Milvus is Vector database built for scalable similarity search. It is "Open-source, highly scalable, and blazing fast".
As Milvus supports meany features, the easiest way to understand what it can do is to head to the relevant documentation.
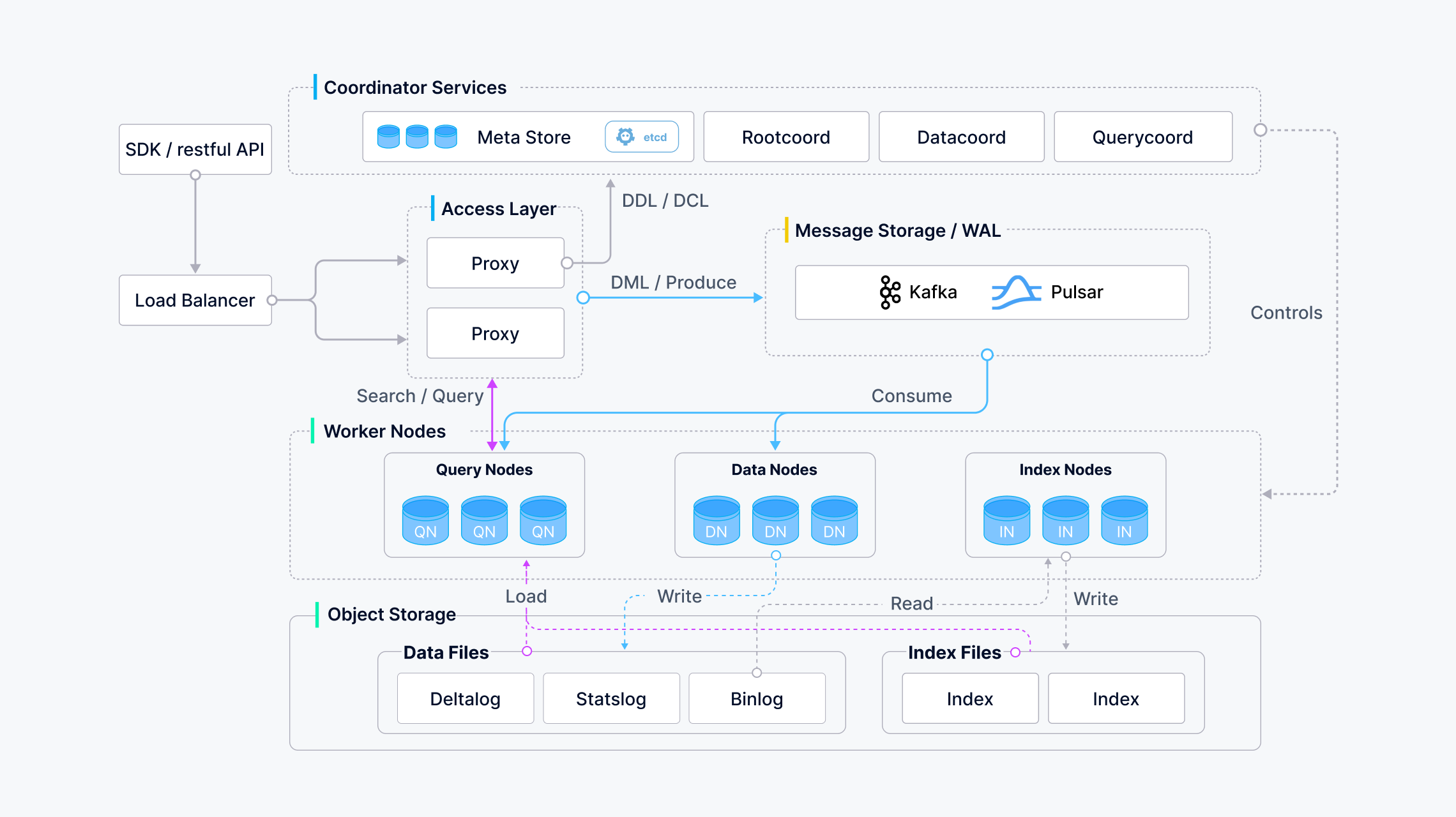
Milvus also provides great documentation, starting with a full description of its architecture.
