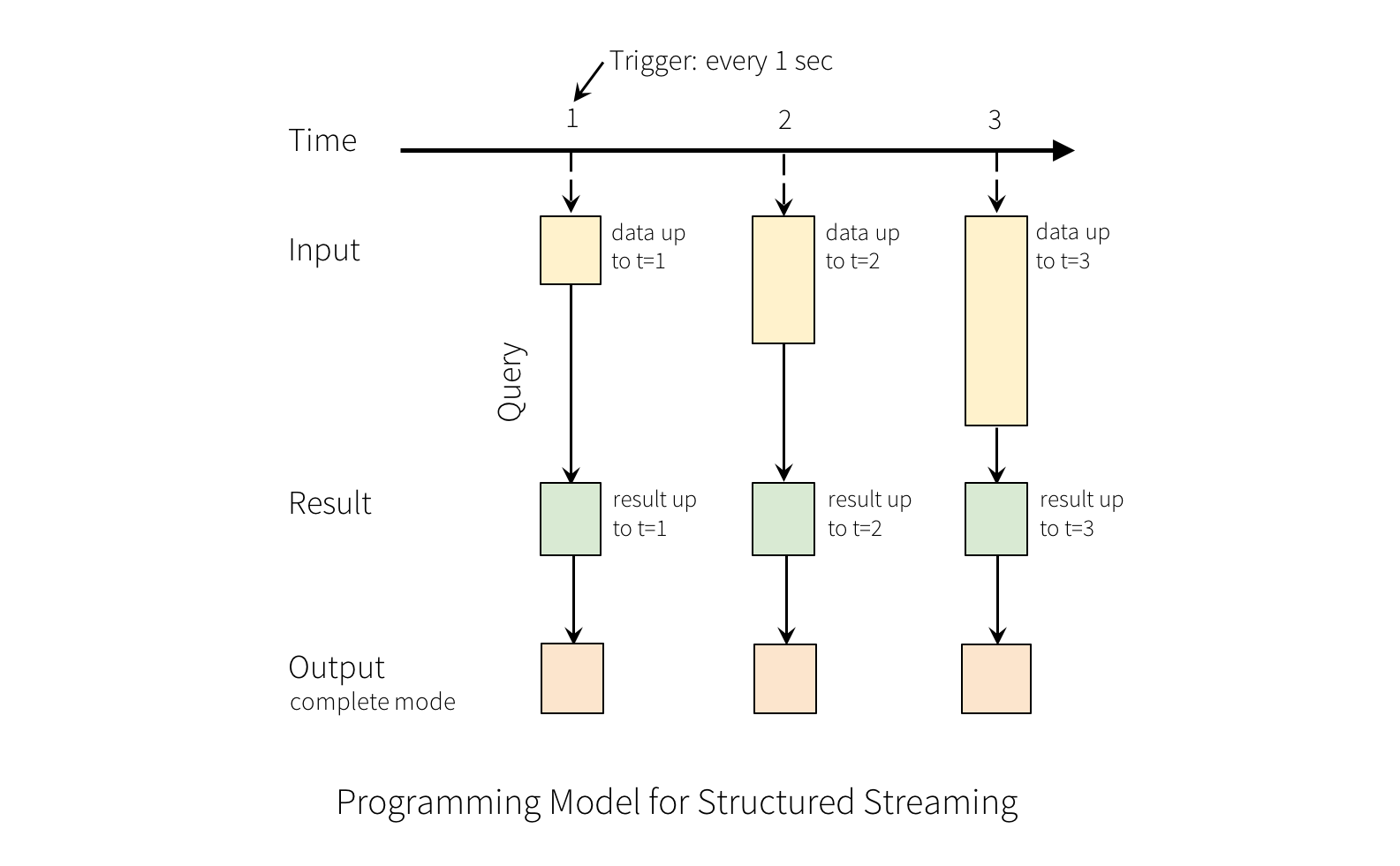-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 125
Structured Streaming
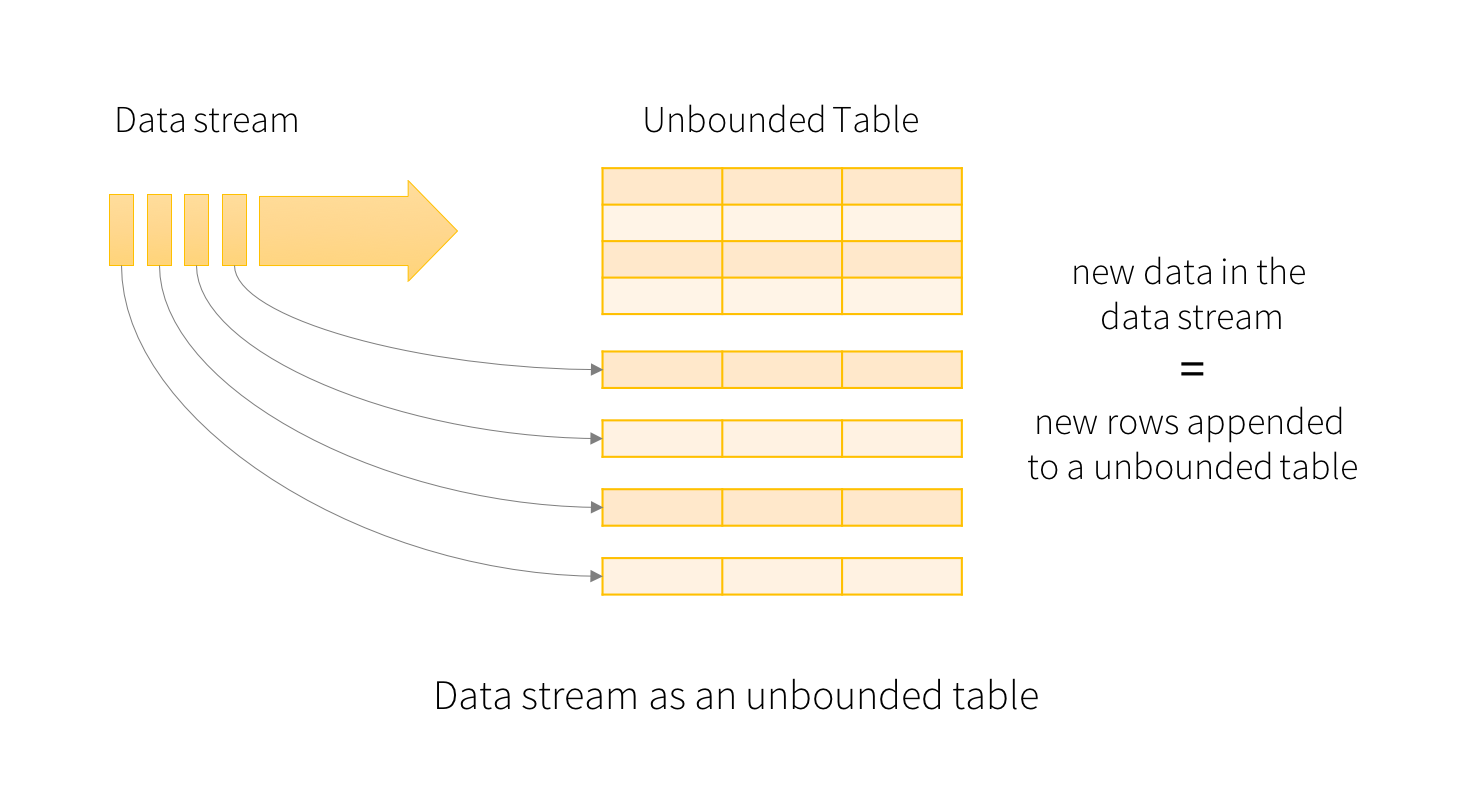
Structured Streaming is a scalable and fault-tolerant stream processing engine built on the Spark SQL engine. You can express your streaming computation the same way you would express a batch computation on static data.The Spark SQL engine will take care of running it incrementally and continuously and updating the final result as streaming data continues to arrive. We can use the Dataset/DataFrame API in Scala, Java or Python to express streaming aggregations, event-time windows, stream-to-batch joins, etc. The computation is executed on the same optimized Spark SQL engine. Finally, the system ensures end-to-end exactly-once fault-tolerance guarantees through checkpointing and Write Ahead Logs.
- In short, Structured Streaming provides fast, scalable, fault-tolerant, end-to-end exactly-once stream processing without the user having to reason about streaming.
