Lego for AI workflows and agents: An open-source tool for composing, customizing and extending multiple MCP servers into a single logical, virtual MCP server
Built for fine grained context-engineering
- Create vMCP, Add MCP servers and Fine-tune
- Extend with your own prompts, tools and resources
- Connect any client (Claude, ChatGPT, Gemini, Cursor, VScode, custom agents) to the vMCP
- Create multiple logical vMCPs based on your workflow and agent needs
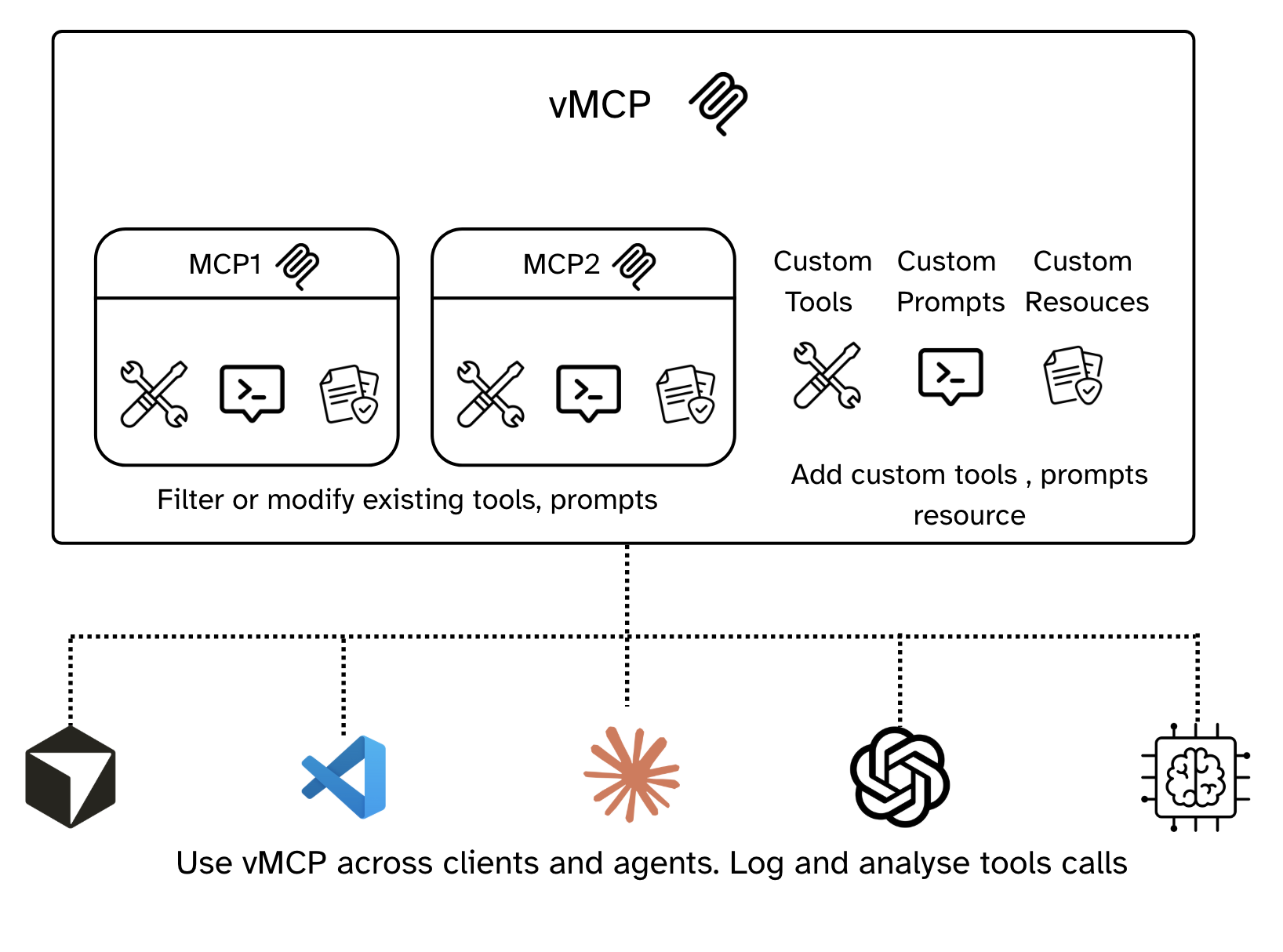
vMCP (virtual Model Context Protocol) is an AI configuration and management platform built on top of the Model Context Protocol. It is both :
- A specification that builds on and extends MCPs: vMCP.json
- A platform to create and deploy vMCP Servers:
The Model Context Protocol has unlocked incredible possibilities for AI integrations, but users and developers quickly hit limitations:
- Configuration Hell: Managing MCP configs across multiple clients (Claude, ChatGPT, VSCode, Cursor, Gemini) is tedious
- Auth: Each mcp client needs its own auth for all the MCPs
- Lack of Customization: Can't modify or extend existing MCPs for specific workflow needs - "context rot / confusion"
- No Composition: Building complex workflows requires piecing together multiple tools from multiple MCPs
vMCP solves these problems by providing a layer of abstraction and a no-code configuration interface on top of standard MCPs.
