PhoneGap/Cordova plugin to connect to external bluetooth GPS devices on Android. Importantly, the plugin does not require the use of Mock Locations (which require developer settings and a third party application). Instead, the plugin communicates directly with the Bluetooth device via BluetoothSerial and then parses the incoming NMEA stream with GPS.js.
Note: This plugin currently only searches the list of paired devices when connecting via Bluetooth. The external GPS should be paired using the default Android Bluetooth settings before using apps built with this plugin.
This plugin uses the official cordova-plugin-geolocation to manage location permissions and provide a relatively consistent API across platforms.
On iPhone and iPad, external GPS devices are automatically integrated into location services, and there is no API to directly control which source is used. The iOS version of this plugin will attempt to guess which source is used when providing location responses.
// Unofficial API (this plugin)
navigator.geolocation.setSource('external', gpsReady); // Android only
function gpsReady() {
// Official API
navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(onLocate);
}
function onLocate(pos) {
// Official result
console.log(pos.coords.latitude); // 45.079936
console.log(pos.coords.longitude); // -93.55493
console.log(pos.coords.accuracy); // 8.4
// Unofficial result (this plugin)
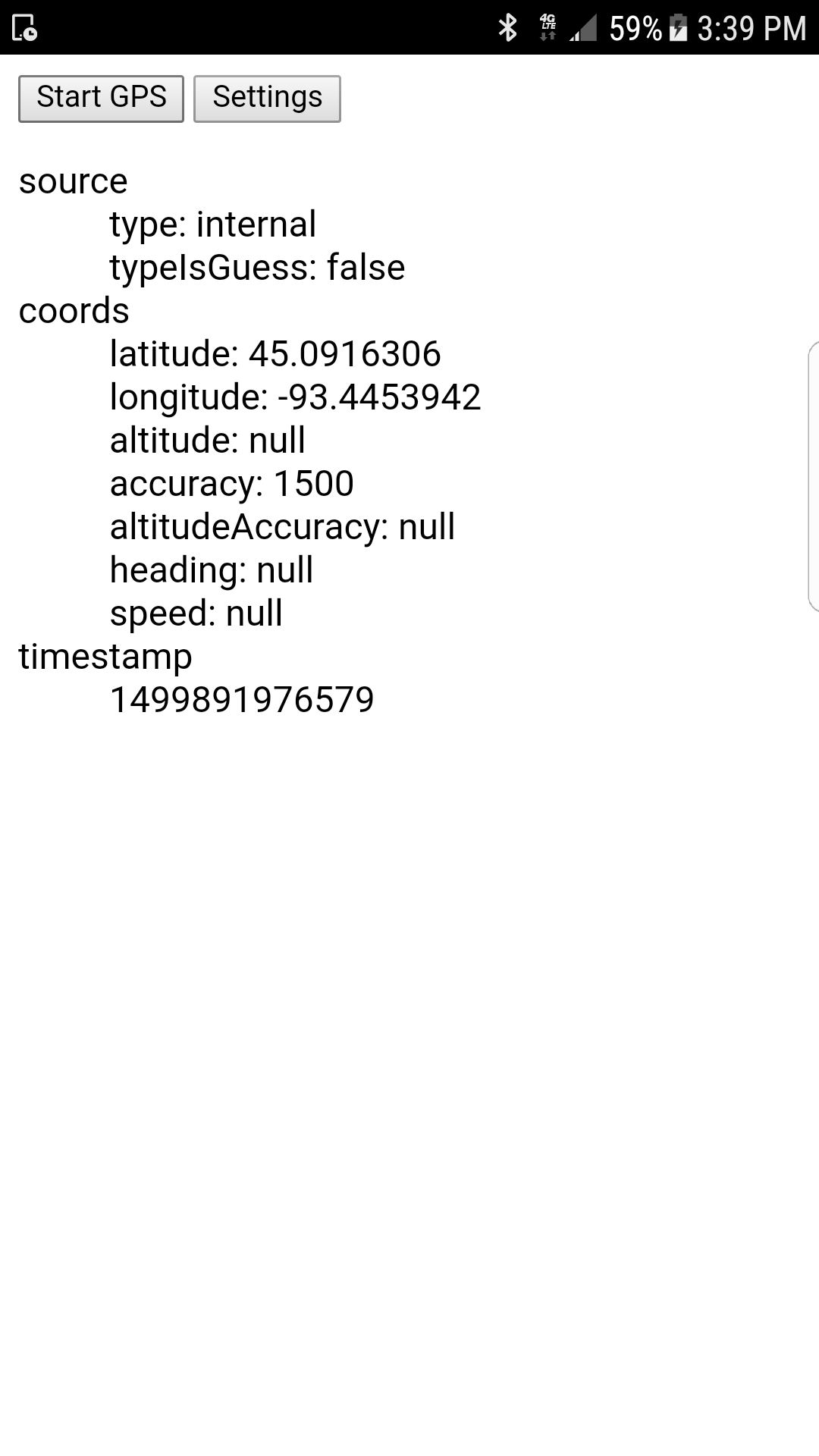
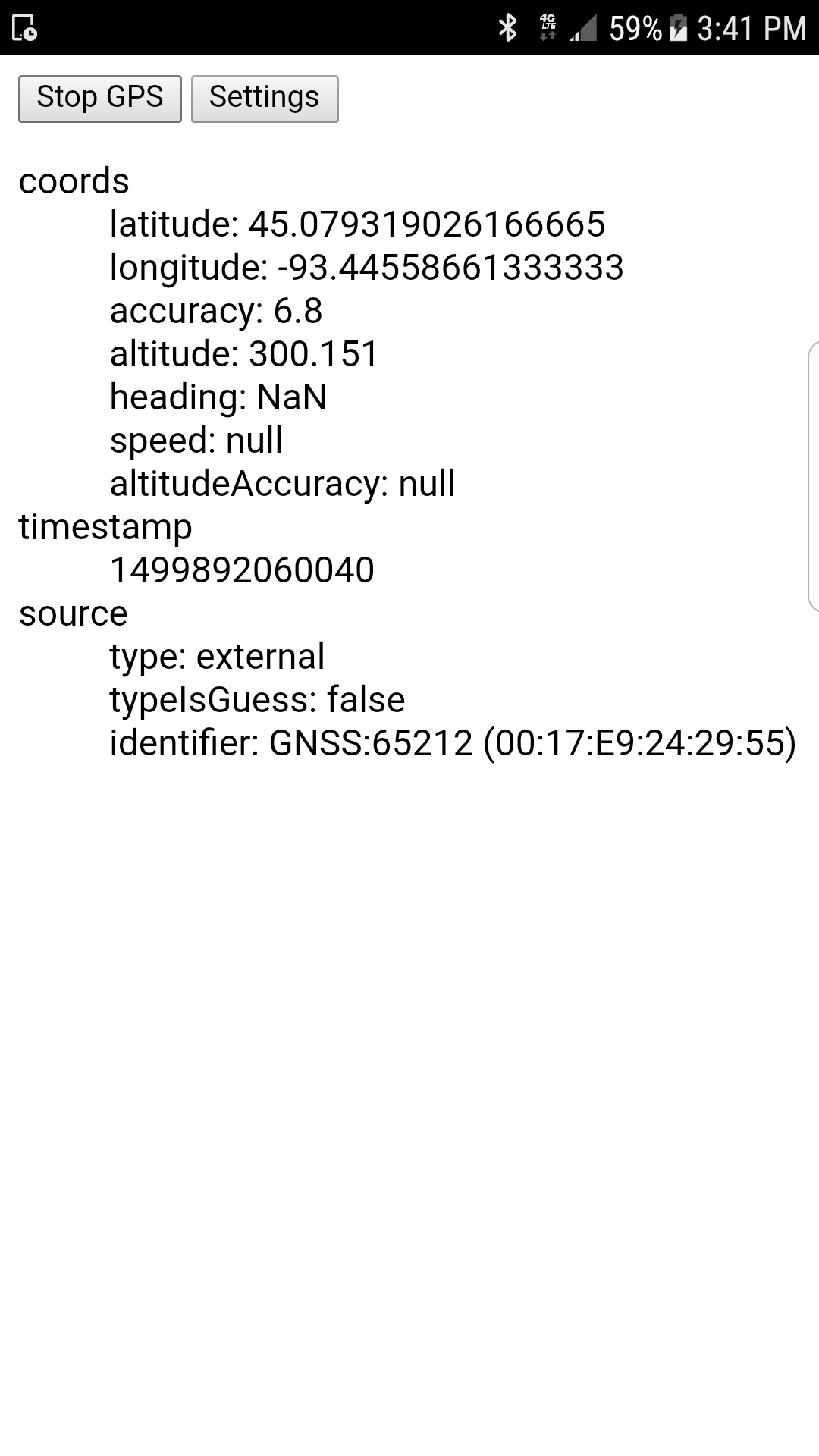
console.log(pos.source.type); // "external"
console.log(pos.source.typeIsGuess); // false (true on iOS)
console.log(pos.source.identifier); // "GNSS:65212 (00:17:E9:24:29:55)"
}cordova plugin add https://github.com/heigeo/cordova-plugin-bluetooth-geolocation<!-- config.xml -->
<plugin spec="https://github.com/heigeo/cordova-plugin-bluetooth-geolocation.git" />- Android
- iOS (partial)
The plugin extends the standard navigator.geolocation API with several non-standard methods and properties.
