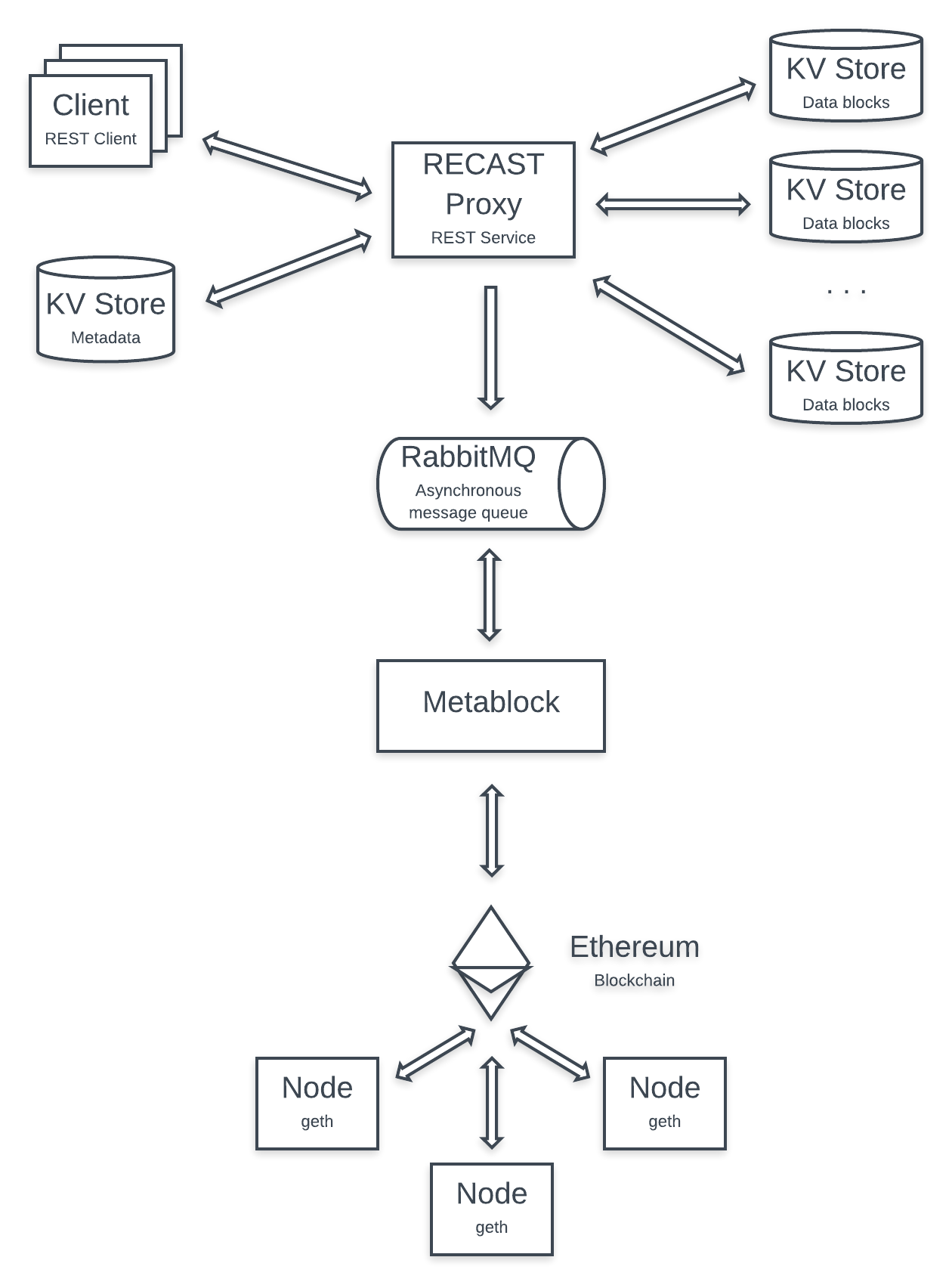
It’s currently the seventh version of Metablock.
You can already launch a private blockchain with a number of nodes that you define, which are automatically detected and linked without any manual intervention required. Moreover, you can use a Docker container which have a client role (./client_put/). A smart contract is integrated with scripts to interact with it. You can store data from Recast automatically. In this new version, we have integrated a automatic rebuild system to recover lost metadata from Redis database, used in Recast to store medatada. To see the performances, a statistics container is integrated and display some information on a website. More information in the Stats and Tests folders.
- Docker
- Docker-compose
- Ethereum
- Solidity compiler
- Recast
- RabbitMQ
- Web Server for statistics container (Apache/ MySQL)
- Python 2.7 / Python 3.6
- Solidity 0.4.0
- HTML / CSS / PHP / SQL
The deployment of the basic configuration, which includes three nodes requires to build the image of Metablock based on the latest version of Ubuntu. After pull the project from Github, go at the the top of the project and run:
docker-compose buildNow you can launch Metablock with this line command:
docker-compose upDocker-compose launchs the bootnode which is used to put in relation the three nodes of the blockchain, and in a second time launchs the first three nodes, and the client.
You can see the architecture of the connexion, using to avoid the technical constraint of Ethereum nodes discovery.
Now you need to install Recast, available on Github. Using Metablock involve to modify two Recast files. You can find them in Metablock/Recast. You have to replace Recast/pyproxy/pyproxy/metadata.py by Metablock/Recast/metadata.py. Also you have to replace Recast/pyproxy/Dockerfile by Metablock/Recast/Dockerfile.
