Building a machine learning model is great, but to provide real business value, it must be made useful and maintained to remain useful over time. Machine Learning Operations (MLOps), overviewed here, is a rapidly growing space that encompasses everything required to deploy a machine learning model into production, and is a crucial aspect to delivering this sought after value.
Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) is everything else required to make that model useful, including capabilities for an automated development and deployment pipeline, monitoring, lifecycle management, and governance, etc. It is a set of practices that combines Machine Learning, DevOps and Data Engineering, which aims to deploy and maintain ML systems in production reliably and efficiently. This Article explain the use of Automation pipelines, MlOps landscape, Governance in detail.
Managing ML systems at scale is not an easy job, and there exist numerous bottlenecks that needs to be taken care of. The following are the major challenges that teams are up against:
- Shortage of Data Scientists
- Communication gaps between technical and business teams with hard-to-find common language to collaborate
- Risk Assessment
- Framing ML problems from business objectives
- Architext ML and data solutions for the problem
- Data preparation and processing
- Model training and experimentation
- Building and automating ML pipelines
- Deploying models to the production system
- Monitor, Optimize and maintain models
Learn More about the skills required to perform mlops here
The following Key topics is discussed in details here
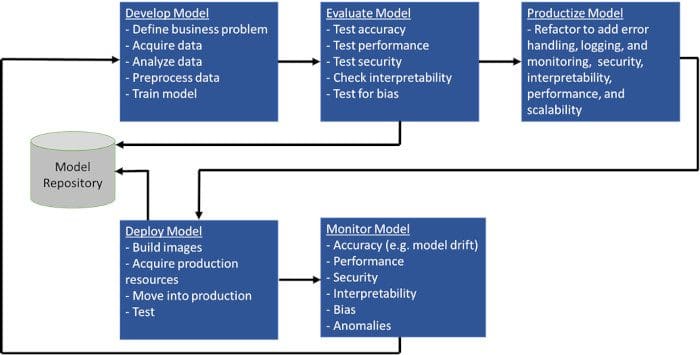
- Automation The level of automation of the Data, ML Model, and Code pipelines determines the maturity of the ML process. With increased maturity, the velocity for the training of new models is also increased. The objective of an MLOps team is to automate the deployment of ML models into the core software system or as a service component. This means, to automate the complete ML-workflow steps without any manual intervention. Triggers for automated model training and deployment can be calendar events, messaging, monitoring events, as well as changes on data, model training code, and application code.
To adopt MLOps, we see three levels of automation, starting from the initial level with manual model training and deployment, up to running both ML and CI/CD pipelines automatically.
Manual process; This is a typical data science process, which is performed at the beginning of implementing ML. This level has an experimental and iterative nature. Every step in each pipeline, such as data preparation and validation, model training and testing, are executed manually. The common way to process is to use Rapid Application Development (RAD) tools, such as Jupyter Notebooks.
ML pipeline automation: The next level includes the execution of model training automatically. We introduce here the continuous training of the model. Whenever new data is available, the process of model retraining is triggered. This level of automation also includes data and model validation steps.
CI/CD pipeline automation: In the final stage, we introduce a CI/CD system to perform fast and reliable ML model deployments in production. The core difference from the previous step is that we now automatically build, test, and deploy the Data, ML Model, and the ML training pipeline components.
-
Continuous X: MLOps is an ML engineering culture that includes the following practices:
Continuous Integration (CI) extends the testing and validating code and components by adding testing and validating data and models.
Continuous Delivery (CD) concerns with delivery of an ML training pipeline that automatically deploys ML model prediction service.
Continuous Training (CT) is unique to ML systems property, which automatically retrains ML models for re-deployment.
Continuous Monitoring (CM) concerns with monitoring production data and model performance metrics, which are bound to business metrics.
-
Versioning: The goal of the versioning is to treat ML training scripts, ML models and data sets for model training as first-class citizens in DevOps processes by tracking ML models and data sets with version control systems. There are many reasons why ML models and data changes, the list can be found here
-
Experiments Tracking: Experiment tracking is the process of saving all experiment related information that you care about for every experiment you run. Learn More here
-
Testing: The process of checking each stage of mlops to verify if it gives the required results. It involves data and feature test, model test, unit test etc
-
Monitoring: Once the ML model has been deployed, it need to be monitored to assure that the ML model performs as expected.
-
Reproducibility in a machine learning workflow means that every phase of either data processing, ML model training, and ML model deployment should produce identical results given the same input.
- Deploying Flask app with on AWS Elastic Beanstalk using Docker In this tutorial, you will learn how to build a Deploy Multi-Container Application using Flask, Redis and PosgreSQL.
you will use NGINX-uWSGI along with Flask as the web service, and connect it with the PostgreSQL and Redis container services. Then, you will understand how to automate the process of deploying the web-app on to Docker Hub, using GitHub and Travis CI. Finally, you will understand how to automate deployments on to AWS Elastic Beanstalk using GitHub and Travis.
-
Deploying Flask app on AWS using RDS and ElastiCache: In this project, you will learn how to use Amazon RDS and Amazon ElastiCache, how to connect them to AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and deploy a project based on these three technologies.
-
AWS Machine Learning SPecialty Course Learn how to apply machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), and deep learning (DL) to your business, unlocking new insights and value. Explore real-world examples and labs based on problems we've solved at Amazon using ML. Access 65+ digital courses (many of them free).
-
Machine Learning Engineer Professional Certificate A Professional Machine Learning Engineer designs, builds, and productionizes ML models to solve business challenges using Google Cloud technologies and knowledge of proven ML models and techniques. The ML Engineer is proficient in all aspects of model architecture, data pipeline interaction, and metrics interpretation and needs familiarity with application development, infrastructure management, data engineering, and security.
-
A collection of resources on how to facilitate Machine Learning Ops with GitHub. Learn how to use GitHub for automation, collaboration and reproducibility in your machine learning workflows.Everything MLOps with github