if (navigator.geolocation.hasSource)
console.log("Using cordova-plugin-bluetooth-geolocation");Indicates that the plugin is present and that the source property will be set on Position objects returned by getCurrentPosition() and watchPosition()
if (navigator.geolocation.canSetSource)
console.log("Using cordova-plugin-bluetooth-geolocation on Android");true on Android and false on iOS.
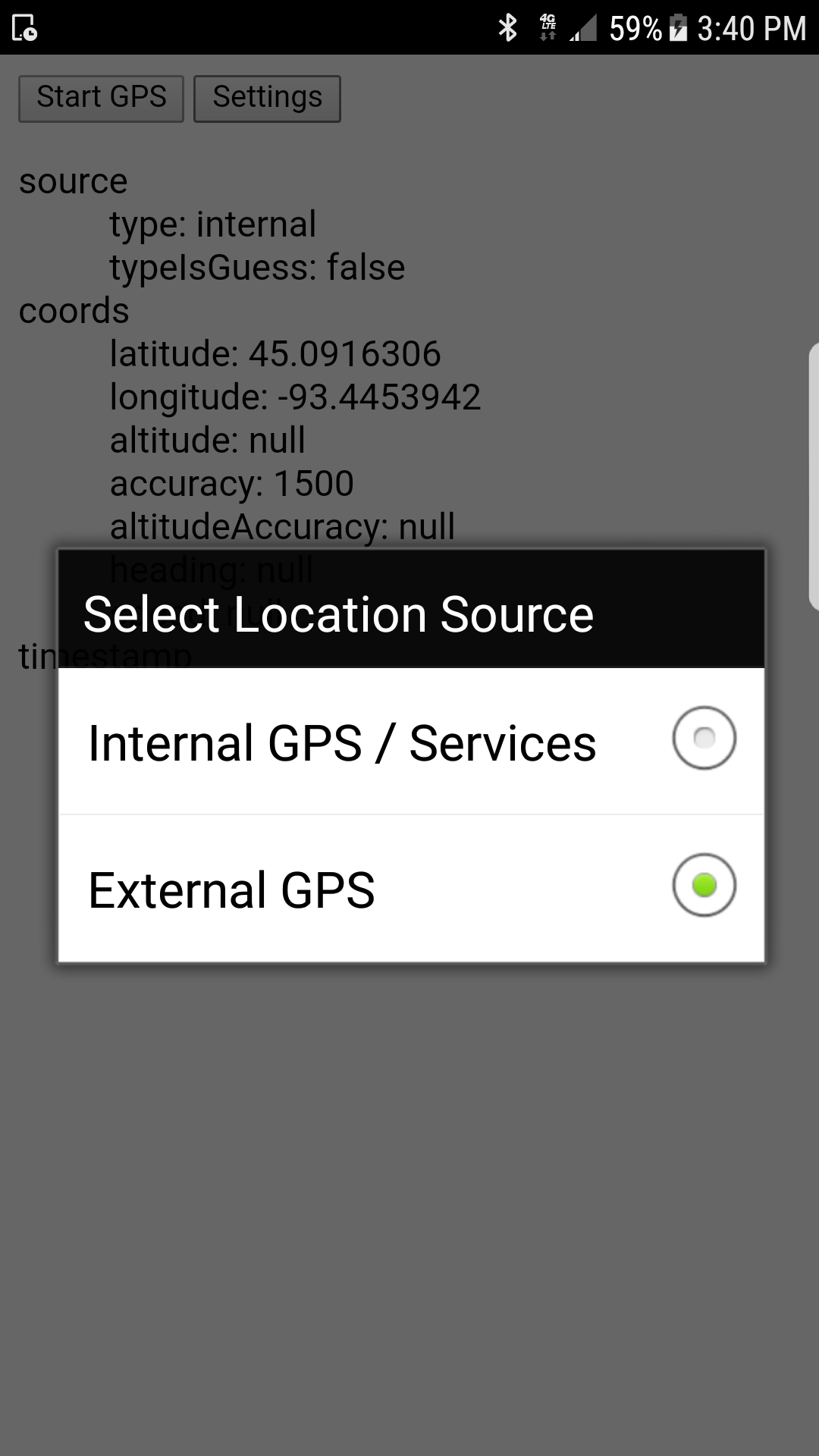
