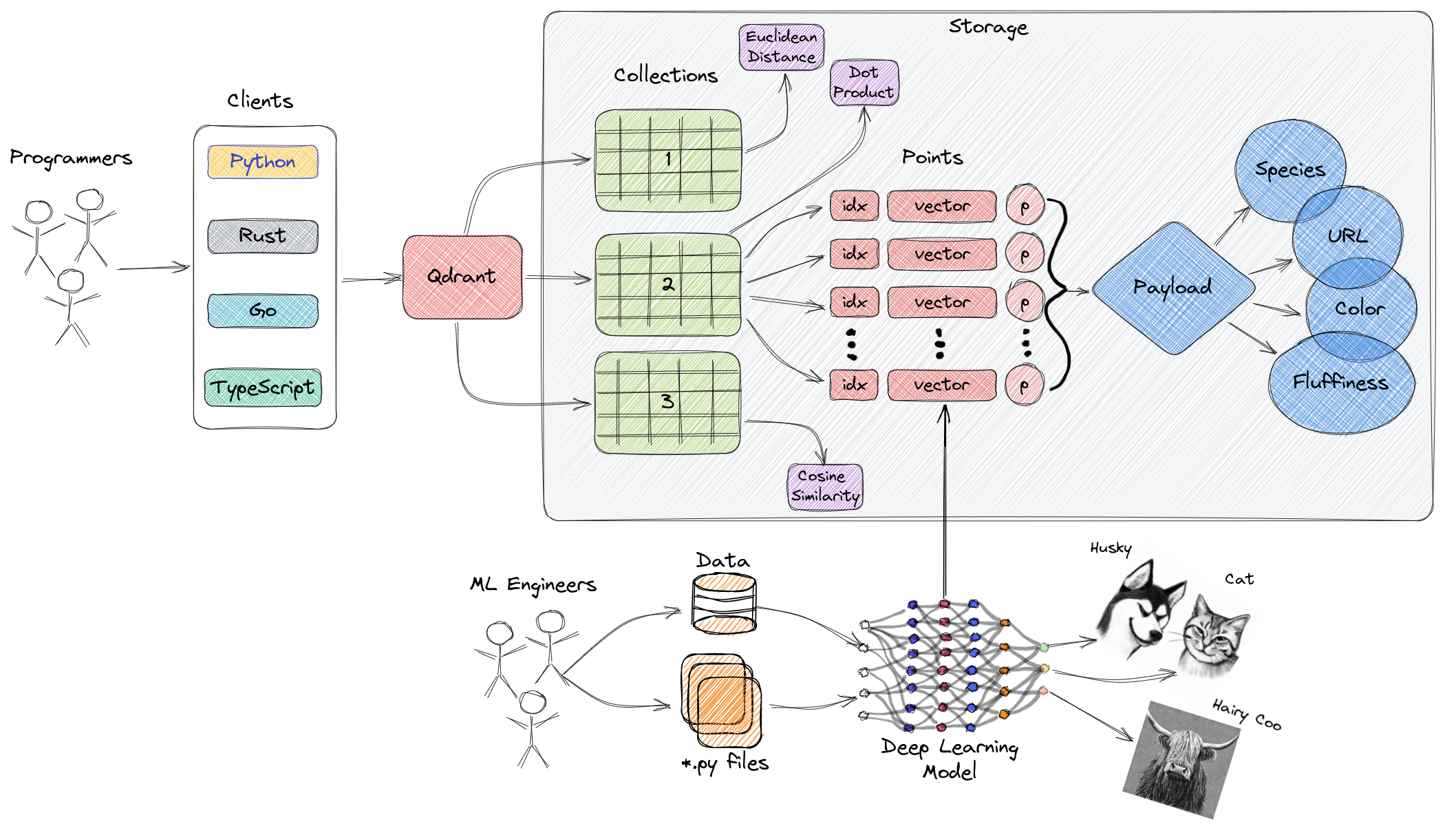
Qdrant is an AI-native vector database and semantic search engine designed to extract meaningful insights from unstructured data.
With Qdrant, embeddings or neural network encoders can be turned into full-fledged applications for matching, searching, recommending, and much more!
Qdrant also provides great documentation, starting with a High-Level Overview of Qdrant's Architecture.
-
Clone or navigate to this repository.
To get started, clone the repository using:
git clone https://github.com/nerc-project/llm-on-nerc.git cd llm-on-nerc/vector-databases/qdrant -
In the
standalonefolder, you will find the following YAML files that allow you to easily deploy a Qdrant instance:-
01-qdrant-secret.yaml: Defines the Secret for storing sensitive data, such as credentials or API keys, used by Qdrant. Change QDRANT__SERVICE__API_KEY value with your own!
-
02-qdrant-pvc.yaml: Defines an additional PVC for storing data, ensuring that Qdrant's data persists across restarts. Adjust the size according to your needs.
-
03-qdrant-persistent-pvc.yaml: Creates a Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) for persistent storage to store Qdrant's data as a managed Qdrant snapshot. Adjust the size according to your needs.
-
04-qdrant-deployment.yaml: Deploys the Qdrant container as a stateless application within your OpenShift cluster.
-
05-qdrant-service.yaml: Exposes the Qdrant deployment as a Service to allow communication between Qdrant and other services in the cluster.
-
06-qdrant-route.yaml: Configures a Route to expose the Qdrant service to external traffic, enabling web access.
-
You can run this oc command: oc apply -f ./standalone/. to execute all of the above described YAML files located in the standalone folder at once.
oc apply -f ./standalone/.
secret/qdrant-key created
persistentvolumeclaim/qdrant-storage-pvc created
persistentvolumeclaim/qdrant-snapshots-pvc created
deployment.apps/qdrant-deployment created
service/qdrant-service created
route.route.openshift.io/qdrant-route createdTo delete all resources if not necessary just run oc delete -f ./standalone/. or oc delete all,pvc,secret -l app=qdrant.
The API is now accessible at the endpoints:
-
defined by your Service, accessible internally on port 6333 using http. E.g.
http://qdrant-service.<your-namespace>.svc.cluster.local:6333. -
defined by your Route, accessible externally through https, e.g.
https://qdrant-route-<your-namespace>.apps.shift.nerc.mghpcc.org.
Accessing Qdrant Dashboard:
Go to https://qdrant-route-<your-namespace>.apps.shift.nerc.mghpcc.org/dashboard. This will prompt you for an API key that has been set up as a secret using the 01-qdrant-secret.yaml.
To get the value of QDRANT__SERVICE__API_KEY from the qdrant-key Secret using the oc command, follow these steps:
oc get secret qdrant-key -o jsonpath='{.data.QDRANT__SERVICE__API_KEY}' | base64 --decode
This command does the following:
-
Fetches the
qdrant-keysecret. -
Extracts the
QDRANT__SERVICE__API_KEYfield from the secret's data. -
Decodes the
base64-encodedvalue to get the original API key.