- Flexible vMCP Creation: Compose different MCP servers into a unified MCP server with a simple no-code interface.
- Context Engineering with MCPs:
- 🛠️ Customizable Tools: Select and override tool names/descriptions from upstream MCPs and prefill tool arguments.
- ✨ Extensible Tooling: Create new tools using Python, REST APIs or plain text (Prompt tools).
- 🗣️ Programmable Prompts: Define prompts that can invoke other tools and resources, enabling user-controlled tool chaining.
- 🔗 Add files as resources: Select MCP resource and add your own knowledge base files
- MCP Server Authentication: Authorize MCP servers once and re-use across clients (Claude, Cursor, ChatGPT, VSCode, Gemini, AI agents)
- Usage Statistics: Track and analyze vMCP usage patterns with full MCP protocol level logging
- Docker and PyPi Ready: Official Docker images for easy deployment. uv and pip command for quick trial
vMCP requires Python 3.10 to 3.13 and uv.
To install vMCP, run:
uvx --from 1xn-vmcp@latest vmcp runOr using uv
pip install 1xn-vmcp
vmcp rundocker pull onexn/vmcp:latest
docker run -it onexn/vmcp:latest vmcp runThis will start the vMCP server on http://localhost:8000.
vmcp/
├── src/vmcp/ # Main package
│ ├── backend/ # FastAPI backend
