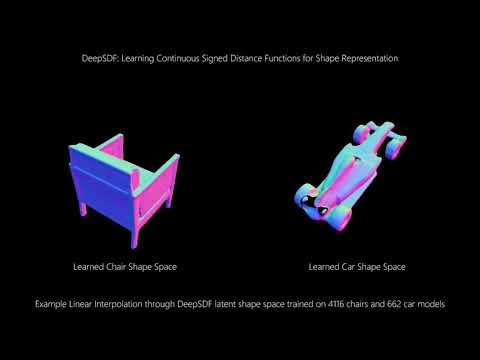
This is an implementation of the CVPR '19 paper "DeepSDF: Learning Continuous Signed Distance Functions for Shape Representation" by Park et al. See the paper here.
If you use DeepSDF in your research, please cite the paper:
@InProceedings{Park_2019_CVPR,
author = {Park, Jeong Joon and Florence, Peter and Straub, Julian and Newcombe, Richard and Lovegrove, Steven},
title = {DeepSDF: Learning Continuous Signed Distance Functions for Shape Representation},
booktitle = {The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2019}
}
The various Python scripts assume a shared organizational structure such that the output from one script can easily be used as input to another. This is true for both preprocessed data as well as experiments which make use of the datasets.
The DeepSDF code allows for pre-processing of meshes from multiple datasets and stores them in a unified data source. It also allows for separation of meshes according to class at the dataset level. The structure is as follows:
<data_source_name>/
.datasources.json
SdfSamples/
<dataset_name>/
<class_name>/
<instance_name>.npz
SurfaceSamples/
<dataset_name>/
<class_name>/
<instance_name>.ply
Subsets of the unified data source can be reference using split files, which are stored in a simple JSON format. For examples, see examples/splits/.
The file datasources.json stores a mapping from named datasets to paths indicating where the data came from. This file is referenced again during evaluation to compare against ground truth meshes (see below), so if this data is moved this file will need to be updated accordingly.
Each DeepSDF experiment is organized in an "experiment directory", which collects all of the data relevant to a particular experiment. The structure is as follows:
<experiment_name>/
specs.json
Logs.pth
LatentCodes/
<Epoch>.pth
ModelParameters/
<Epoch>.pth
OptimizerParameters/
<Epoch>.pth
Reconstructions/
<Epoch>/
Codes/
<MeshId>.pth
Meshes/
<MeshId>.pth
The only file that is required to begin an experiment is 'specs.json', which sets the parameters, network architecture, and data to be used for the experiment.
In order to use mesh data for training a DeepSDF model, the mesh will need to be pre-processed. This can be done with the preprocess_data.py executable. The preprocessing code is in C++ and has the following requirements:
With these dependencies, the build process follows the standard CMake procedure:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make -j
Once this is done there should be two executables in the DeepSDF/bin directory, one for surface sampling and one for SDF sampling. With the binaries, the dataset can be preprocessed using preprocess_data.py.
The preprocessing script requires an OpenGL context, and to acquire one it will open a (small) window for each shape using Pangolin. If Pangolin has been compiled with EGL support, you can use the "headless" rendering mode to avoid the windows stealing focus. Pangolin's headless mode can be enabled by setting the PANGOLIN_WINDOW_URI environment variable as follows:
export PANGOLIN_WINDOW_URI=headless://
Jeong Joon Park, Peter Florence, Julian Straub, Richard Newcombe, Steven Lovegrove
We want to acknowledge the help of Tanner Schmidt with releasing the code.
DeepSDF is relased under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for more details.