Optimization for Machine Learning project by Robin Junod, Arthur Lamour and Nicolas Reategui
- How do varying delays impact the convergence of distributed asynchronous SGD?
- Does the partitioning of data among workers enhance convergence during the training process? Is it beneficial to distribute labels among workers as well?
- What is the influence of momentum on asynchronous SGD? Does it serve as a regularization factor?
Source: Truly Sparse Neural Networks at Scale
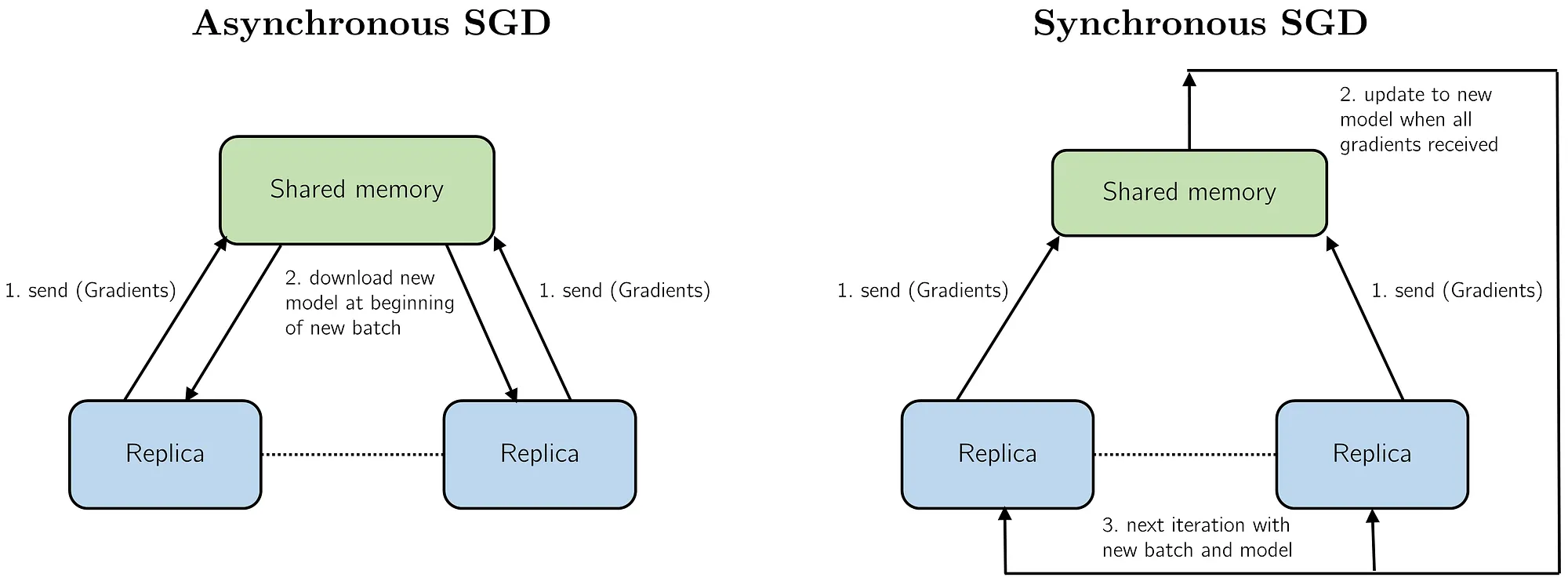
- Asynchronous SGD: workers update and fetch the global model without waiting for other workers.
- Synchronous SGD: workers send their gradient to the parameter server, once the gradients of each worker are received, the parameter server averages them and update the global model and workers fetch the same global model.
- Parameter server: master responsible for the global model and coordination among workers.
- Workers: training nodes.
Option 1 (Docker conda OS independant):
In order to avoid compatibility issues, you can use docker. This will allow you to use a lightweight Linux image in your computer for CLI programs which is enough for the scope of this project as we don't need a GUI. First install Docker or Docker desktop which will enable the docker service. Once docker is installed run the following command PS: docker build --pull --rm -f "docker/Dockerfile" -t optml "docker" --shm-size=1g from the repo folder, this will create the image. It is necessary to use a Linux distribution in order to use the PyTorch RPC functionalities. After building the image run docker run -v path_to_your_repo:mount_path --rm --shm-size=5g -it optml this will initialize the container, mount your repo to the specified path to use it within the container and the --rm will remove everything from your container after killing it to avoid waisting memory. To use VS Code with your container, download the Docker extension and once the container is running attach VS to it. Activate the base environment inside the container, to do so you can execute conda activate. It may be necessary to execute conda init bash in a terminal inside the container and then open a new one to be able to use conda. Once the base environment is activated you can run python.