│ │ ├── mcps/ # MCP server management
│ │ ├── vmcps/ # Virtual MCP management
│ │ ├── storage/ # Database models
│ │ ├── proxy_server/ # Main app
│ │ └── utilities/ # Logging & tracing
│ └── cli/ # CLI commands
├── frontend/ # React frontend (Vite)
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/1xn-labs/1xn-vmcp
cd 1xn-vmcp
make build-frontend
make runThis guide walks you through the process of creating and managing virtual MCP servers with vMCP. Follow these steps to get started with aggregating multiple MCP servers into a unified interface.
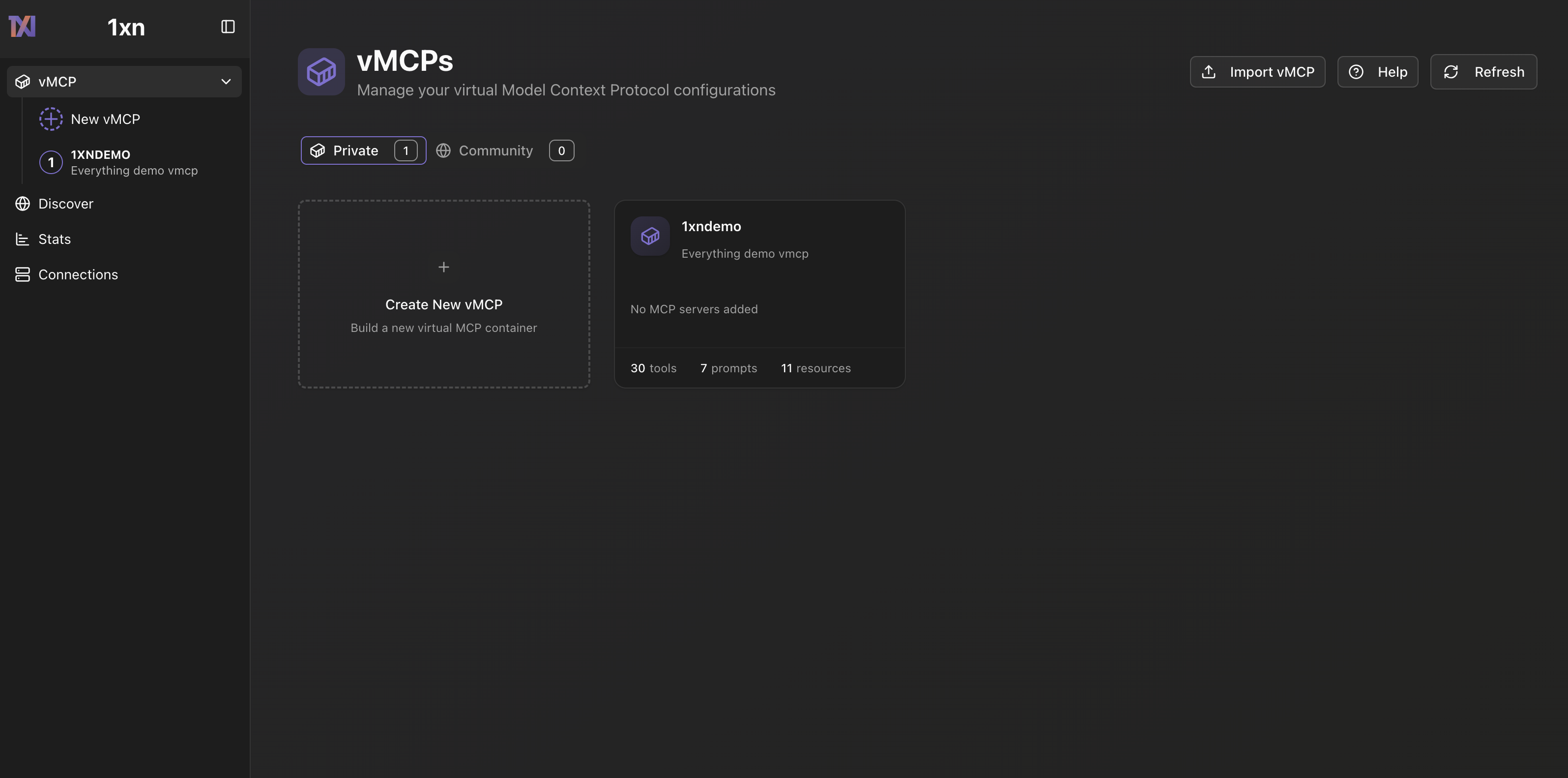
After starting vMCP with vmcp run, navigate to http://localhost:8000 in your browser. The vMCP home page provides a centralized dashboard where you can manage your virtual MCP configurations
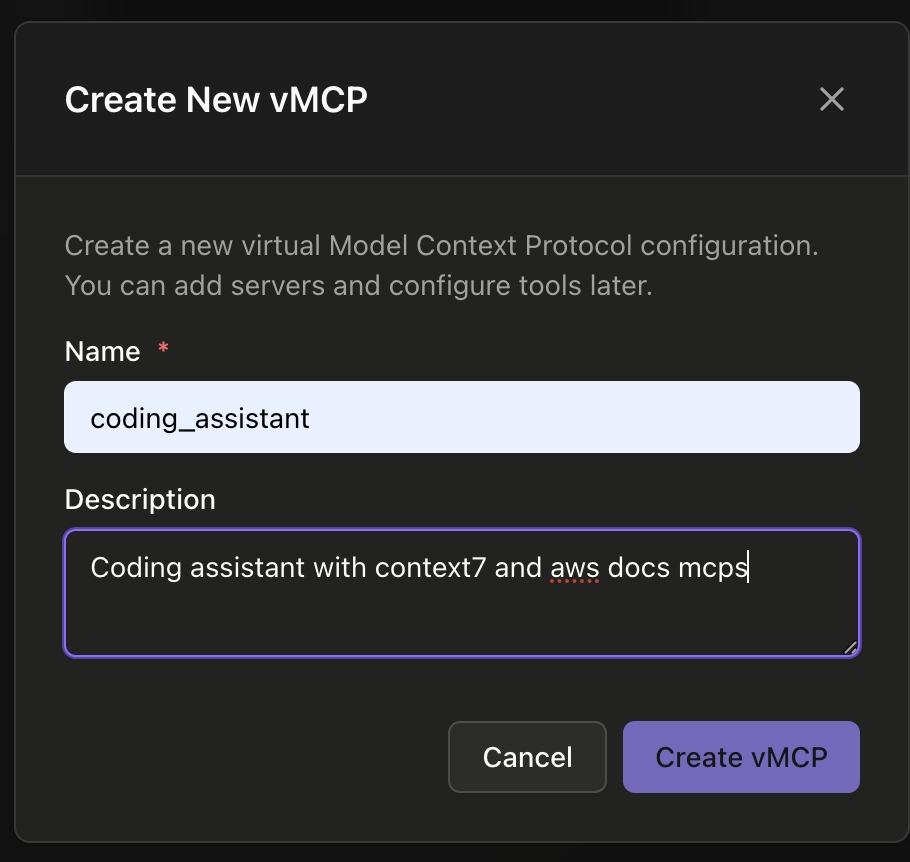
Click the "+ Create Your First vMCP" button to start building your virtual MCP. In the creation dialog, provide a name and description for your vMCP. A vMCP allows you to combine tools, resources, and prompts from multiple MCP servers into a single unified endpoint. You can add servers and configure tools later, so start with a descriptive name like "Coding_assistant" for a development-focused vMCP.
