Data Science Research Group WHZ - University of Applied Sciences, Prof. Dr. Mike Espig
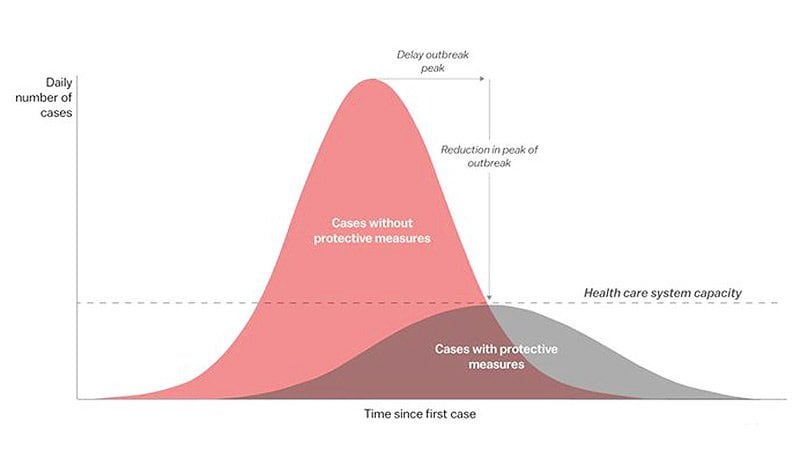
COVID-19 pandemic impacted the whole world, overwhelming healthcare systems - unprepared for such intense and lengthy request for ICU beds, professionals, personal protection equipment and healthcare resources. Brazil recorded first COVID-19 case on February 26 and reached community transmission on March 20.
Sírio-Libanês hospital, São Paulo
e-mail: [email protected]
The Hospital Sírio-Libanês (Syrian-Lebanese Hospital) is one of the most important hospitals in Brazil and South America. The hospital was founded by the large Syrian and Lebanese community of São Paulo in 1921. It is one of the most well-known health facilities in Brazil due to the high quality of care, wiki.
COVID-19 pandemic impacted the whole world, overwhelming healthcare systems - unprepared for such intense and lengthy request for ICU beds, professionals, personal protection equipment and healthcare resources. Brazil recorded first COVID-19 case on February 26 and reached community transmission on March 20.
There is urgency in obtaining accurate that to better predict and prepare healthcare systems and avoid collapse, defined by above capacity need of ICU beds (assuming human resources, PPE and professionals are available), using individual clinical data - in lieu of epidemiological and populational data.
Predict admission to the ICU of confirmed COVID-19 cases. Based on the data available, is it feasible to predict which patients will need intensive care unit support? The aim is to provide tertiary and quarternary hospitals with the most accurate answer, so ICU resources can be arranged or patient transfer can be scheduled.
Predict NOT admission to the ICU of confirmed COVID-19 cases. Based on the subsample of widely available data, is it feasible to predict which patients will need intensive care unit support? The aim is to provide local and temporary hospitals a good enough answer, so frontline physicians can safely discharge and remotely follow up with these patients.
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected millions of individuals and caused hundreds of thousands of deaths worldwide. Predicting mortality among patients with COVID-19 who present with a spectrum of complications is very difficult, hindering the prognostication and management of the disease. We aimed to develop an accurate prediction model of COVID-19 mortality using unbiased computational methods, and identify the features most predictive of this outcome, see.
Label output
ICU should be considered, as the first version of this dataset, the target variable.
Window Concept
We were carefull to include real life cenarios of with window of events and available data. Data was obtain and grouped
- patient
- patient encounter
- aggregated by windows in chronological order
Window Description 0-2 From 0 to 2 hours of the admission 2-4 From 2 to 4 hours of the admission 4-6 From 4 to 6 hours of the admission 6-12 From 6 to 12 hours of the admission Above-12 Above 12 hours from admission
- Beware NOT to use the data when the target variable is present, as it is unknown the order of the event (maybe the target event happened before the results were obtained). They were kept there so we can grow this dataset in other outcomes latter on.
