Translated in 🇰🇷Korean
Ludwig is an open-source, declarative machine learning framework that makes it easy to define deep learning pipelines with a simple and flexible data-driven configuration system. Ludwig is suitable for a wide variety of AI tasks, and is hosted by the Linux Foundation AI & Data.
Ludwig allows users to define their deep learning pipeline by simply providing a configuration file, which lists the inputs and outputs, and their respective data types. Ludwig will then assemble and train a deep learning model and based on the configuration file, determine how inputs and outputs are preprocessed, encoded, decoded and which metrics and loss criterion to use.
Writing a configuration file for Ludwig is easy. The configuration file flexibility allows for full control of every aspect of the end-to-end pipeline. This includes exploring state-of-the-art model architectures, running a hyperparameter search, scaling up to larger than available memory datasets and multi-node clusters, and finally serving the best model in production. All of this is achieved through simple configuration file changes.
Finally, the use of abstract interfaces throughout the codebase makes it easy for users to extend Ludwig by adding new models, metrics, losses, preprocessing functions and register them to make them available immediately in the configuration system.
-
Data-Driven configuration system
A config YAML file that describes the schema of your data (input features, output features, and their types) is all you need to start training deep learning models. Ludwig uses declared features to compose a deep learning model accordingly.
input_features: - name: data_column_1 type: number - name: data_column_2 type: category - name: data_column_3 type: text - name: data_column_4 type: image ... output_features: - name: data_column_5 type: number - name: data_column_6 type: category ...
-
Training, prediction, and evaluation from the command line
Simple commands can be used to train models and predict new data.
ludwig train --config config.yaml --dataset data.csv ludwig predict --model_path results/experiment_run/model --dataset test.csv ludwig eval --model_path results/experiment_run/model --dataset test.csv -
Ludwig also provides a simple programmatic API for all of the functionality described above and more.
from ludwig.api import LudwigModel # train a model config = { "input_features": [...], "output_features": [...], } model = LudwigModel(config) data = pd.read_csv("data.csv") train_stats, _, model_dir = model.train(data) # or load a model model = LudwigModel.load(model_dir) # obtain predictions predictions = model.predict(data)
-
Train models in a distributed setting using Horovod, which allows training on a single machine with multiple GPUs or multiple machines with multiple GPUs.
-
Serve models using FastAPI.
ludwig serve --model_path ./results/experiment_run/model curl http://0.0.0.0:8000/predict -X POST -F "movie_title=Friends With Money" -F "content_rating=R" -F "genres=Art House & International, Comedy, Drama" -F "runtime=88.0" -F "top_critic=TRUE" -F "review_content=The cast is terrific, the movie isn't."
-
Run hyperparameter optimization locally or using Ray Tune.
ludwig hyperopt --config config.yaml --dataset data.csv
-
Ludwig AutoML takes a dataset, the target column, and a time budget, and returns a trained Ludwig model.
-
Ludwig provides an extendable interface to integrate with third-party systems for tracking experiments. Third-party integrations exist for Comet ML, Weights & Biases, WhyLabs and MLFlow.
-
Ludwig is built from the ground up with extensibility in mind. It is easy to add new data types by implementing clear, well-documented abstract classes that define functions to preprocess, encode, and decode data.
Furthermore, new
torch nn.Modulemodels can be easily added by them to a registry. This encourages reuse and sharing new models with the community. Refer to the Developer Guide for further details.
For a full tutorial, check out the official getting started guide, or take a look at end-to-end Examples.
Install from PyPi. Be aware that Ludwig requires Python 3.7+.
pip install ludwigCreate a config that describes the schema of your data.
Assume we have a text classification task, with data containing a sentence and class column like the following.
| sentence | class |
|---|---|
| Former president Barack Obama ... | politics |
| Juventus hired Cristiano Ronaldo ... | sport |
| LeBron James joins the Lakers ... | sport |
| ... | ... |
A configuration will look like this.
input_features:
- name: sentence
type: text
output_features:
- name: class
type: categoryStarting from a simple config like the one above, any and all aspects of the model architecture, training loop, hyperparameter search, and backend infrastructure can be modified as additional fields in the declarative configuration to customize the pipeline to meet your requirements.
input_features:
- name: sentence
type: text
encoder: transformer
layers: 6
embedding_size: 512
output_features:
- name: class
type: category
loss: cross_entropy
trainer:
epochs: 50
batch_size: 64
optimizer:
type: adamw
beat1: 0.9
learning_rate: 0.001
backend:
type: ray
cache_format: parquet
processor:
type: dask
trainer:
use_gpu: true
num_workers: 4
resources_per_worker:
CPU: 4
GPU: 1
hyperopt:
metric: f1
sampler: random
parameters:
title.num_layers:
lower: 1
upper: 5
trainer.learning_rate:
values: [0.01, 0.003, 0.001]For details on what can be configured, check out Ludwig Configuration docs.