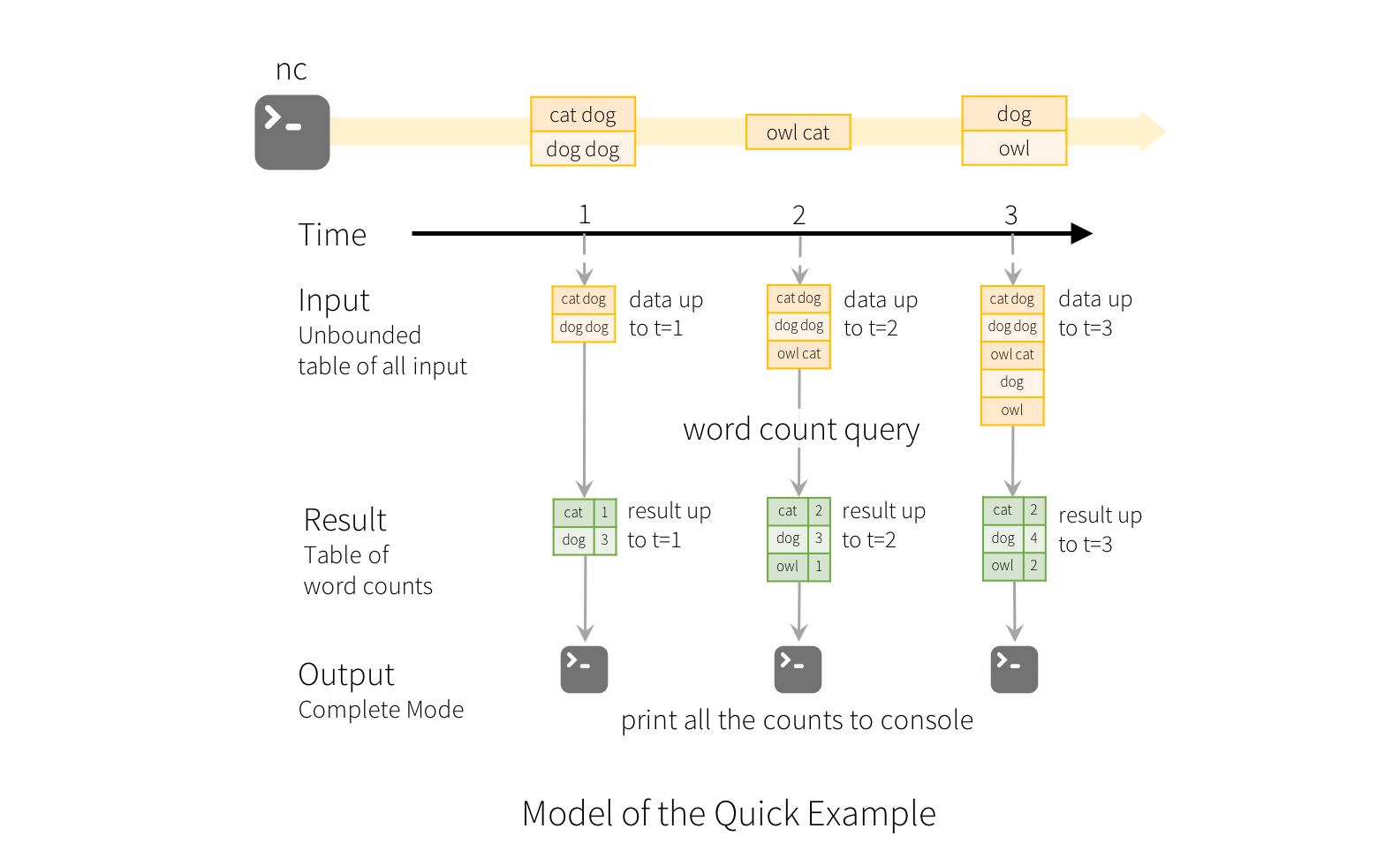
The “Output” is defined as what gets written out to the external storage. The output can be defined in different modes
- Complete Mode - The entire updated Result Table will be written to the external storage. It is up to the storage connector to decide how to handle writing of the entire table.
- Append Mode - Only the new rows appended in the Result Table since the last trigger will be written to the external storage. This is applicable only on the queries where existing rows in the Result Table are not expected to change.
- Update Mode - Only the rows that were updated in the Result Table since the last trigger will be written to the external storage (not available yet in Spark 2.0). Note that this is different from the Complete Mode in that this mode does not output the rows that are not changed.