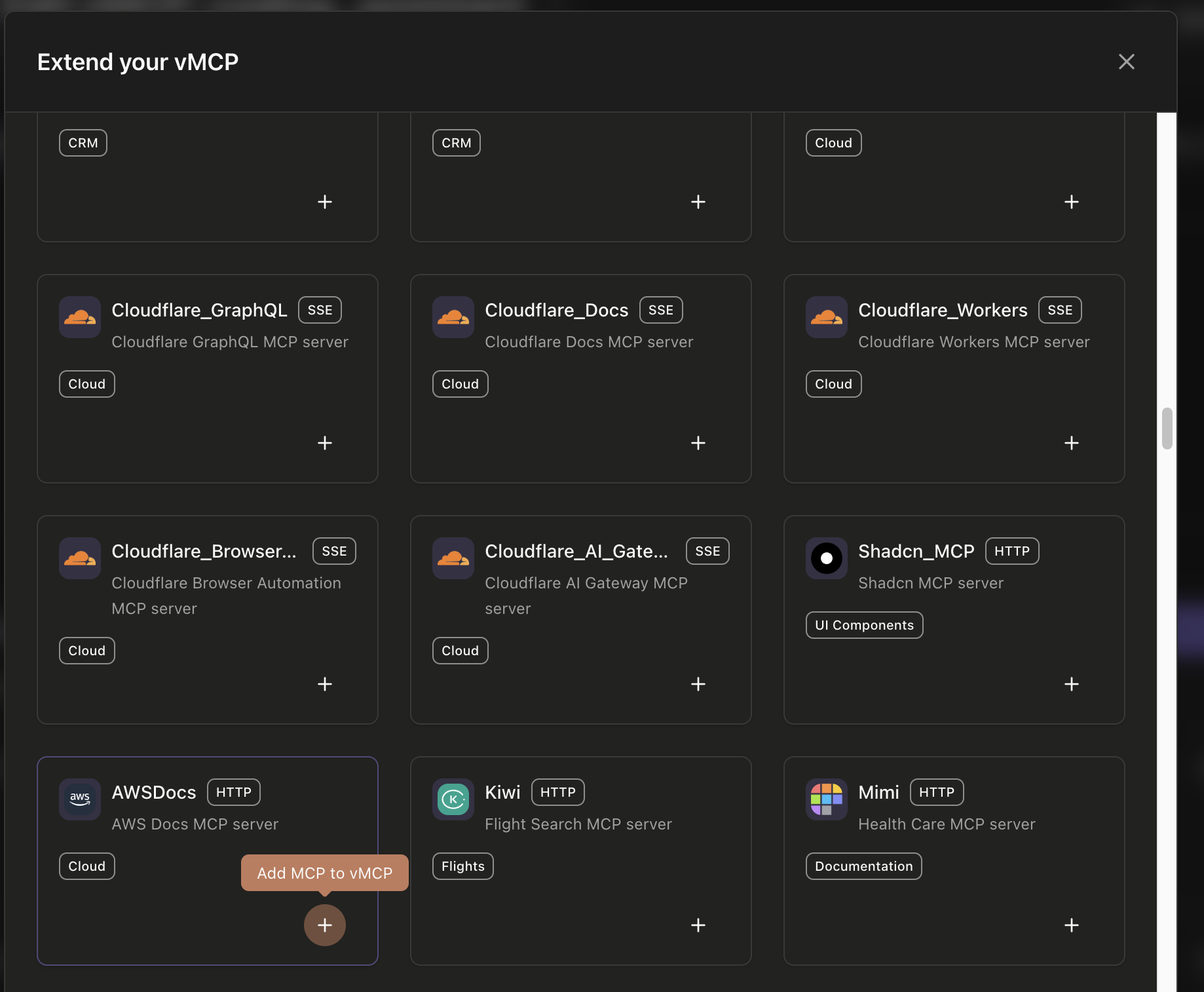
After creating your vMCP, you'll see the "Add MCP Connector" button which displays a grid of well known remote mcp servers. You can browse and add the servers to Vmcp
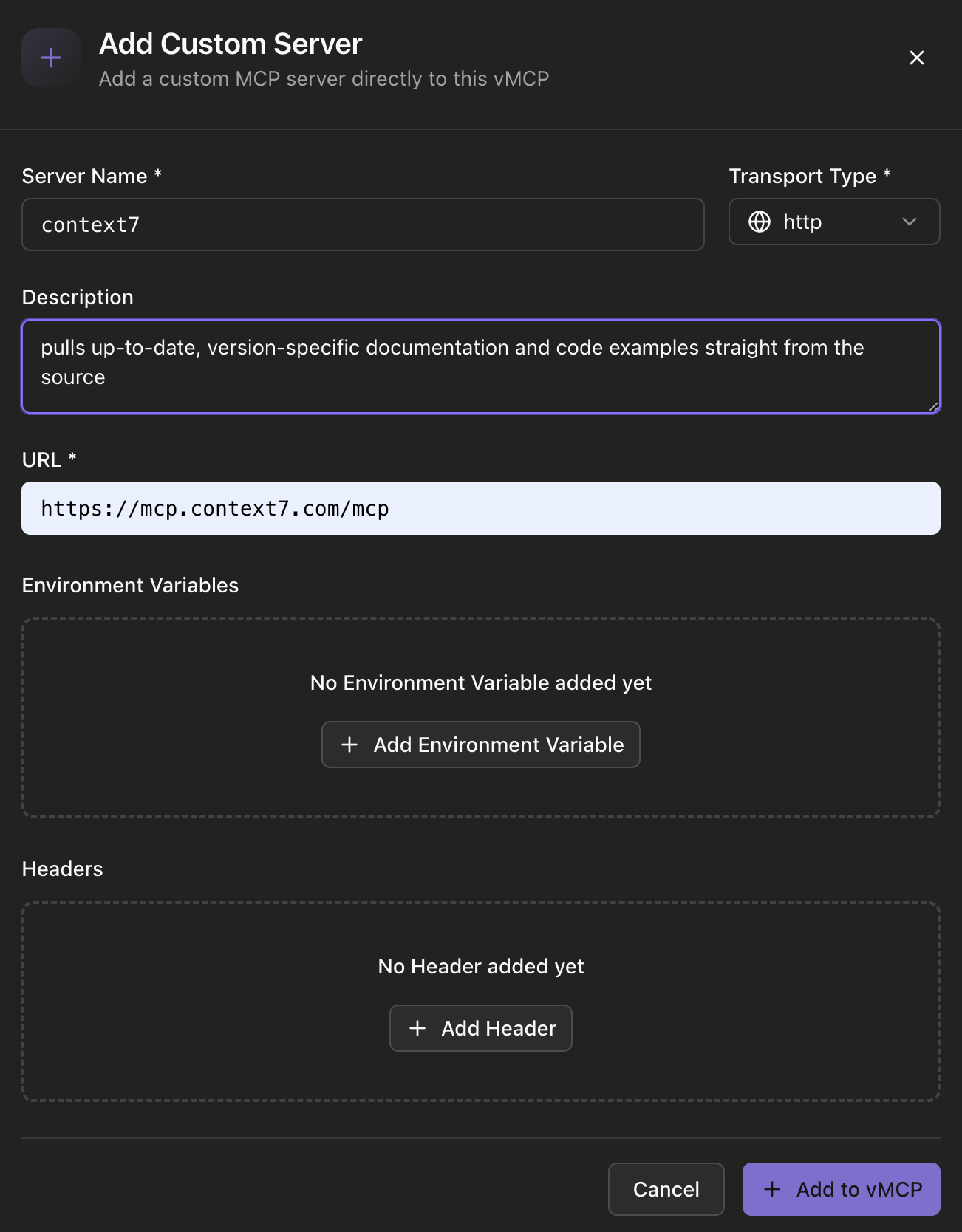
If you need to connect to a custom MCP server that's not in the community library, click "Add Custom Server" or use the custom server option. In the dialog, provide the server name, select the transport type (HTTP, SSE), enter the server URL, and optionally add environment variables and headers. This allows you to connect to any MCP-compatible server, including your own custom implementations.