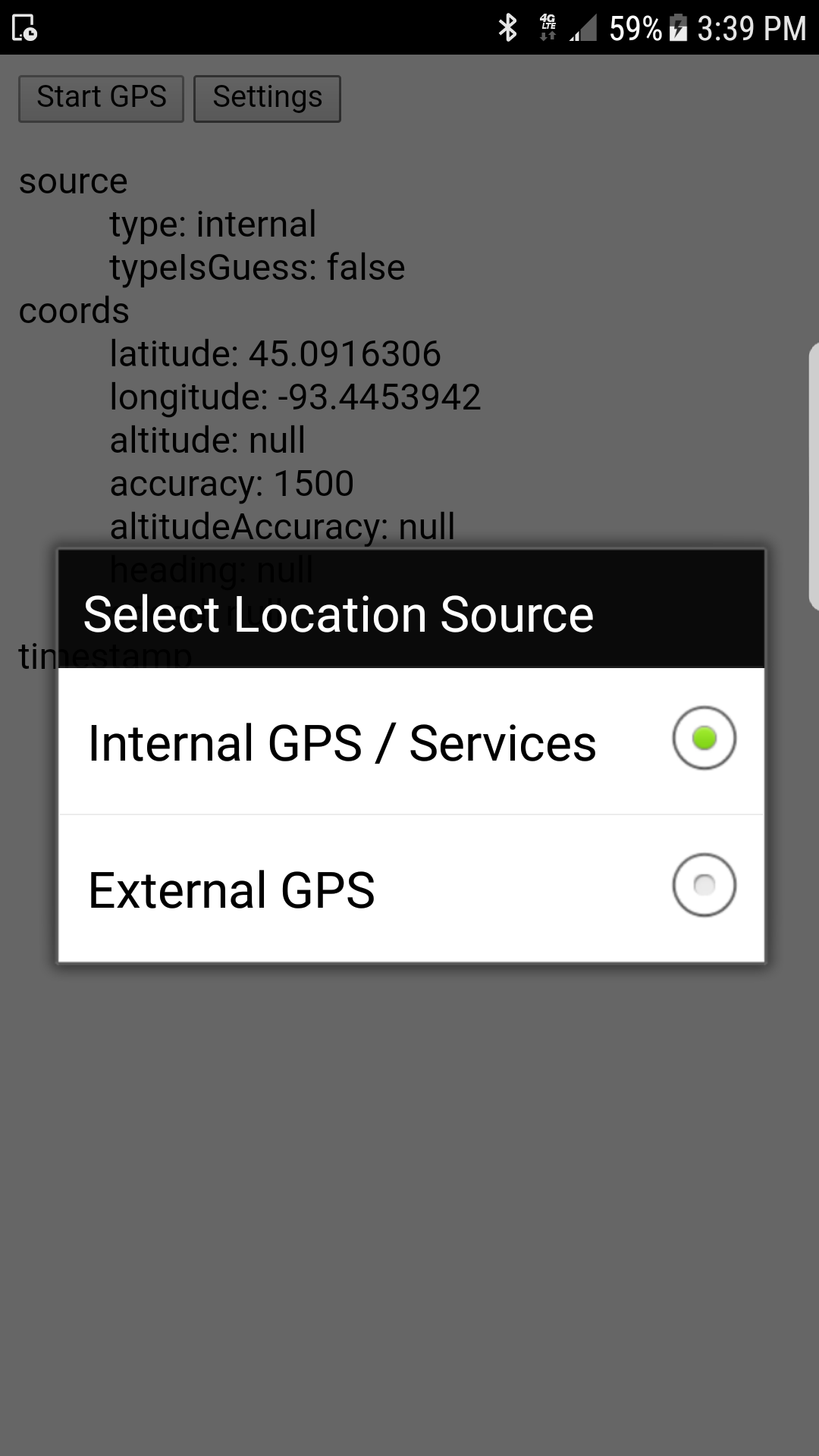
navigator.geolocation.showSourcePicker();This function provides a simple user interface (at right) to allow the user to select whether to use internal device or an external Bluetooth reciever. The plugin calls setSource() internally. If there are any errors switching to the external device, the dialog will re-appear until the user selects internal or cancels.