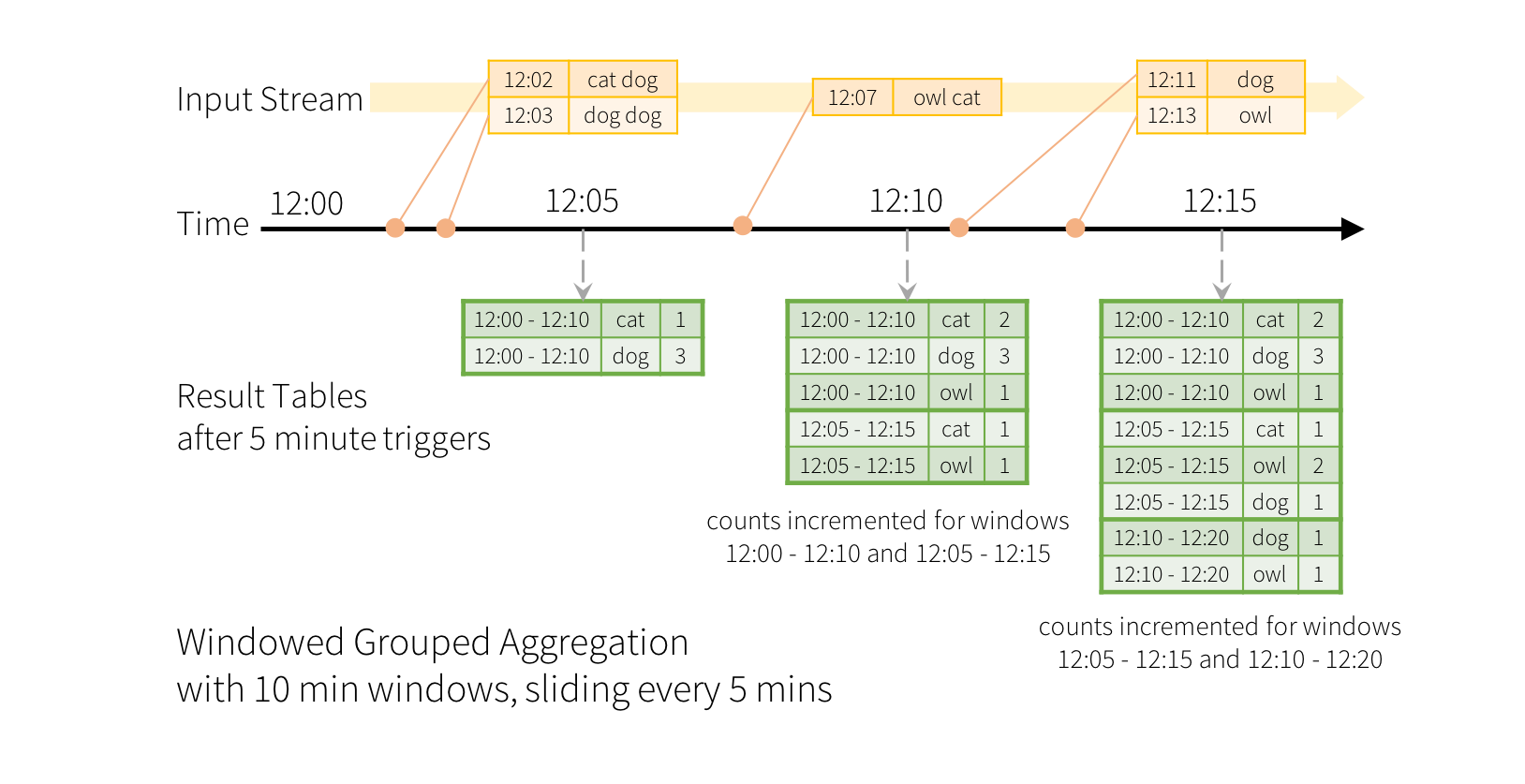
- Aggregations over a sliding event-time window are straightforward with Structured Streaming.
- The key idea to understand about window-based aggregations are very similar to grouped aggregations.
- In a grouped aggregation, aggregate values (e.g. counts) are maintained for each unique value in the user-specified grouping column.
- In case of window-based aggregations, aggregate values are maintained for each window the event-time of a row falls into.
- Understanding Spark
- Spark Jobs & API
- Architecture
- RDD Internals
- Creating RDD
- Understanding Deployment & Program Behaviour
- RDD Transformation & Action
- Assignments 1
- Best Practices -1
- Introduction to DataFrame
- PySpark SQL
- Pandas to DataFrames
- Machine Learning with PySpark
- Transformers
- Estimators
- Spark Streaming
- Structured Streaming
- GraphX & GraphFrames
- Data Processing Architectures
- Problems