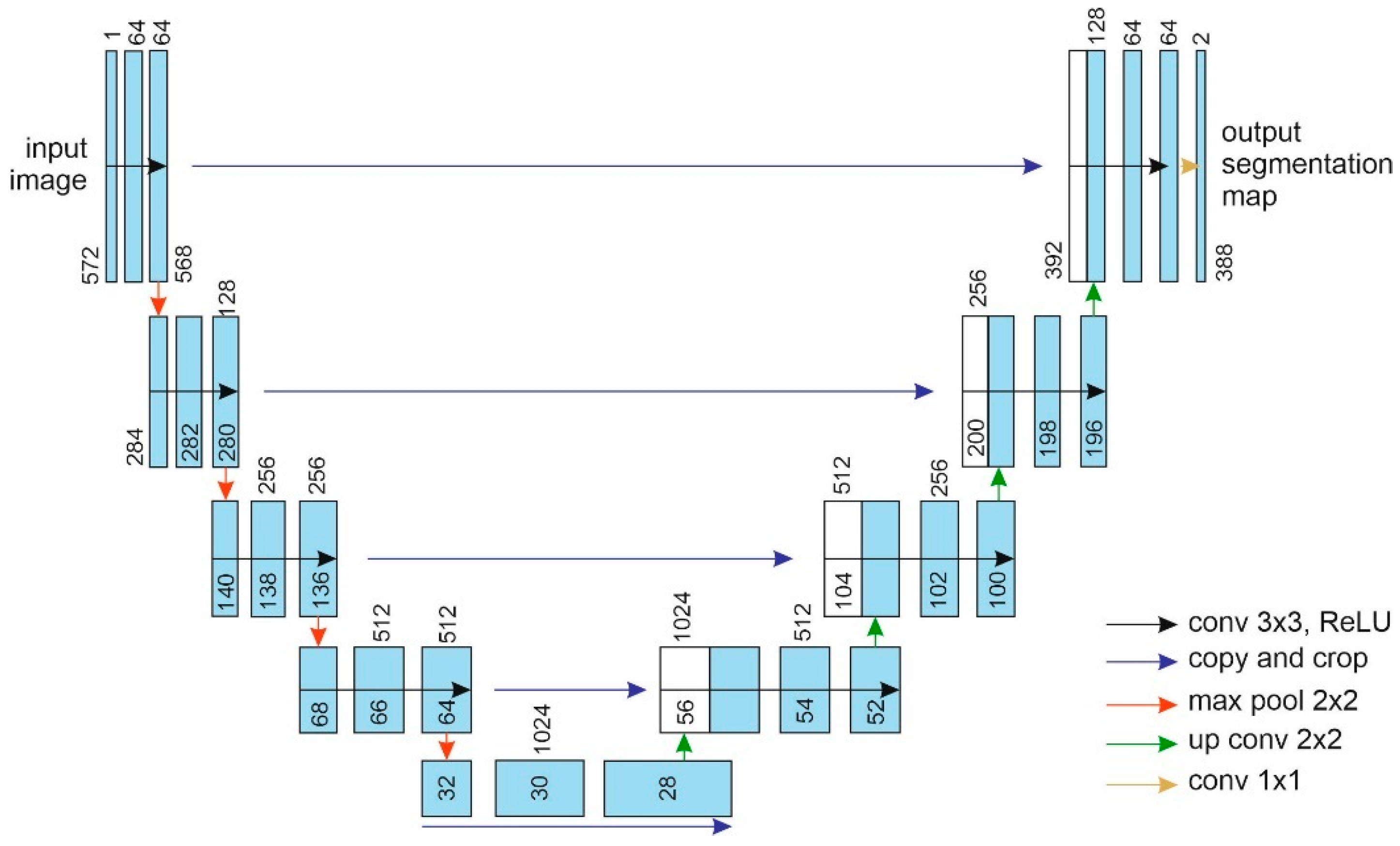
Blood Vessel Segmentation of Diabetic Retinopathy Fundus Image. The dataset on the Unet model Tested is Messidor In this project, we present a approach for segmenting blood vessels from retinal fundus images using the popular UNet architecture. The UNet model has been widely recognized for its outstanding performance in medical image segmentation tasks. Leveraging this powerful architecture, we aim to accurately identify and extract blood vessels from retinal fundus images, which is crucial for diagnosing various eye-related diseases and conditions.
Retinal fundus images contain valuable information about the blood vessels in the eye's retina. Accurate segmentation of these vessels can aid in the early detection and monitoring of various retinal pathologies, including diabetic retinopathy and glaucoma. Our project focuses on leveraging the UNet architecture to perform pixel-wise segmentation of blood vessels in retinal fundus images. By training the model on a large dataset of annotated fundus images, we enable the network to learn the intricate patterns and characteristics of blood vessels. Once trained, the UNet model can then be used to automatically segment blood vessels in unseen fundus images, assisting healthcare professionals in making faster and more precise diagnoses.
- Utilized the UNet architecture for retinal fundus image blood vessel segmentation.
- Preprocessed and augmented the dataset to enhance model robustness.
- Implemented a pixel-wise cross-entropy loss function to train the model effectively.
- Leveraged transfer learning techniques for improved generalization and performance.
- Conducted extensive hyperparameter tuning to optimize model accuracy.
- Evaluated the model on a separate test set and quantified its performance using various metrics (e.g., Jaccard index).
- Deployed the trained model in a user-friendly interface for easy interaction and visualization.