NOTICE: This package is being deprecated in favor of the StarryNight utility, which resolves most all of the configuration and launching issues that this package had.
starrynight.meteor.com
=================== Ultra-easy acceptance testing for your Meteor app with Selenium and Nightwatch.
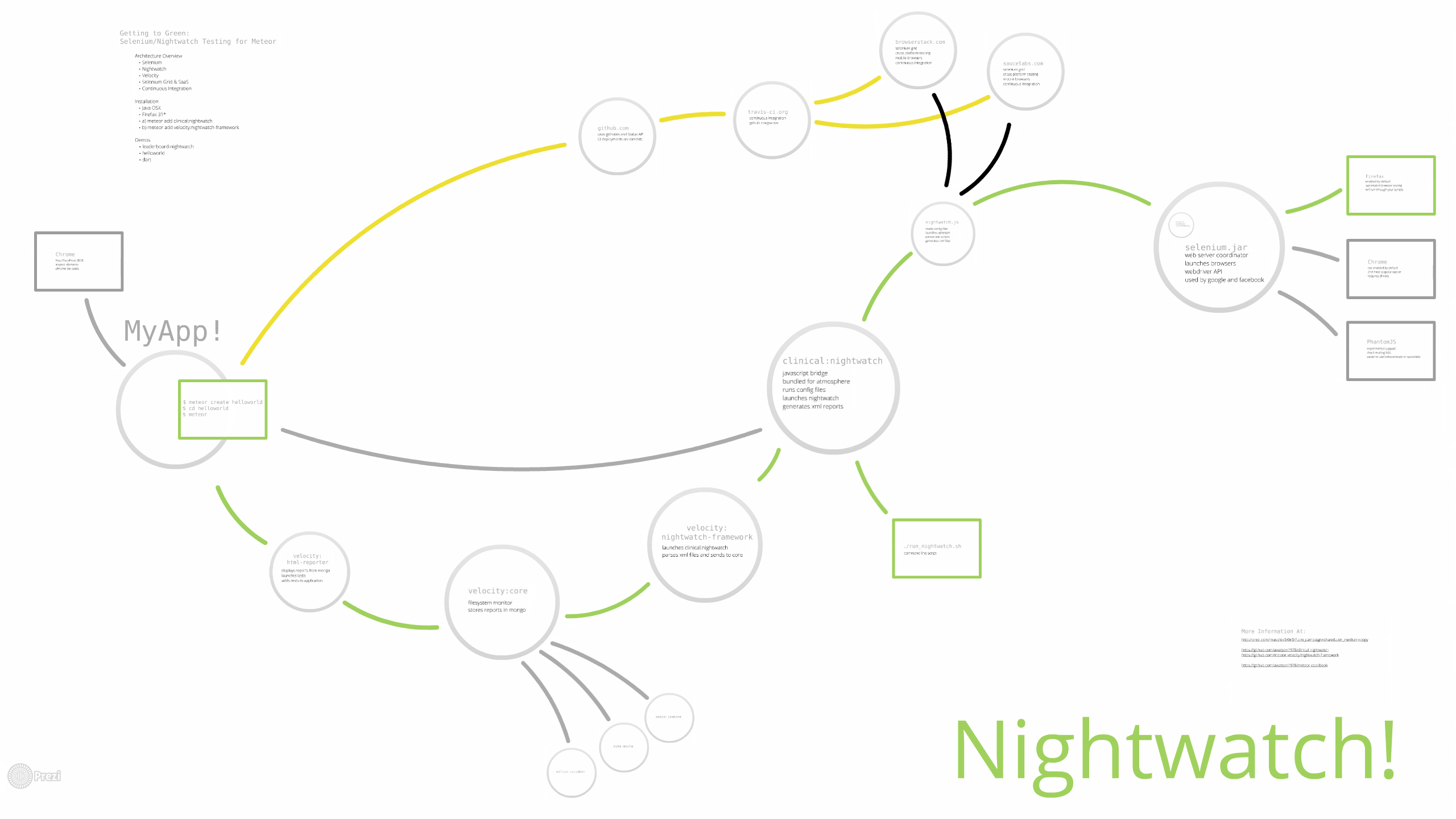 View the Prezi on Nightwatch Architecture for Meteor Applications
View the Prezi on Nightwatch Architecture for Meteor Applications
This package is 11mb large, because of the Selenium browser automation server, and will increase the overall size of your application by 11mb! The good news, however, is that this extra weight won't be shipped down to the client, and is simply bloats the bundle file and adds an unnecessary file to the server.