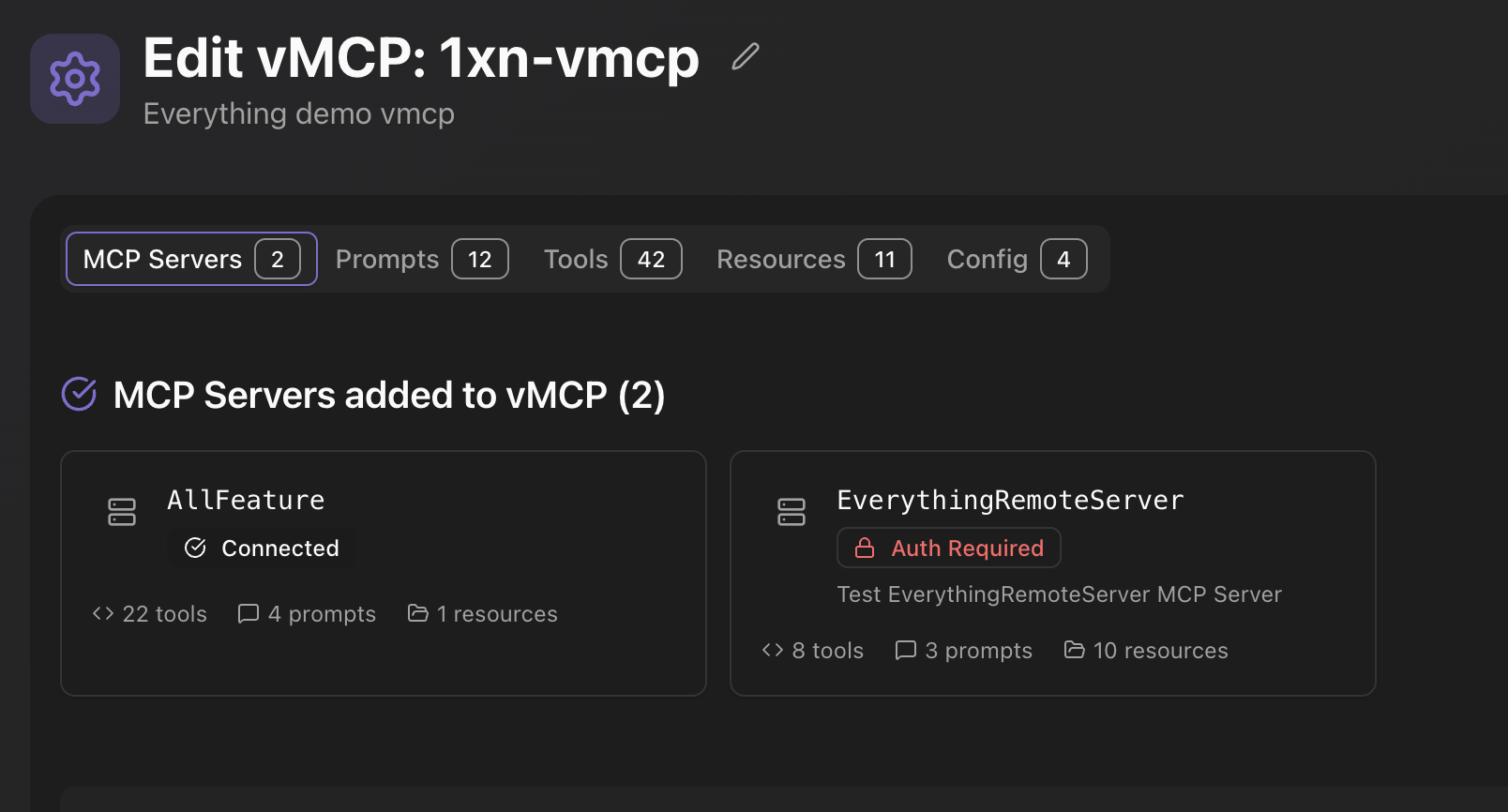
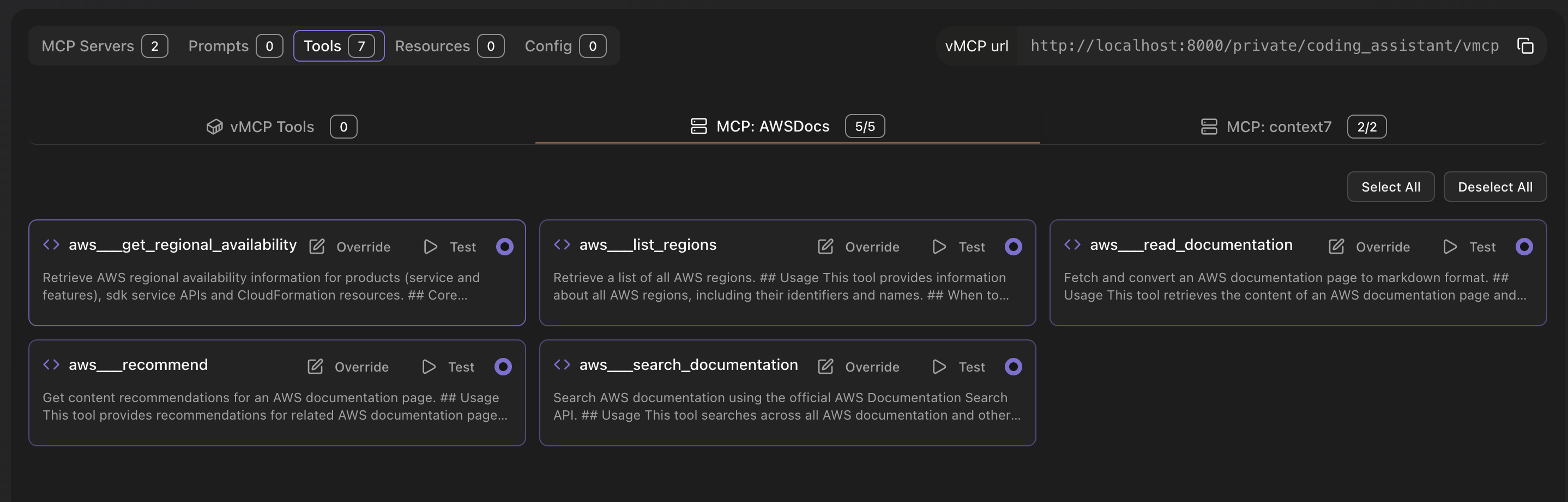
Once MCP servers are added to your vMCP, navigate to the "Tools" tab in the vMCP editor. Here you can view all available tools from your connected MCP servers. Use the search and filter options to find specific tools, enable or disable them, and override tool names and descriptions. You can also test individual tools or select/deselect all tools from a specific MCP server at once.