Option 2 (WSL Windows only): Use Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). To install WSL2 take the following steps:
- Open PowerShell or Windows Command Prompt in administrator and run
wsl install - Install the default Ubuntu distribution
wsl --install -d Ubuntu - In bash run (disable firewall if needed):
sudo apt updatesudo apt upgradesudo apt install python3-pip dos2unix bcpip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio tqdm --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpupip3 install matplotlib scikit-learn plotly
Here is the list of our python scripts, they are meants to be run from the terminal: python script.py --flags or python3 script.py --flags
nn_train.py: implements non distributed trainingdnn_sync_train.py: simulates distributed synchronous SGD on CPUdnn_async_train.py: simulates distributed asynchronous SGD on CPUtest_model.py: computes the train and test performance and generates training plotsloss_landscape.py: generates a 3D plot of the loss landscape and 2D contour plot with the training trajectoryloss_landscape_multi_traj.py: generates a 3D plot of the loss landscape with multiple training trajectories and 2D contour plot with multiple training trajectorieskfold.py: implements grid search on hyperparameters to find the optimal onesmodels_size.py: prints the number of parameters of the available models: Lenet5 and CNN1 for MNIST and Fashion MNIST, Resnet18 and CNN2 for CIFAR10 and CIFAR100 (CNN1 and CNN2 are inspired CNNs from PyTorch RPC)common.py: all the common functions used by the other scripts
Here below is the data flow diagram:
Here is the list of our bash scripts, they are meants to be run from the terminal: bash script.sh
-
run_async_momentums.sh: for different momentum values: train asynchrounously save the model and weights during training. Then, generates the loss landscape with the different training trajectories -
run_delay_exps.sh: runs mulitple experiences associated with the delay:- For
world_size$=[2,6,11]$ , different delay intensities (small, medium, long), different data partitioning strategies (--split_datasetand--split_labels), constant delay being applied to all workers and for some cases worker 1 being slowded down additionally, train asynchronously. - For
world_size$=[2,6,11]$ , different delay intensities (small, medium, long), using--split_labelsand constant delay being applied to all workers and worker 1 being slowed even more, train asynchronously. - For
world_size$=[2,6,11]$ , formomentum$=[0,0.5,0.99]$ , different delay intensities (small, medium, long), using--split_labels, and constant delay being applied to all workers and worker 1 being slowed even more, train asynchronously. - For
world_size$=[2,6,11]$ , formomentum$=[0,0.5,0.9,0.99]$ , different delay intensities (small, medium, long), different data partioning strategies (--split_datasetor--split_labels), and gaussian delay being applied to all workers, with or without delay compension, train asynchronously.
- For
-
run_kfold.sh: K Fold Cross Validation for chosen datasets and optimizer -
run_kfold_full.sh: executesrun_kfold.shfor both SGD and Adam optimizers -
run_speed_comp.sh: compares the performance of synchronous SGD vs asynchronous SGD forworld_size$=[2,6,11]$ , different data partioning strategies (default,--split_dataset,--split_labels) and different network architectures (Lenet5 vs PyTorch CNN) -
loss_landcape.sh: computes the loss landscape for all the.pt(models) and associated.npy(saved weights during training) located in a folder -
test_model.sh: computes the test performance for all the.pt(models) and associated.log(log file with training logs) located in a folder
On WSL, when modifying the scripts you may encounter a similar error: line 2: $'\r': command not found, to solve this issue run: dos2unix script.sh
Summaries of some experiences can be found in the summaries folder, to get access to all the results go to our Google Drive with ~ 10 GB of data including models, weights during training, classification reports, loss landscape plots and contour plots.
The final plots of the report can be found in the plots folder, the .html are interactive figures created with Plotly.
