| layout | background-class | body-class | title | summary | category | image | author | tags | github-link | github-id | featured_image_1 | featured_image_2 | accelerator | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
hub_detail |
hub-background |
hub |
FastPitch 2 |
The FastPitch model for generating mel spectrograms from text |
researchers |
nvidia_logo.png |
NVIDIA |
|
NVIDIA/DeepLearningExamples |
fastpitch_model.png |
no-image |
cuda |
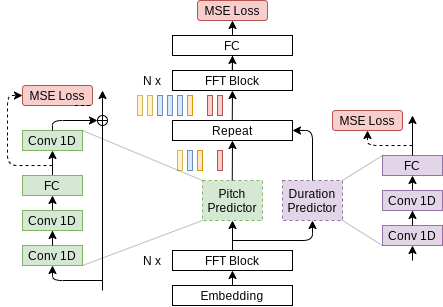
This notebook demonstrates a PyTorch implementation of the FastPitch model described in the FastPitch paper. The FastPitch model generates mel-spectrograms and predicts a pitch contour from raw input text. In version 1.1, it does not need any pre-trained aligning model to bootstrap from. To get the audio waveform we need a second model that will produce it from the generated mel-spectrogram. In this notebook we use HiFi-GAN model for that second step.
The FastPitch model is based on the FastSpeech model. The main differences between FastPitch vs FastSpeech are as follows:
- no dependence on external aligner (Transformer TTS, Tacotron 2); in version 1.1, FastPitch aligns audio to transcriptions by itself as in One TTS Alignment To Rule Them All,
- FastPitch explicitly learns to predict the pitch contour,
- pitch conditioning removes harsh sounding artifacts and provides faster convergence,
- no need for distilling mel-spectrograms with a teacher model,
- capabilities to train a multi-speaker model.
In the example below:
- pretrained FastPitch and HiFiGAN models are loaded from torch.hub
- given tensor representation of an input text ("Say this smoothly to prove you are not a robot."), FastPitch generates mel spectrogram
- HiFiGAN generates sound given the mel spectrogram
- the output sound is saved in an 'audio.wav' file
To run the example you need some extra python packages installed. These are needed for preprocessing of text and audio, as well as for display and input/output handling. Finally, for better performance of FastPitch model, we download the CMU pronounciation dictionary.
apt-get update
apt-get install -y libsndfile1 wget
pip install numpy scipy librosa unidecode inflect librosa matplotlib==3.6.3
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NVIDIA/NeMo/263a30be71e859cee330e5925332009da3e5efbc/scripts/tts_dataset_files/heteronyms-052722 -qO heteronyms
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NVIDIA/NeMo/263a30be71e859cee330e5925332009da3e5efbc/scripts/tts_dataset_files/cmudict-0.7b_nv22.08 -qO cmudict-0.7bimport torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython.display import Audio
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
device = torch.device("cuda") if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device("cpu")
print(f'Using {device} for inference')Download and setup FastPitch generator model.
fastpitch, generator_train_setup = torch.hub.load('NVIDIA/DeepLearningExamples:torchhub', 'nvidia_fastpitch')Download and setup vocoder and denoiser models.
hifigan, vocoder_train_setup, denoiser = torch.hub.load('NVIDIA/DeepLearningExamples:torchhub', 'nvidia_hifigan')Verify that generator and vocoder models agree on input parameters.
CHECKPOINT_SPECIFIC_ARGS = [
'sampling_rate', 'hop_length', 'win_length', 'p_arpabet', 'text_cleaners',
'symbol_set', 'max_wav_value', 'prepend_space_to_text',
'append_space_to_text']
for k in CHECKPOINT_SPECIFIC_ARGS:
v1 = generator_train_setup.get(k, None)
v2 = vocoder_train_setup.get(k, None)
assert v1 is None or v2 is None or v1 == v2, \
f'{k} mismatch in spectrogram generator and vocoder'Put all models on available device.
fastpitch.to(device)
hifigan.to(device)
denoiser.to(device)Load text processor.
tp = torch.hub.load('NVIDIA/DeepLearningExamples:torchhub', 'nvidia_textprocessing_utils', cmudict_path="cmudict-0.7b", heteronyms_path="heteronyms")Set the text to be synthetized, prepare input and set additional generation parameters.
text = "Say this smoothly, to prove you are not a robot."batches = tp.prepare_input_sequence([text], batch_size=1)gen_kw = {'pace': 1.0,
'speaker': 0,
'pitch_tgt': None,
'pitch_transform': None}
denoising_strength = 0.005for batch in batches:
with torch.no_grad():
mel, mel_lens, *_ = fastpitch(batch['text'].to(device), **gen_kw)
audios = hifigan(mel).float()
audios = denoiser(audios.squeeze(1), denoising_strength)
audios = audios.squeeze(1) * vocoder_train_setup['max_wav_value']Plot the intermediate spectorgram.
plt.figure(figsize=(10,12))
res_mel = mel[0].detach().cpu().numpy()
plt.imshow(res_mel, origin='lower')
plt.xlabel('time')
plt.ylabel('frequency')
_=plt.title('Spectrogram')Syntesize audio.
audio_numpy = audios[0].cpu().numpy()
Audio(audio_numpy, rate=22050)Write audio to wav file.
from scipy.io.wavfile import write
write("audio.wav", vocoder_train_setup['sampling_rate'], audio_numpy)For detailed information on model input and output, training recipies, inference and performance visit: github and/or NGC