Simple commands can be used to train models and predict new data.
ludwig train --config config.yaml --dataset data.csvThe training process will produce a model that can be used for evaluating on and obtaining predictions for new data.
ludwig predict –model path/to/trained/model –dataset heldout.csv
ludwig evaluate –model path/to/trained/model –dataset heldout.csvLudwig provides a suite of visualization tools allows you to analyze models' training and test performance and to compare them.
ludwig visualize --visualization compare_performance --test_statistics path/to/test_statistics_model_1.json path/to/test_statistics_model_2.jsonFor the full set of visualization see the Visualization Guide.
Try applying Ludwig to your data. Reach out if you have any questions.
Ludwig is a profound utility for research scientists, data scientists, and machine learning engineers.
Ludwig takes care of the engineering complexity of deep learning out of the box, enabling research scientists to focus on building models at the highest level of abstraction.
Data preprocessing, hyperparameter optimization, device management, and distributed training for newly registered torch.nn.Module models come completely free.
Creating a state-of-the-art baseline and comparing it with a new model is a simple config change.
Apply new models across the extensive set of tasks and datasets that Ludwig supports. Ludwig includes a full benchmarking toolkit accessible to any user, for running experiments with multiple models across multiple datasets with just a simple configuration.
Any and all aspects of the model architecture, training loop, hyperparameter search, and backend infrastructure can be modified as additional fields in the declarative configuration to customize the pipeline to meet your requirements.
For details on what can be configured, check out Ludwig Configuration docs.
Mix and match tabular data, text, images, and even audio into complex model configurations without writing code.
Automatically track all trials and metrics with tools like Tensorboard, Comet ML, Weights & Biases, and MLflow.
