An application allows a user to control redirection to another URL. A threat actor may exploit that by sending a malicious redirect to a victim using the application, leading the victim to be sent to a malicious website controlled by the threat actor.
Clone this current repo recursively
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/qeeqbox/open-redirectRun the webapp using Python
python3 open-redirect/vulnerable-web-app/webapp.pyOpen the webapp in your browser 127.0.0.1:5142
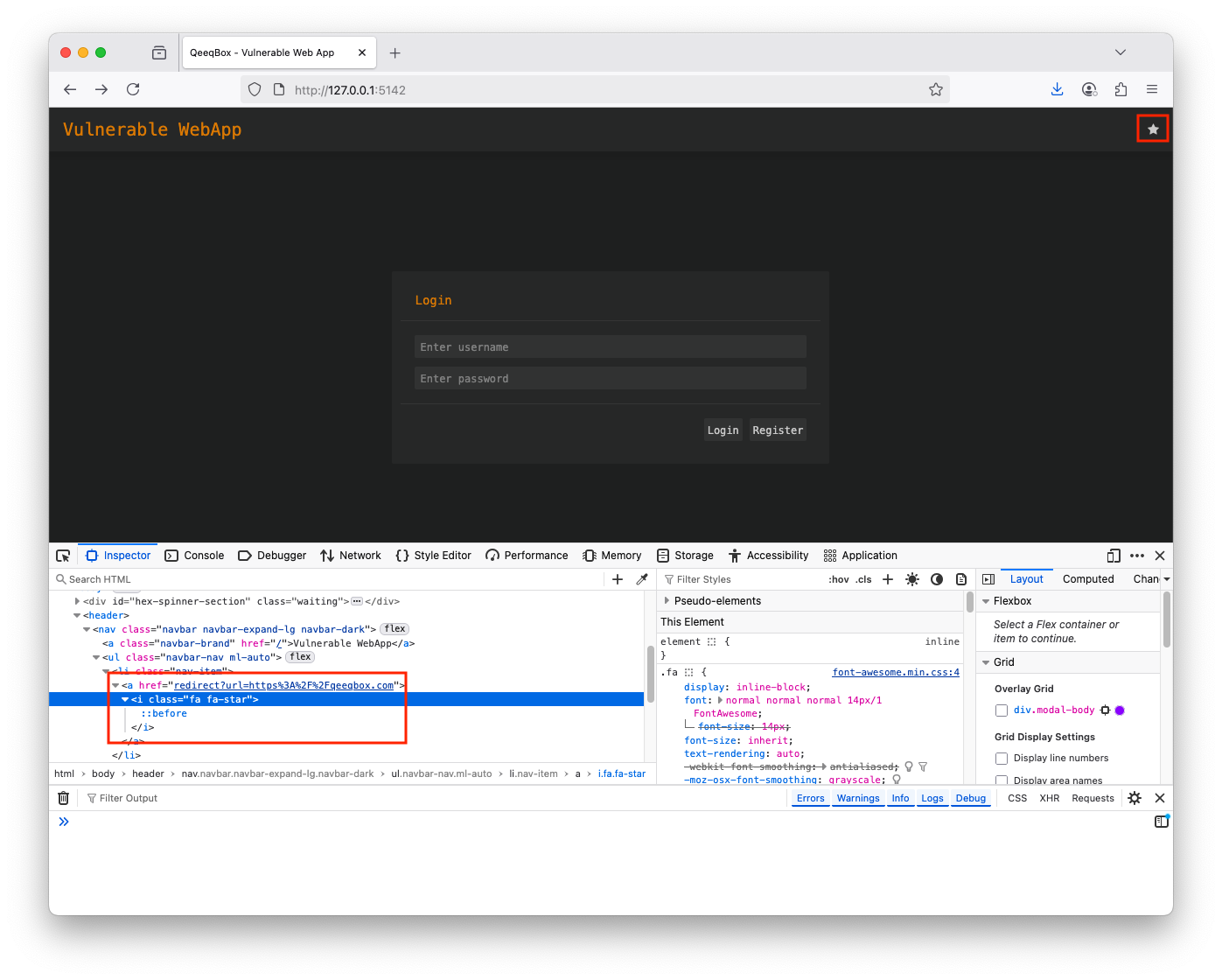
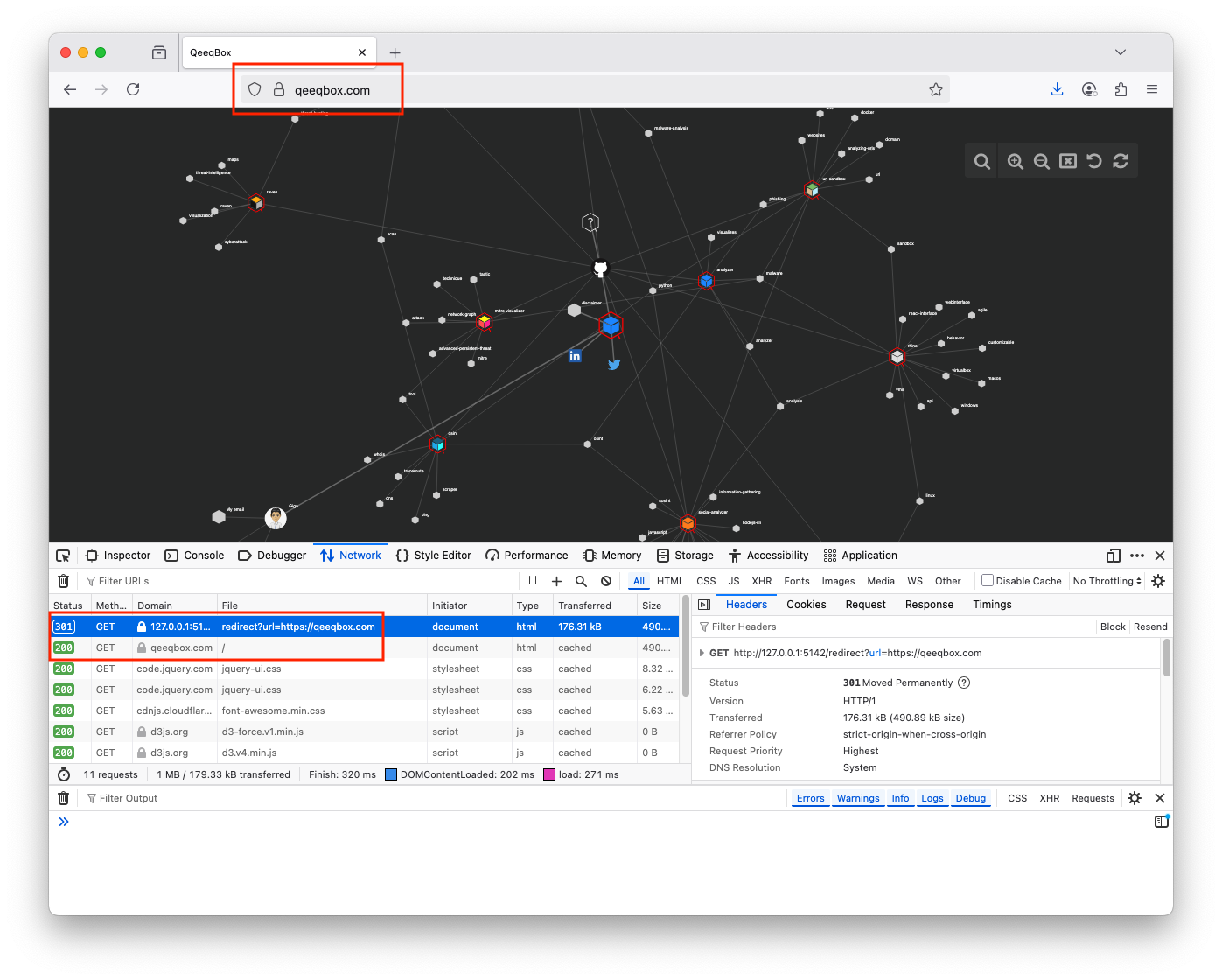
Right-click on the start icon and click Inspect from the menu. The icon has a hyperlink Go to the network tab and then click on the star icon to see the network requests. The redirect request was sent back to qeeqbox.com from the webapp. The client makes a new GET request to qeeqbox.com A threat actor could send a malicious link, such as http://127.0.0.1:5142/redirect?url=http%3A%2F%2Fmalicious.xyz123, using social engineering attacks. If the victim falls for it, they will be redirected to the malicious website. If the victim clicks on update Firefox, they will install a malicious fileWhen a client sends a GET request to the redirect route with a URL parameter, the URL is passed to the redirect() function
def do_GET(self):
....
elif parsed_url.path == "/redirect":
self.redirect(get_request_data["url"][0])
return
....There redirect() function in the backend that takes a URL parameter. This function sends the 301 HTTP response code along with the URL to redirect to
def redirect(self, url):
self.send_response(301)
self.send_header('Location', url)
self.end_headers()