-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 76
Hadoop Zip Artifacts
(Since version 0.5.14 - Contributed by Anant Nag) The Hadoop Plugin includes a number of features for building Hadoop zip artifacts that can be uploaded to your Hadoop workflow scheduler. These features are declarative in nature - you declare the exact contents of your zip files and how they are laid out.
These features were specifically designed this way to reduce the amount of "magic" that happens while building your Hadoop zips. Previous generations of Hadoop developer tools at LinkedIn did a lot of magic when built zips, and as a consequence users had a very difficult time understanding errors related to launching their Hadoop jobs.
To configure what zip artifacts you want to build, declare a hadoopZip block. Each zip you build will contain all of the dependencies in the hadoopRuntime dependency configuration.
By default, these dependencies will be placed in the root directory of the zip. However, you can customize this path within the zip by setting the libPath property in the hadoopZip block. Most users either set this property to lib or just leave it set to the default value.
Within a hadoopZip block, invoke the zip method to declare a Hadoop zip artifact. Invoking the zip method creates a Gradle Zip task whose artifact name is set to projectName-projectVersion-zipName.zip (with zipName as the artifact classifier).
With this method, you can declare zip artifacts for different Hadoop clusters or workflow managers. You can customize the contents of each zip by using Gradle CopySpecs.
// In your <rootProject>/<project>/build.gradle:
// Declare that your build depends on the Hadoop zips, and that Hadoop zips depend on building the Hadoop DSL
startHadoopZips.dependsOn buildAzkabanFlows
build.dependsOn buildHadoopZips
hadoopZip {
// Declare the directory in the zip file to which the contents of the hadoopRuntime configuration will be added.
// By default, this is set to the root directory of the zip, but users often set it to "lib".
libPath = "lib"
// Declare Hadoop zip artifacts by using "zip". The idea is to give you an easy to way generate zips that are customized
// for different Hadoop clusters or workflow managers. The zip name is added as a classifier to the artifact name.
zip("azkabanDev") {
// Add extra brackets for lazy evaluation of the Hadoop DSL buildPath folder
from { fileTree("azkabanDev").files }
}
// You can use zip more than once to specify many zips for different clusters or workflow managers
zip("azkabanProd") {
// Add extra brackets for lazy evaluation of the Hadoop DSL buildPath folder
from { fileTree("azkabanProd").files }
}
}
Within a hadoopZip block, you can declare a base block containing Gradle CopySpecs that should be added to every Hadoop zip you declare (including the main zip, if you declare one). The idea behind this method is to provide an easy way to specify common files that should be added to every zip. Using this declaration is optional. Using base is an especially convenient way to add the files that are the same for every cluster to your Hadoop zip artifacts.
// In your <rootProject>/<project>/build.gradle:
hadoopZip {
// Declare base CopySpecs that will be included in all the other Hadoop zips you declare
base {
from("src/main/pig") {
into "src/main/pig"
}
}
// Declare Hadoop zip artifacts for your project for dev and prod grids
zip("azkabanDev") {
// Automatically includes files from "src/main/pig" since this CopySpec was declared in base
}
zip("azkabanProd") {
// Automatically includes files from "src/main/pig" since this CopySpec was declared in base
}
}
Within a hadoopZip block, invoking the main method results in the creation of a zip whose name is projectName-projectVersion.zip with no classifier. The idea behind this method is to provide a way to declare your zip when you know you only want to produce a single zip artifact. Using this method is optional.
At LinkedIn, you probably DO NOT want to declare a main zip. You usually want to use the LinkedIn-specific CRT method to declare a zip artifact that is setup correctly for CRT. This method is intended for open source users.
For each zip artifact you declare in the hadoopZip block using the zip method, a Gradle Zip task will be generated called <zipName>HadoopZip. If you run gradle tasks and look in the Hadoop Plugin tasks section, you should see all of the generated Zip tasks there.
// Declaring the "azkaban" zip in the hadoopZip block will generate the Zip task named azkabanHadoopZip
hadoopZip {
zip("azkaban") {
// ...
}
}
For the example above, when you run gradle tasks you should see the task there: 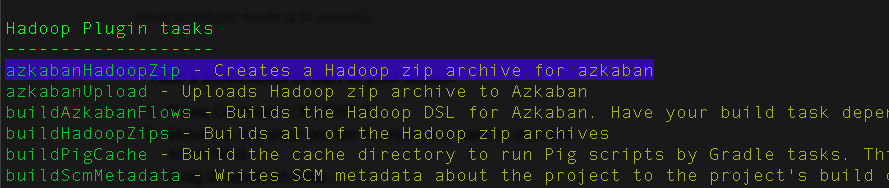
These are no-op placeholder tasks that allow you to setup task dependencies related to building the Hadoop zip artifacts you declared in the hadoopZip block.
When the Hadoop zip artifacts are built, first the startHadoopZips task runs, then the generated Zip tasks for each zip you declared in the hadoopZip block run, and finally the buildHadoopZips task runs. If you declare that startHadoopZips depends on task A, you are guaranteed that task A will run before any Hadoop zip artifacts are built. Similarly, if you declare that task B depends on buildHadoopZips, you are guaranteed that the Hadoop zips will have finished building before task B starts.
Usually, you want to declare that the task that builds the Hadoop DSL depends on the startHadoopZips task, and that the build task depends on the buildHadoopZips task. See the section on Building the Hadoop DSL for Azkaban for more information: Building the Hadoop DSL for Azkaban.