Data Description
* 3 rows patient information
* patient is part of a certain disease group
* blood results
* vital data
* 385 patients
* 5 time windows
* 50 – 60 % missing data
* 2 patients : no observations documented
* 42 features each containing MEDIAN, MEAN, MIN, MAX und DIFF und relative diff (some)
* Normalization values between -1 and 1
| attribute | description | time dependency |
|---|---|---|
| PATIENT_VISIT_IDENTIFIER | Eindeutiger Identifikator (0 bis 384) | |
| AGE_ABOVE65 | 0/1 group at risk | |
| AGE_PERCENTILE | 10th, 20th ... above 90 | |
| GENDER | 0 / 1 | |
| DISEASE GROUPING 1 | 0 / 1 | x |
| DISEASE GROUPING 2 | 0 / 1 | x |
| DISEASE GROUPING 3 | 0 / 1 | x |
| DISEASE GROUPING 4 | 0 / 1 | x |
| DISEASE GROUPING 5 | 0 / 1 | x |
| DISEASE GROUPING 6 | 0 / 1 | x |
| HTN | 0 / 1 Bluthochdruck | x |
| IMMUNOCOMPROMISED | 0 / 1 eingeschränktes / unterdrücktes Immunsystem | x |
| OTHER | ? | x |
| ALBUMIN | Eiweiß – Flüssigkeitsverteilung der Zellen Test im Blut oder Urin | x |
| BE_ARTERIAL | Base Excess – Basenüberschuss im arteriellen Blut - Blutgasanalyse | x |
| BE_VENOUS | Base Excess – Basenüberschuss im venösen Blut - Blutgasanalyse | x |
| BIC_ARTERIAL | Bicarbonate - arteriell | x |
| BIC_VENOUS | Bicarbonat - venös | x |
| BILLIRUBIN | Gelber Gallenfarbstoff – entsteht beim Abbau von Hämoglobin. Erhöht bei Erkrankungen des Entgiftungssystems | x |
| BLAST | ? | x |
| CALCIUM | Kalzium im Blut | x |
| CREATININ | Beurteilung der Nierenfunktion | x |
| FFA | Free Fatty Acid | x |
| GGT | Gamma Glutamyltransferase - Leberenzym | x |
| GLUCOSE | Blutzuckerspiegel im Blut | x |
| HEMATOCRITE | Anteil der roten Blutkörperchen in Relation zum gesamten Blutvolumen | x |
| HEMOGLOBIN | Eisenwert im Blut für den roten Blutfarbstoff | x |
| INR | Wert für die Blutgerinnung | x |
| LACTATE | Milchsäuregehalt im Blut | x |
| LEUKOCYTES | Anzahl der weißen Blutkörperchen im Blut | x |
| LINFOCITOS | Lymphozytenanteil im Blut | x |
| NEUTROPHILES | Spezielle Immunzellen im Blut – Neutrophile Granulozyten | x |
| P02_ARTERIAL | Menge des im arteriellen Blut gelösten Sauerstoffs – Kennzahl für die Funktion der Lunge | x |
| 02_VENOUS | Menge des im venösen Blut gelösten Sauerstoffs | x |
| PC02_ARTERIAL | Menge des im arteriellen Blut gelösten CO2 | x |
| PC02_VENOUS | Menge des im venösen Blut gelösten CO2 | x |
| PCR | ? | x |
| PH_ARTERIAL | Blutgasanalyse – PH Wert des arteriellen Blutes | x |
| PH_VENOUS | Blutgasanalyse – PH Wert des venösen Blutes | x |
| PLATELETS | Anzahl der Blutplättchen – Thrombozyen | x |
| POTASSIUM | Kaliumgehalt im Blut | x |
| SAT02_ARTERIAL | Sauerstoffsättigung im arteriellen Blut | x |
| SAT02_VENOUS | Sauerstoffsättigung im venösen Blut | x |
| SODIUM | Natriumgehalt im Blut | x |
| TGO | Glukose im Blut | x |
| TGP | Thymocyte Growth Peptide | x |
| TTPA | Treponema-pallidum-Partikel-Agglutination, kurz TPPA ist ein mikrobiologischer Schnelltest zum Screening auf Antikörper gegen Treponema pallidum | x |
| UREA | Harnstoffwerte - Nierenfunktion | x |
| DIMER | Die D-Dimere sind Spaltprodukte des Fibrins. Sie werden bestimmt, um eine Thromboembolie auszuschließen | |
| BLOODPRESSURE_DIASTOLIC | Diastolischer Blutdruckwert | x |
| BLOODPRESSURE_SISTOLIC | Systolischer Blutdruckwert | x |
| HEART_RATE | Puls | x |
| RESPIRATORY_RATE | Atemfrequenz | x |
| TEMPERATURE | Körpertemperatur (Hinweis auf Fieber) | x |
| OXYGEN_SATURATION | Sauerstoffsättigung im Blut | x |
| ICU (target variable) | 0 / 1 – Einlieferung auf Intensivstation |
Beware NOT to use the data when the target variable is present, as it is unknown the order of the event (maybe the target event happened before the results were obtained). They were kept there so we can grow this dataset in other outcomes latter on.
Problem: One of the major challenges of working with health care data is that the sampling rate varies across different type of measurements. For instance, vital signs are sampled more frequently (usually hourly) than blood labs (usually daily).
Tips & Tricks: It is reasonable to assume that a patient who does not have a measurement recorded in a time window is clinically stable, potentially presenting vital signs and blood labs similar to neighboring windows. Therefore, one may fill the missing values using the next or previous entry. Attention to multicollinearity and zero variance issues in this data when choosing your algorithm.