- Installation
- Quckstart
- Acceptance Tests
- Databases
- Continous Integration with Travis CI
- Leaderboard Example Using Velocity & Nightwatch-Framework
Step 1 - Configure the Filesystem
Begin by creating the following files in your /tests directory. For now, the contents of global.json can be an empty json object {}.
/tests/nightwatch/globals.json
/tests/nightwatch/logs
/tests/nightwatch/commands
/tests/nightwatch/assertions
/tests/nightwatch/walkthroughs
terminal-a$ chmod -R 777 tests/nightwatchStep 2 - Add Nightwatch To Your Application
Nightwatch works a lot like when you run the meteor mongo command. That is, you need to have an instance of meteor running for it work. More specifically, Nightwatch will attach itself to the compiled version of your app in the .meteor/local/build directory, and spin up a mirror copy of your app to test with. Your other app doesn't actually have to be running, but it does need to be run at least once before.
# go to the root of your application
terminal-a$ cd myappdir
terminal-a$ meteor add clinical:nightwatch
# Go to the root of your application
terminal-a$ cd myappdir
# run the leaderboard application
terminal-a$ meteorStep 3 - Set up the Launch Script and Run Nightwatch
Copy the run_nightwatch.sh script into your application root. Once you do that, make sure your permissions are set correctly.
# In the same way that we run 'meteor mongo' in a separate terminal while our application is already running,
# we want to open up a new terminal, and run nightwatch
terminal-b$ chmod -R 777 .meteor
terminal-b$ chmod 777 run_nightwatch.sh
terminal-b$ ./run_nightwatch.sh
# you might want to do something clever like pass in arguments and run specific tests
terminal-b$ ./run_nightwatch.sh -t tests/nightwatch/leaderboard.js
# of run only the tests that have been tagged with a specific label
terminal-b$ ./run_nightwatch.sh --tag fooCheck out this super simple syntax for writing acceptance tests. All you need to do is copy the following code into a file in the /tests directory, and Nightwatch will parse it accordingly.
// tests/helloworld.js
module.exports = {
"Hello World" : function (client) {
client
.url("http://127.0.0.1:3000")
.waitForElementVisible("body", 1000)
.assert.title("Hello World")
.end();
}
};
// tests/google.js
module.exports = {
tags: ["foo"],
"Demo Test Google" : function (client) {
client
.url("http://www.google.com")
.waitForElementVisible("body", 1000)
.assert.title("Google")
.assert.visible("input[type=text]")
.setValue("input[type=text]", "nightwatch")
.waitForElementVisible("button[name=btnG]", 1000)
.click("button[name=btnG]")
.pause(1000)
.assert.containsText("#main", "The Night Watch")
.end();
}
};You may notice that your database has gotten out of sync with your tests. Don't worry, as that's normal. The easy thing to do is just reset your database. But you'll eventually need to write your tests so they don't destructively modify your database, or you'll need to create tearUp and tearDown methods, or set up a testing database, or any number of other activities to manage your test data.
# if you want to rerun the acceptance tests, go back to the first terminal
# and be sure to reset the database
terminal-a$ ctrl-c
terminal-a$ meteor reset
terminal-a$ meteorWith bigger test suites, you'll maybe want to set up an entire test database, in which case you'll want to attach your Nightwatch instance against a test database. That's probably getting past the extent of this README, but here's a quick reference to how to do that...
# launch your application against a test database
terminal-a$ MONGO_URL=mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017 PORT=3000 node .meteor/local/build/main.jsCustom Commands
Using Globals.js to Define Test Data
File Upload Dialog
Download File Assertion
Testing Minimongo and Browser Console with execute()
Code Injection using execute()
Connecting to SauceLabs
MIT License. Use as you wish, including for commercial purposes.