A lot of apps we use today recommend various things to us such as Netflix recommending movies, Facebook recommending friends and many others. In this project I look at potential ways I could do this myself.
This project is inspired by the University of Washington Computer Science Assignment
-
Clone repo
-
Create a virtual environment and activate it
python3.10 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate- Install all dependencies
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt- To run all tests
python -m pytest --cov- To generate results
python main.pyThe actual algorithms used by big tech companies are well guarded secrets, but generally there are two approaches: collaborative filtering and content-based filtering.
-
Collaborative Filtering says that, if your past behavior/preferences were similar to some other user's, then your future behavior may be as well. As a concrete example, suppose that you like John, Paul, and George, and other people like John, Paul, George, and Ringo. Then it stands to reason that you will like Ringo as well, even if you had never previously heard of him. The recommender system does not have to understand anything about what “John”, “Paul”, “George”, and “Ringo” are — they could even be brands of toilet paper, and the algorithm would work identically.
-
Content-based Filtering considers the characteristics of the things you like, and it recommends similar sorts of things. For instance, if you like “Billie Jean”, “Crazy Train”, and “Don't Stop the Music”, then you might like other songs in the key of F-sharp minor, such as Rachmaninoff's “Piano Concerto No. 1”, even if no one else has ever had that particular set of favorite songs before.
A graph represents relationships among things. The things are represented as nodes, and the relationships are represented as edges.
One common use for a graph is to represent travel possibilities, such as on a road map or airline map. The nodes of the graph are cities, and the edges show which cities are directly connected. Then, you can use the graph to plan travel.
The NetworkX library is used to represent graphs in python. Work through the tutorial up to and including Accessing edges and neighbours
Note: Look at the intro directory for sample networkx code
If someone, that is not your friend, is your friends friend then maybe this person should be your friend too. If this person is friends with more of your friends then they become an even better recommendation. The best friend recommendation is the person with whom you have the largest number of mutual friends.
Consider this hypothetical situation:
-
Two of your friends are X and Y
-
X has only 2 friends (You and one other person)
-
Y has 7 billion friends
-
Y and X have no other friends on common other than you
Since X is highly selective in terms of friendship, and is a friend of yours, you are likely to have a lot in common with Xs other friends. On the other hand, Yis indiscriminate and there is little reason to believe that you should be friendly with any particular one of Ys other friends.
Incorporate the above idea into your friend recommendation algorithm. Here is the concrete way that you will do so. We call the technique “influence scoring”. Suppose that user1 and user2 have three friends in common: f1, f2, and f3. The score for user2 as a friend of user1 is 1/numfriends(f1) + 1/numfriends(f2) + 1/numfriends(f3), where numfriends(f) is the number of friends that f has. In other words, each friend F of user1 has a total influence score of 1 to contribute, and divides it equally among all of F's friends.
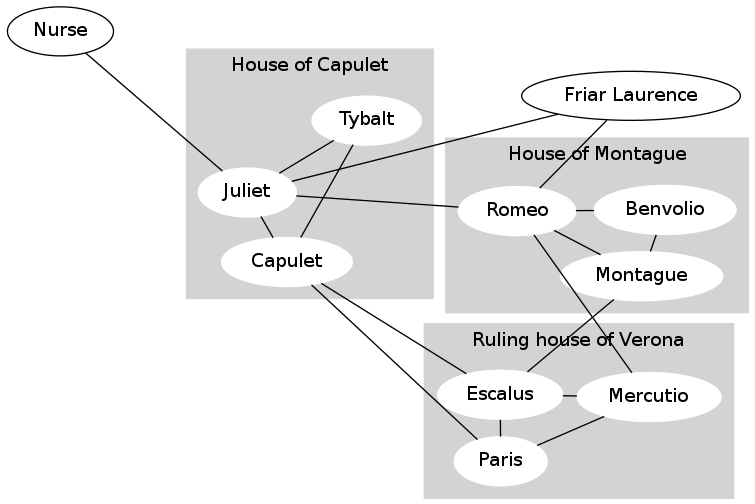
Here we shall analyse whether the recommendation algorithm matters. We are going to create a graph from the Romeo and Juliet story and try out the different algorithms and see if the results differ.
Note: Look at the main.py for this implementation
Results: After running both recommendation algorithms against the same user and comparing results I have come to the conclusion that the algorithm matters.
-
Algorithms returning same results: 5
-
Algorithms returning different results: 6
Now that we have come to the conclusion that the algorithm matters, we need to know which algorithm is better
-
Randomly choose a real connection. Lets say the 2 friends are F1 and F2
-
Remove their friendship from the graph
-
Compute the friend recommendations for F1 and F2
-
Determine the rank of F1 in F2s list of recommended friends and do the same for F2 in F1s list
-
If either does not exist (F2 is not recommended as a friend to F1), discard the pair from the experiment
-
Otherwise average the two numbers
-
The rank also known as index or position. It starts from 1 not 0
-
-
Don't forget to put their friendship back in the graph
-
Run the above test 100 times
Results: From the results obtained from the above test it can be seen that the Influence method provides better friend recommendations than the Common friends recommendation algorithm.