Available flags for nn_train.py, dnn_sync_train.py, dnn_async_train.py:
| Flag | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
| --dataset {mnist,fashion_mnist,cifar10,cifar100} | Choose a dataset to train on: mnist, fashion_mnist, cifar10, or cifar100. | |
| --train_split TRAIN_SPLIT | Fraction of the training dataset to be used for training (0,1]. | |
| --lr LR | Learning rate of optimizer (0,+inf). | |
| --momentum MOMENTUM | Momentum of SGD optimizer [0,+inf). | Not used with Adam optimizer. |
| --batch_size BATCH_SIZE | Batch size of Mini batch SGD [1,len(train set)]. | |
| --epochs EPOCHS | Number of epochs for training [1,+inf). | |
| --model_accuracy | If set, will compute the train accuracy of the global model after training. | |
| --no_save_model | If set, the trained model will not be saved. | |
| --seed | If set, it will set seeds on torch and numpy for reproducibility purposes. | |
| --subfolder SUBFOLDER | Subfolder where the model and log.log will be saved. | |
| --saves_per_epoch SAVES_PER_EPOCH | Number of times the model weights will be saved during one epoch. | The first weights are saved directly after initialization (model has not trained yet). |
| --alr | If set, use adaptive learning rate (Adam optimizer) instead of SGD optimizer. | |
| --lrs {exponential,cosine_annealing} | Applies a learning rate scheduler: exponential or cosine_annealing. | |
| --alt_model | Will train using alternate CNN models instead of LeNet5 (MNIST & FashionMNIST) or ResNet18 (CIFAR10 & CIFAR100). | |
| --val | If set, will create a validation dataloader and compute the loss and accuracy of train set and val set at the end of each epoch. | For asynchronous, the number of batches received (pseudo epochs) are used instead of epochs. |
| --master_port MASTER_PORT | Port that master is listening on, will default to 29500 if not provided. Master must be able to accept network traffic on the host and port. | Not avaiable for nn_train.py. |
| --master_addr MASTER_ADDR | Address of master, will default to localhost if not provided. Master must be able to accept network traffic on the address + port. | Not avaiable for nn_train.py. |
| --world_size WORLD_SIZE | Total number of participating processes. Should be the sum of master node and all training nodes [2,+inf]. | Not avaiable for nn_train.py. If world_size exceeds the number of available CPU threads, PyTorch RPC will crash. |
| --delay | Add a delay to all workers at each mini-batch update. | Not avaiable for nn_train.py. |
| --slow_worker_1 | Add a longer delay only to worker 1 at each mini-batch update. | Not avaiable for nn_train.py. |
| --delay_intensity {small,medium,long} | Applies a delay intensity of: small 10ms, medium 20ms, long 30ms. | Not avaiable for nn_train.py. |
| --delay_type {constant,gaussian} | Applies a delay of type: constant or gaussian. | Not avaiable for nn_train.py. |
| --split_dataset | After applying train_split, each worker will train on a unique distinct dataset (samples will not be shared between workers). Do not use with --split_labels or --split_labels_unscaled. | Not avaiable for nn_train.py. |
| --split_labels | If set, it will split the dataset in {world_size -1} parts, each part corresponding to a distinct set of labels, and each part will be assigned to a worker. Workers will not share samples and the labels are randomly assigned. Don't use with --split_dataset or --split_labels_unscaled. Depending on the chosen dataset the --world_size should be total_labels mod (world_size-1) = 0, with world_size = 2 excluded. | Not avaiable for nn_train.py. |
| --split_labels_unscaled | If set, it will split the dataset in {world_size -1} parts, each part corresponding to a distinct set of labels, and each part will be assigned to a worker. Workers will not share samples and the labels are randomly assigned. Note, the training length will be the DIFFERENT for all workers, based on the number of samples each class has. Don't use --split_dataset or split_labels. Depending on the chosen dataset the --world_size should be total_labels mod (world_size-1) = 0, with world_size = 2 excluded. | Not avaiable for nn_train.py and dnn_sync_train.py. |
| --compensation | If set, enables delay compensation. | Not avaiable for nn_train.py and dnn_sync_train.py. |
For kfold.py , test_model.py, loss_landscape.py, loss_landscape_multi_traj.py use -h or --help to see the available flags and required arguments to give. For example: python3 kfold.py -h or python3 test_model.py --help.
The following image illustrates the different data partioning strategies implemented on the MNIST train dataset for distributed learning on two workers:
After performing KFold Cross Validation, we recommend using the following hyperparameters:
| Dataset | Model | Optimizer | learning rate | momentum | batch size | epochs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNIST | Lenet5 | SGD | 0.9 | 64 | 6 | |
| MNIST | Lenet5 | ADAM | / | 64 | 6 | |
| Fashion MNIST | Lenet5 | SGD | 0.9 | 32 | 6 | |
| Fashion MNIST | Lenet5 | ADAM | / | 32 | 6 | |
| Fashion MNIST | CNN1 | SGD | 0.9 | 64 | 6 | |
| Fashion MNIST | CNN1 | ADAM | / | 32 | 6 | |
| CIFAR10 | ResNet18 | SGD | 0.9 | 32 | 6 | |
| CIFAR10 | ResNet18 | ADAM | / | 64 | 6 | |
| CIFAR10 | CNN2 | SGD | 0.9 | 32 | 6 | |
| CIFAR100 | ResNet18 | SGD | 0.9 | 32 | 6 | |
| CIFAR100 | ResNet18 | ADAM | / | 128 | 6 |
Note, for CIFAR10 and CIFAR100 due to training time being very long (without GPU) KFold Cross Valdiation was performed on 2 and 3 epochs. The optimal number of epochs for training was found using 10% of the training set for validation, and we computed the training and validation accuracy and loss for 50 epochs, the resutls can be found in the Validation_results folder of our Google Drive.