Go from training on your local machine to the cloud without code changes.
Ludwig also natively integrates with pre-trained models, such as the ones available in Huggingface Transformers. Users can choose from a vast collection of state-of-the-art pre-trained PyTorch models to use without needing to write any code at all. For example, training a BERT-based sentiment analysis model with Ludwig is as simple as:
ludwig train --dataset sst5 -–config_str “{input_features: [{name: sentence, type: text, encoder: bert}], output_features: [{name: label, type: category}]}”Ludwig AutoML allows users to obtain trained models by providing just a dataset, the target column, and a time budget.
auto_train_results = ludwig.automl.auto_train(dataset=my_dataset_df, target=target_column_name, time_limit_s=7200)Ludwig makes it easy to serve deep learning models, including on GPUs. Launch a REST API for your trained Ludwig model.
ludwig serve --model_path=/path/to/modelLudwig supports exporting models to efficient Torschscript bundles.
ludwig export_torchscript -–model_path=/path/to/model- Named Entity Recognition Tagging
- Natural Language Understanding
- Machine Translation
- Chit-Chat Dialogue Modeling through seq2seq
- Sentiment Analysis
- One-shot Learning with Siamese Networks
- Visual Question Answering
- Spoken Digit Speech Recognition
- Speaker Verification
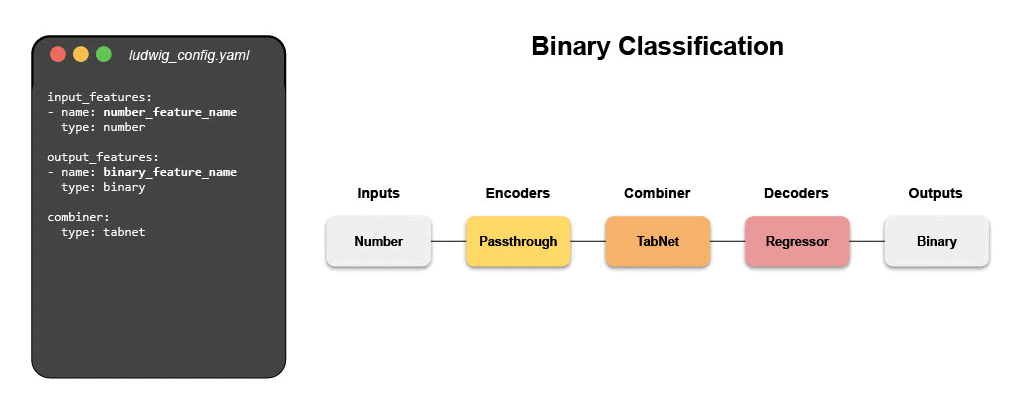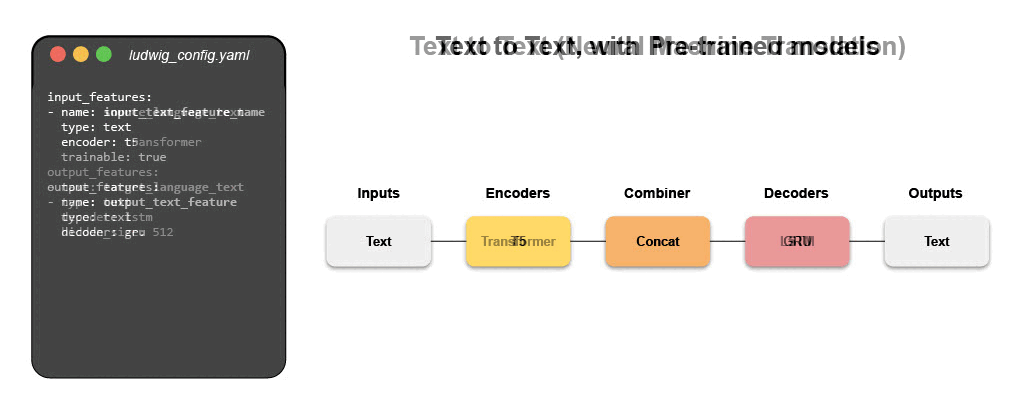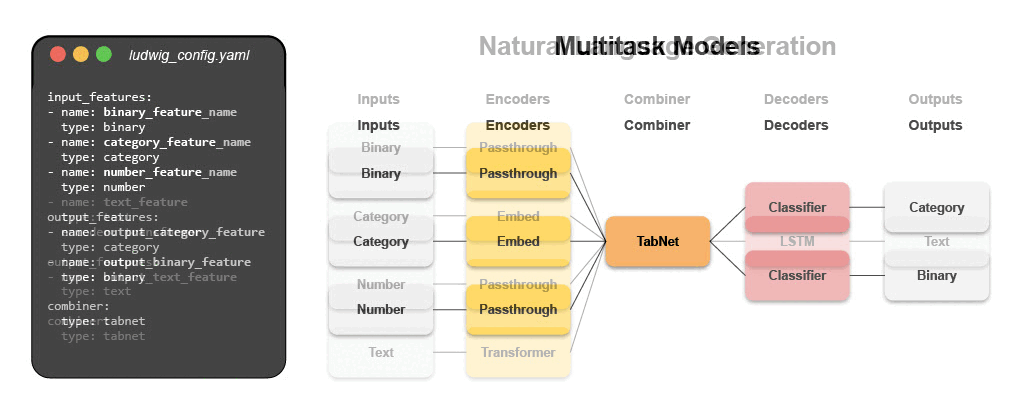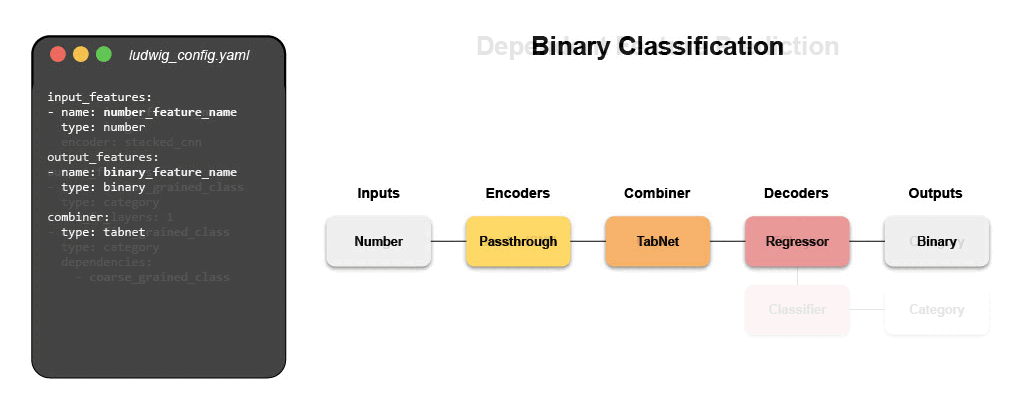
- Binary Classification (Titanic)
- Timeseries forecasting
- Timeseries forecasting (Weather)
- Movie rating prediction
- Multi-label classification
- Multi-Task Learning
- Simple Regression: Fuel Efficiency Prediction
- Fraud Detection
Read our publications on Ludwig, declarative ML, and Ludwig’s SoTA benchmarks.
Learn more about how Ludwig works, how to get started, and work through more examples.
If you are interested in contributing, have questions, comments, or thoughts to share, or if you just want to be in the know, please consider joining the Ludwig Slack and follow us on Twitter!