navigator.geolocation.setSource(source[, callback, errorCallback]);Sets source to one of "internal" or "external". On Android, the source is "internal" until Bluetooth is enabled by calling this function with "external". Once the location is sucessfully set to external, future calls to watchPosition and getCurrentPosition will use the connected bluetooth device instead of the internal location services.
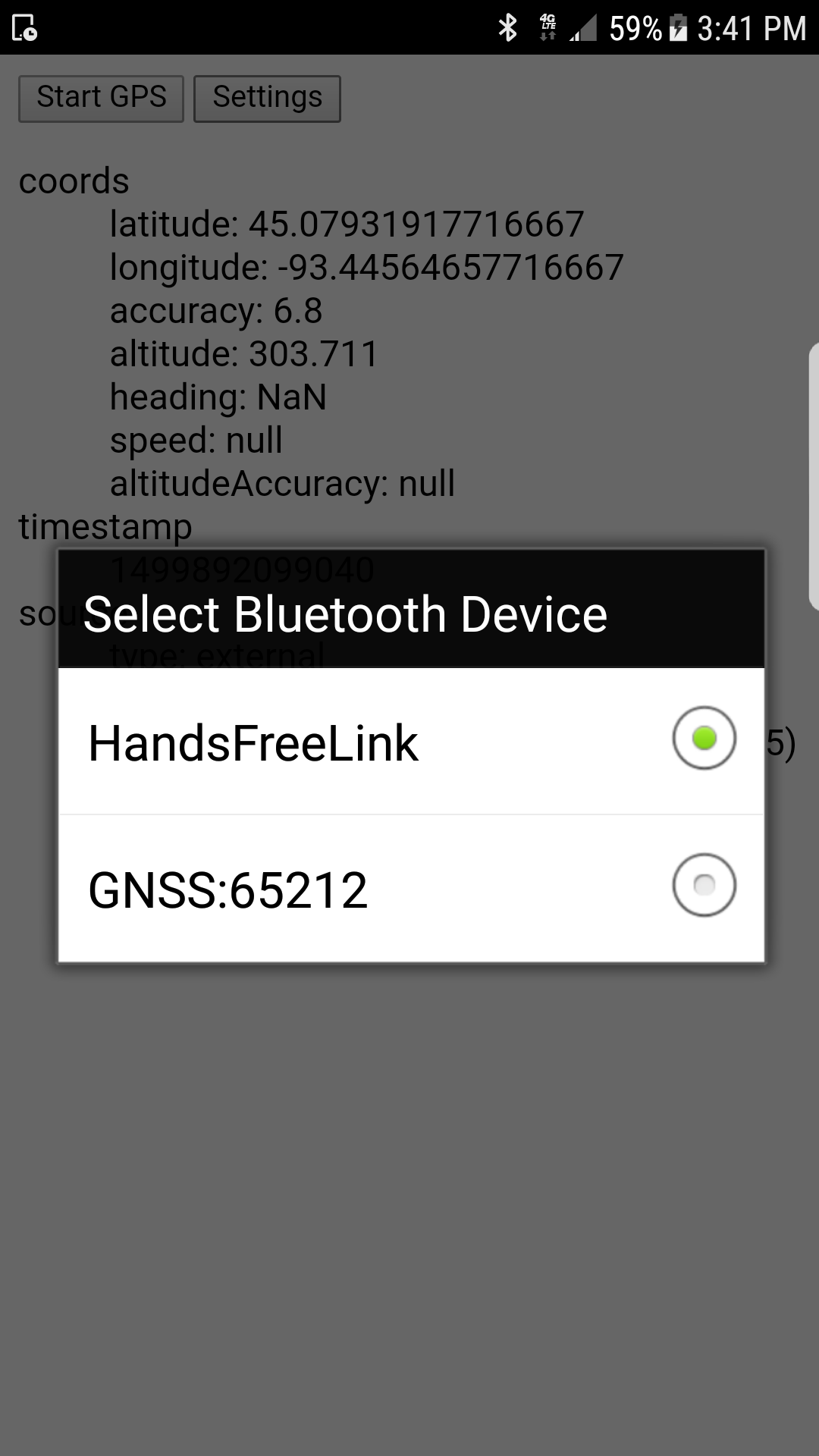
The GPS device should be paired with your phone before calling this function. If there is only one paired GPS device, the plugin should automatically detect it and call the success callback. If there is more than one possibility, the plugin will show a dialog (at right) for selecting which device to use. If the user cancels the dialog or there are no available bluetooth devices, the error callback will be called instead.