The following recipes will deploy a default installation of Milvus in standalone mode, with authentication enabled. Here, we will also deploy Attu, that provides an interactive management UI for Milvus.
However, many things can be modified in this configuration, through the provided standalone/config/openshift-values.yaml file.
-
The default Milvus deployment leverages Minio to store logs and index files. This can be replaced by another S3 storage system.
To modify those components, as well many other configuration parameters, please refer to the configuration documentation and modify the values file according to your needs.
-
Clone or navigate to this repository.
To get started, clone the repository using:
git clone https://github.com/nerc-project/llm-on-nerc.git cd llm-on-nerc/vector-databases/milvus -
In the
standalonefolder, you will find the following YAML files:-
attu-deployment.yaml: Deploys Attu, the web-based UI for managing and visualizing Milvus vector database operations.
-
etcd-resources.yaml: Defines the etcd resources, which provide a distributed key-value store for Milvus metadata management.
-
milvus-config.yaml: Contains the configuration settings for Milvus, specifying parameters like storage, indexing, and query performance. This includes
milvus.yamlkey to set different configurations, you need to update them as required. -
milvus-resources.yaml: Defines the Milvus deployment and related Kubernetes resources necessary to run the vector database.
-
minio-resources.yaml: Deploys MinIO, an object storage service used by Milvus to store and manage vector data.
NOTE: Etcd is a distributed key-value store that provides a reliable solution for storing and managing configuration data, service discovery, and remote procedure calls (RPCs) in distributed systems. It is widely used in container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes, Docker Swarm, and Mesos to manage system configuration and state.
Milvus can be deployed on the NERC OpenShift in Standalone mode. You can run this
occommand:oc apply -f ./standalone/.to execute all of the above described YAML files located in the standalone folder at once.oc apply -f ./standalone/. deployment.apps/attu-deployment created service/attu-service created route.route.openshift.io/attu-route created persistentvolumeclaim/etcd-pvc created deployment.apps/etcd-deployment created service/etcd-service created configmap/milvus-config created persistentvolumeclaim/milvus-pvc created deployment.apps/milvus-deployment created service/milvus-service created route.route.openshift.io/milvus-route created persistentvolumeclaim/minio-pvc created deployment.apps/minio-deployment created service/minio-service created route.route.openshift.io/minio-console created
Authentication:
Milvus has now been deployed with
authenticationenabled, which is configured asmilvus-configConfigMap through themilvus-config.yamlfile. This is because, themilvus.yamlkey is set with the following configuration:... security: authorizationEnabled: true ... -
This enables authentication in Milvus. The default admin user is root with the default password Milvus.
To delete all resources if not necessary just run oc delete -f ./standalone/. or oc delete all,pvc,configmap -l app=milvus.
The API is now accessible at the endpoints:
-
defined by your Service, accessible internally on port 11434 using http. E.g.
http://ollama-service.<your-namespace>.svc.cluster.local:11434. -
defined by your Route, accessible externally through https, e.g.
https://ollama-route-<your-namespace>.apps.shift.nerc.mghpcc.org. -
defined by your Attu Route, accessible externally through https, e.g.
https://attu-route-<your-namespace>.apps.shift.nerc.mghpcc.org.
Access deployed Attu web-based UI for Milvus:
To access the deployed Attu web-based UI for Milvus, follow these steps:
Find the Route URL: The URL to access the Attu web UI should be in the following format: https://attu-route-<your-namespace>.apps.shift.nerc.mghpcc.org.
NOTE: Replace with the appropriate namespace where your deployment is run.
Access the Attu: Open a web browser and navigate to the route URL to access the Attu web-based UI for Milvus.
Since, Milvus has been deployed with authorizationEnabled: true security setting in milvus.yaml key of the milvus-config ConfigMap:
To login the Attu web UI, please make sure to connect to:
-
Milvus Server: milvus-service:19530
-
Milvus Database: default
-
Toggle on: "Authentication"
-
Token: Empty
-
username: root
-
password: Milvus
NOTE: The default admin user is root with the default password Milvus.