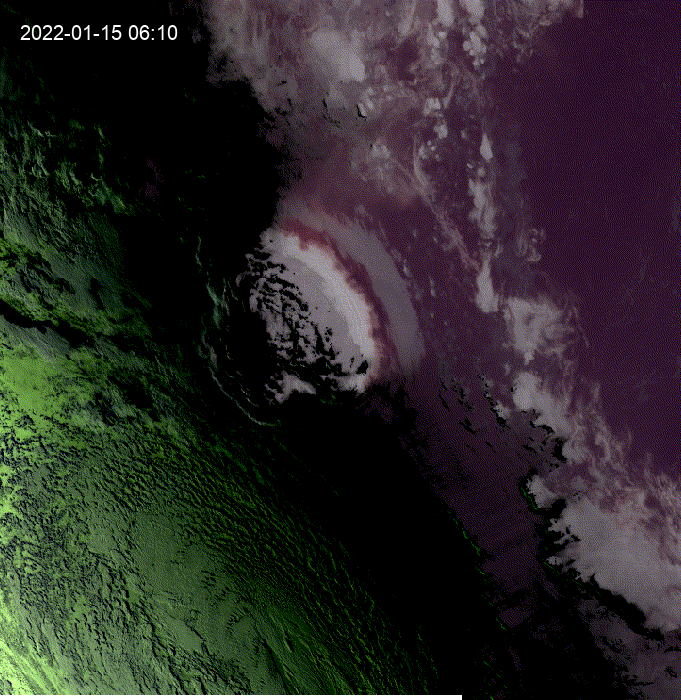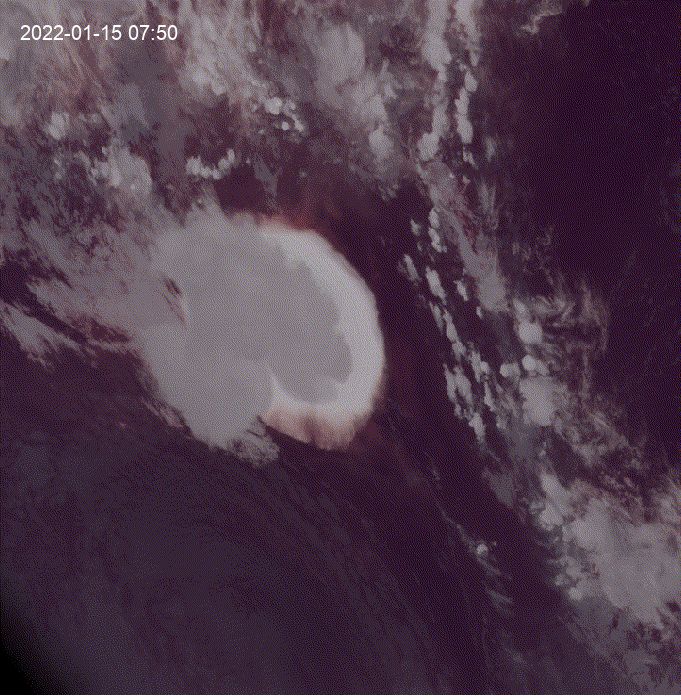
Hi, I was exploring this example and I got the question of how to see clouds at night using GOES.
This is a modification of the
geemap.goes_timeseries()function to solve the question.These results are from the unmodified function.
These results are from the modified function.
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
All reactions