On iOS, this function is not supported and will immediately call the error callback (see above).
When the plugin is present, Position objects returned by getCurrentPosition() and watchPosition() will have additional attribute, source, with the following attributes set:
| name | description |
|---|---|
type |
"internal" or "external" |
typeIsGuess |
false (on Android), true (on iOS) |
identifier |
Bluetooth device name and MAC Address, if known |
On Android, the source type is known with certainty (since the plugin itself is controlling the API). On iOS, the type is a guess based on a heuristic that (currently) looks at the number of decimal places in the altitude value.
Note that when using "external" source on Android, the accuracy value on Position.coords is a rough estimate based on the HDOP reported by the GPS unit. This value should usually be within an order of magnitude of the accuracy that would be computed by a standard implementation of navigator.geolocation.
Since this plugin transparently overwrites the built-in navigator.geolocation API, it will automatically work with Leaflet and other mapping libraries. However, leaflet LocationEvent objects returned via map.locate() will not make use of the custom source property. If you are using Leaflet's API instead of navigator.geolocation, you can use the following code to store this information and include it in your application:
var map = L.map("...", {...}),
lastSource;
if (navigator.geolocation.hasSource) {
map._handleGeolocationResponse = function(pos) {
lastSource = pos.source;
L.Map.prototype._handleGeolocationResponse.call(map, pos);
}
if (navigator.geolocation.canSetSource) {
navigator.geolocation.setSource('external');
}
}
map.on('locationfound', function(evt) {
console.log(evt.latlng.lat); // 45.079936
console.log(evt.latlng.lng); // -93.55493
console.log(lastSource ? lastSource.type : "unknown"); // "external"
});
map.locate({...});If you are using the latest wq/locate.js from wq.app, the Leaflet patching is handled automatically. The Locator widget will populate any provided "source" <input> with information about the GPS source. See the documentation for wq/locate.js for more information. Using the examples below, you can also use custom location modes to avoid the need for a separate call to geolocation.showSourcePicker().
// myapp/gpsinit.js
define({
'run': function($page, routeInfo) {
var mapId = map.getMapId(routeInfo);
var locator = locate.locators[mapId];
if (!locator) {
return;
}
if (navigator.geolocation.canSetSource) {
locator.internalStart = function() {
navigator.geolocation.setSource(
'internal', locator.gpsStart, locator.onerror
);
};
locator.externalStart = function() {
navigator.geolocation.setSource(
'external', locator.gpsStart, locator.onerror
);
};
locator.internalStop = locator.externalStop = locator.gpsStop;
} else {
$page.find('label[for=gpstest-toggle-internal]').text("GPS");
$page.find('#gpstest-toggle-internal').val("gps");
$page.find('label[for=gpstest-toggle-external], #gpstest-toggle-external').hide();
}
}
});
// myapp/main.js
define(['wq/app', 'wq/map', './gpsinit', ...],
function(app, map, gpsInit) {
app.use(map);
app.use(gpsInit);
app.init(config).then(...);
);var map = L.map("...", {...});
var fields = {
'toggle': $('input[name=toggle]'),
'latitude': $('input[name=latitude]'),
'longitude': $('input[name=longitude]'),
'accuracy': $('input[name=accuracy]'),
'source': $('input[name=source]')
};
var locator = locate.locator(map, fields);
if (navigator.geolocation.canSetSource) {
locator.internalStart = function() {
navigator.geolocation.setSource(
'internal', locator.gpsStart, locator.onerror
);
};
locator.externalStart = function() {
navigator.geolocation.setSource(
'external', locator.gpsStart, locator.onerror
);
};
locator.internalStop = locator.externalStop = locator.gpsStop;
} else {
$('label[for=gpstest-toggle-internal]').text("GPS");
$('#gpstest-toggle-internal').val("gps");
$('label[for=gpstest-toggle-external], #gpstest-toggle-external').hide();
}