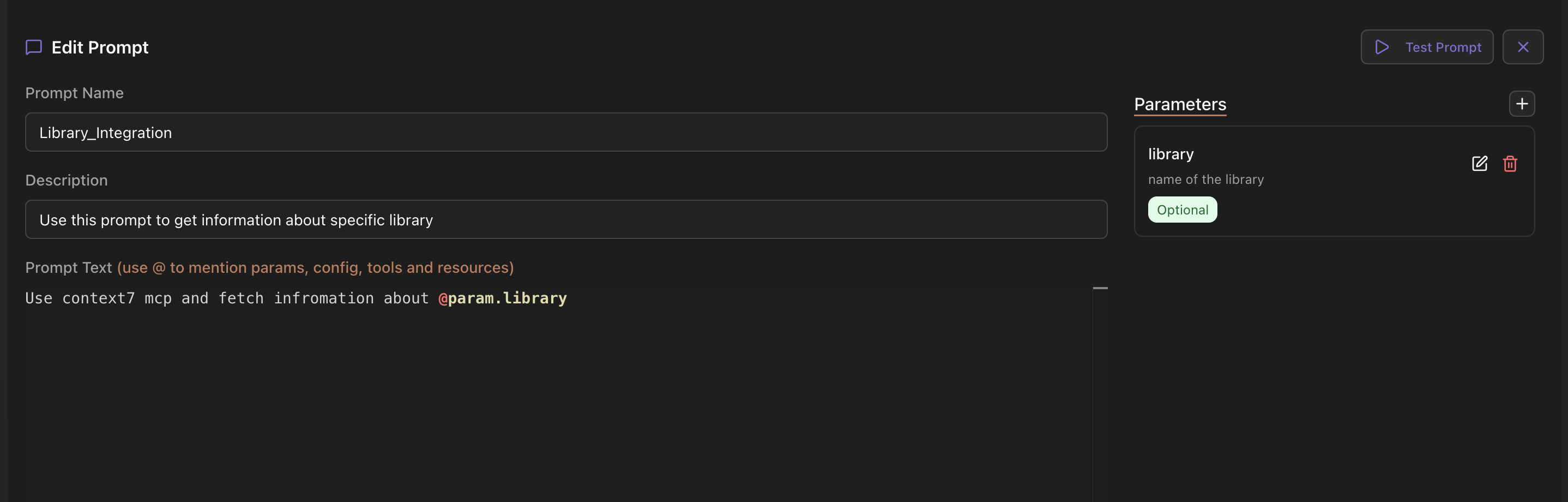
In addition to tools from MCP servers, you can create custom tools and prompts directly in your vMCP. Navigate to the "Prompts" tab to create programmable prompts that can invoke other tools, enabling user-controlled tool chaining. You can define prompt parameters, descriptions, and use the @ syntax to mention params, config, tools, and resources. Similarly, you can create custom tools using Python snippets or REST APIs.
