In this repository, we provide a code for experimenting with various ways of enhancing AIoD search and user interactions.
To properly set up this repository to be fully functional you need to perform the following steps:
- Create a new Conda environment with Python 3.11 and install necessary dependencies
conda create --name <env_name> python=3.11.9
conda activate <env_name>
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Create
.envfile based on.env.samplefile containing all mandatory environment variables our scripts rely on. Further replace the placeholder values with the correct valid values. - Compute textual representations of the JSON objects and store them locally in the file system.
This can be achieved by executing
setup.pyfile.
python src/setup.py --collection=<name-of-document-collection> --outdir=<path-to-store-extracted-data> --function=<path-to-function-for-extracting-data>
You can also create a new function for extracting relevant information out of AIoD objects and use it instead of a default extraction function.
Your newly provided extraction function needs to adhere to the following function signature: def func(obj: dict) -> str
Default values for flags of src/setup.py file:
--collection datasets--outdir temp/texts--function preprocess.text_operations.ConvertJsonToString.extract_relevant_info
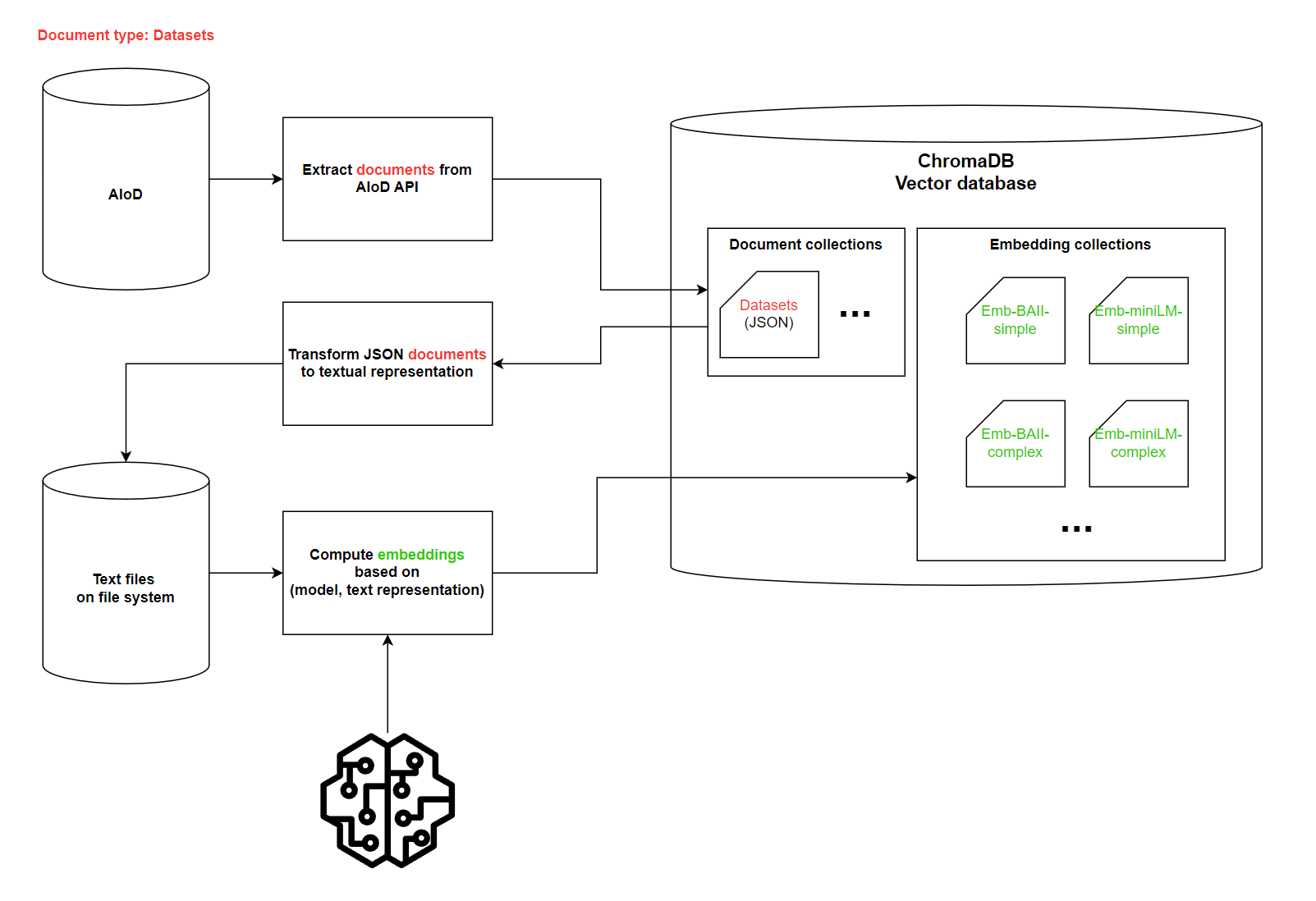
In the ChromaDB, vector database, we connect to when working on this project, we distinguish between two different types of collections:
- Document collections
- Embedding collections
These collections contain the stringified JSONs of specified object types in their metadata attributes, and these collections could be considered as snapshots of AIoD database.
For instance, ChromaDB collection datasets contains stringified JSONs of Dataset instances that individual end users of this repository can further build upon and create new
functions for extracting relevant information and converting it to textual representations. Subsequently, these representations are further fed into embedding models to create embeddings
representing the textual content of AIoD objects.
We don't perform any semantic search on top of this type of collections.
{
id: doc_id # original AIoD IDs
document: None # this field is empty
embeddings: [0] # placeholder, dummy embeddings
metadata: {
"json_string": stringified JSONs of AIoD objects
}
}
These collections contain the computed embeddings of AIoD objects that are constructed after utilizing a combination of a specific extraction approach and a embedding model.
To identify what specific steps have been taken prior to computing embeddings, we try to adhere to the following collection naming approach embeddings-<model_name>-<text_function> that
mentions what model and what text preprocessing function has been used.
(We don't necessarily need to use full names of the embeddings models or text extract functions, however we need to have additional table that further describes the mapping between the simplified name used in the collection name itself and a more specific description of assets used)
For instance, ChromaDB collection embeddings-BAAI-simple contains embeddings computed using transformer encoder-only model BAAI/bge-base-en-v1.5 on textual data created by executing the ConvertJsonToString.extract_relevant_info function.
{
id: Unique UUID
document: None
embeddings: emb # Embeddings computed by a specific model
metadata: {
"doc_id": doc_id # ID referring to document collection
}
}
In this section, we can find descriptions of tasks we want to perform in efforts to enhance the AIoD search experience
Based on user specified query, we want to find the assets that are the most similar to the query in an embedding space. The embedding space itself can be built by choosing a specific information extraction function and an embedding model.
To create new embeddings, execute code found in src/embed.py file.
To properly perform the embeddings computation, you need to set the correct hyperparameters of a model you wish to use