Once finished, containers from Recast and Metablock need to communicate between them.
You can create a new docker network:
docker network create recast_blockYou must add this network in the docker-compose file of Recast in Recast/docker-compose.yml, at the end of the file (The network is already added in Metablock docker-compose file):
networks:
default:
external:
name: recast_blockRecast is ready to be launched.
For the utilization of Metablock go to the second part “Use Metablock”.
In the basic configuration you have only three nodes which run the blockchain. If you want to add more, you need to change the Docker-compose file at the top of the project:
You need to copy lines of one node like node1 and paste at the end of the file. You must change the name (node1_copy => node4). Change the build path (build : ./node4) and ports by another ports which are not used by other services. By convention you can increase the port number. (8003=>8004, 9003=>9004, 30306=>30307).
Secondly, you have to add a new directory called node4 at the top of the project. It’s a clone of node1 or node2 so you can copy node2, paste and rename it node4.
Go at ./node4/scripts and open INIT_PRIV_CHAIN.sh. You need to change all ports by ports that you define for node4 in the docker-compose file. Save it and do the same modification for START_CHAIN_DAEMON.sh. If you want to add more than four node, you just need to repeat these steps. When finished, you can build it (be sure to be at the top of project):
docker-compose buildAnd now you can launch Metablock:
docker-compose upIf you want manage accounts and do transactions, you can access to the JavaScript console:
geth attach ipc:http://127.0.0.1:NODE_PORT
# Example: geth attach ipc:http://127.0.0.1:8001 for the first node
If Ethereum isn’t installed on your computer, you can connect you to Ubuntu bash and run geth.
docker exec –ti CONTAINER_ID /bin/bash
> geth attach /home/priv/data/geth.ipcYou can now use commands. For more information please consult https://ethereum.gitbooks.io/frontier-guide/content/jsre.html
If you want to play with the contract, you have to send a request to Recast. You can find more information of the Github page of Recast.
Before to send requests, the receiving script from Recast to the blockchain must be received by the client. You can to connect on the client container :
docker exec –ti CONTAINER_CLIENT_PUT_ID /bin/bash And run the script:
- "meta_blockchain/store_in_in_map.py" It uses multithreading.
python3 meta_blockchain/store_in_in_map.pyCurrently, the client interacts only with node1. If you don't have a contract running in the blockchain, go in meta_blockchain/ and launch the python script "creation_of_contract.py" to write a new contract based on "contrat.sol" file.
python3 creation_of_contract.pyYou have to wait until sealers (nodes which validate your contract) accept and write the contract and a address contract is returned. Copy the address contract returned by the command and replace it in the line :
store_var_contract = w3.eth.contract(
address="YOUR_ADDRESS_CONTRACT",
abi=contract_interface['abi'])Do it for all scripts in client_put and client_rebuild which uses the connection to a node of blockchain.
Notice that when you execute a transaction, it needs to be validate by sealers node. It can take some times.
A container called "client_rebuild" is used to ensure rebuilding. You can connect to it and launch python script "/home/meta_blockchain/rebuild_one_entry.py". As the storage function, it uses a asynchronous message queue to get key name of file which a client want to access but where Recast doesn't find metadata in Redis database. A error is returns to the client but the key name is sent to the message queue, and rebuilding script ask to the blockchain metadata and correct them in Redis database.
Design :
A audit script has been developed to automate detection of corrupted entries, missing entries or unexpected entries.
It compares all entries in the blockchain with Redis entries and check if metadata are identical. It compares in the other wxy to find possible unexpected entries.
You can launch it when you are connected to the "client_rebuild" container with this command line:
cd /home/meta_blockchain/
python3 check_corruption.pyResults of performance can be found in the Tests Github folder.
If you are interesting about performance and benchmarking of the Metablock implementation in Recast, please go in the "Tests" folder on the Github's project for more information.
A statistics container allows you to see in real time performances of storage in the blockchain and display how much time it took to store metadatas on your configuration.
Since the 07/16/2018 version, Metablock use a dynamic IP address writing, so you don't have to modify anything in the starting node script. In the basic version, Metablock has three nodes on the same network. When docker launches nodes, it can have different IP address. You can check it by using
docker psYou can check the internet configuration of your bootnode
docker inspect BOOTNODE_CONTAINER_IDIP address must be the same that in file "START_CHAIN_DAEMON.sh" for the line
BOOTNODEIP="your_bootnode_ip"Check it for all your start scripts nodes.
/!\ In the last version of Metablock, IP detection is automatic, but information still in README in case of problem will reappear in the future /!\
Scripts of client nodes need to communicate with one node on the blockchain. In the basic configuration, client communicates with node1.
In creation_of_contract.py, the IP address of node1 is defined. Check if the IP address of node1 in scripts matches with IP address of your node1 container by using. About store_in_map.py file, IP detection is automatic so you don't have to touch it to change the IP adress.
docker inspect NODE1_CONTAINER_ID/!\ In the last version of Metablock, IP detection is automatic, but information still in README in case of problem will reappear in the future /!\
Scripts of client_put and client_rebuild need to communicate with the statistic container to send request and save information of performance time.
In store_in_map.py and rebuild.py, the IP address of statistics container is defined. Check if the IP address of the statistics container in script matches with IP address of your container by using
docker inspect STATISTIC_CONTAINER_IDThe line in store_in_map.py is in the "TransactionBlockchainMetadoc" class, at the beginning of the "run" function.