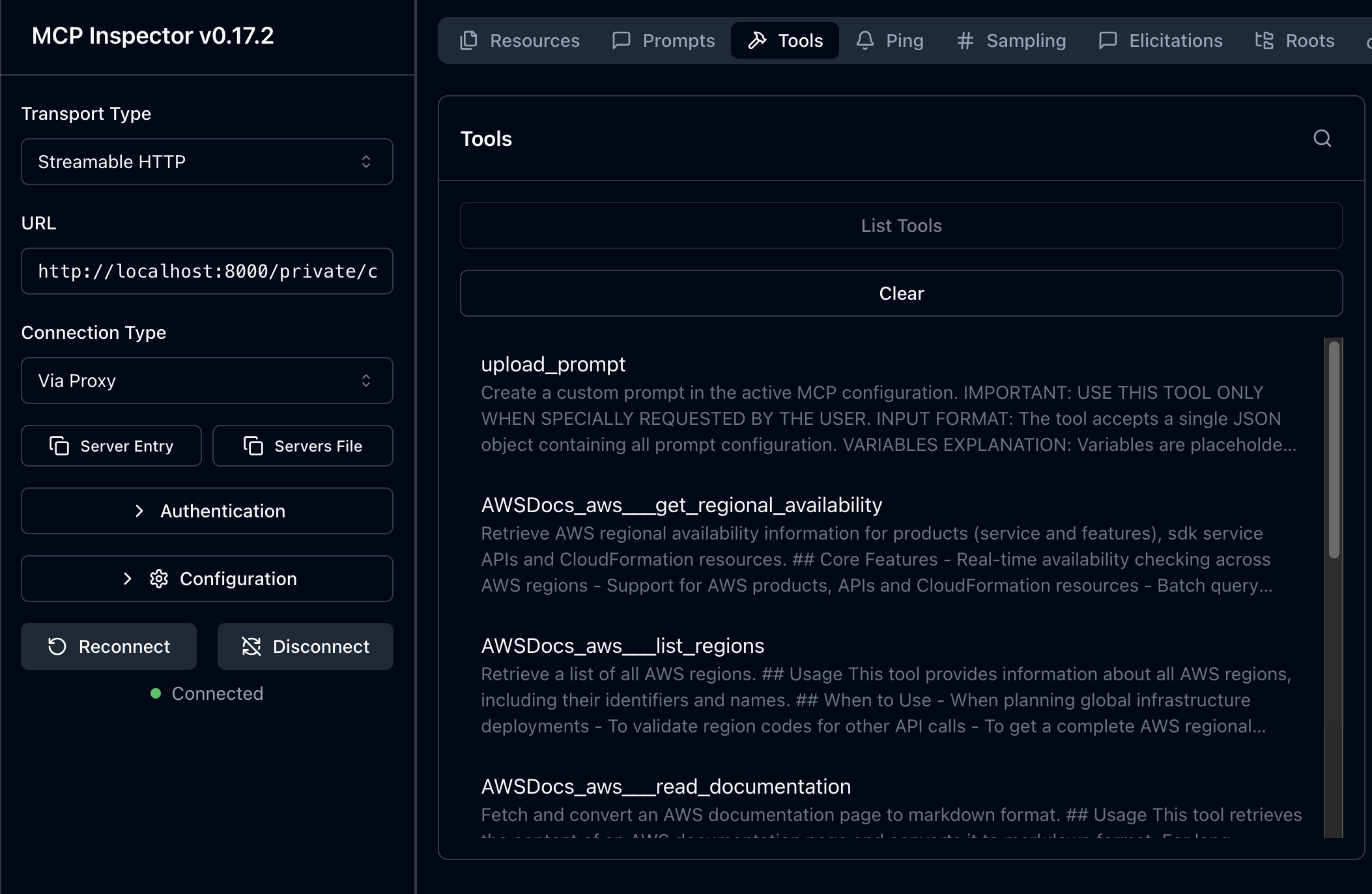
Once your vMCP is configured and saved, you can use it with any MCP-compatible client. Copy the vMCP URL from the editor (e.g., http://localhost:8000/private/Coding_asstistant/vmcp) and connect to it using tools like MCP Inspector or directly from AI applications like Claude, Cursor, or Copilot. The vMCP will aggregate all your selected tools, resources, and prompts into a single unified endpoint.
For comprehensive documentation, guides, and API references, visit the vMCP Documentation.
We welcome contributions! Please see CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines.
# start test mcp server and rest api server.
make test-servers
# run test with pytest
make run-testsvMCP is open-source software licensed under the MIT License.
We want to give a huge shoutout to Anthropic and the entire Model Context Protocol community for creating such an incredible foundation. MCP has fundamentally changed how we think about AI integrations
- 🐛 Report Issues
- 📧 Email: [email protected]
Made with ❤️ by the 1xn Team