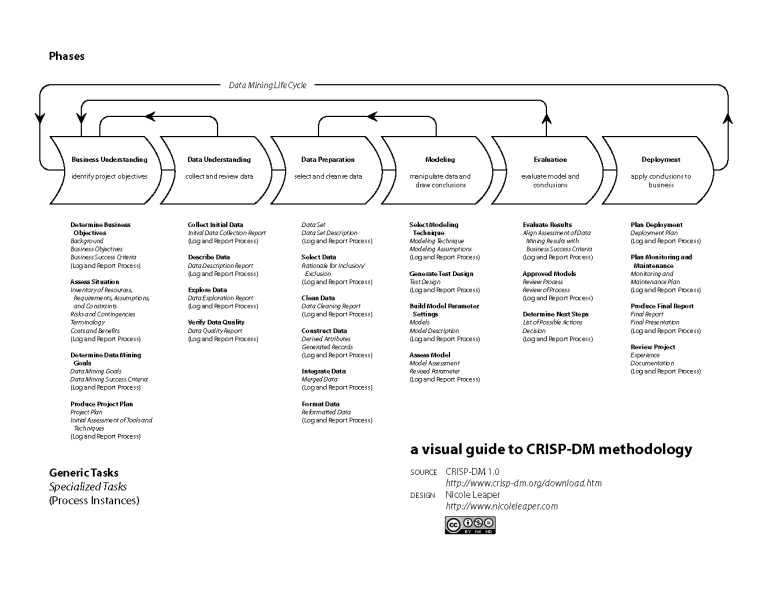
This repository was developed as part of the Discover track at the Jheronimus Academy of Data Science (JADS). The aim of these 'discovery projects' is to facilitate the participants in getting hands-on experience in building a model following the CRISP-DM framework. Learning-by-doing is arguably the best way to get through the valley of despair as quickly as possible.
Made with creative commons in mind, we have used and remixed what we think are the most useful datasets, notebooks, articles available in the public domain. Each folder contains a set of materials for a given dataset, with specific assignments and questions. Examples of solutions and best practices are included in R and Python notebooks. In due course we aim to add H2O Flow for those preferring to work with a graphical UI.
An alternative, more detailed and rich dataset than the Boston housing dataset (which dates from 1978). Available on Kaggle's Getting Started Prediction Competition with a lot of useful tutorials. Alternatively, use the AmesHousing R package.
The Otto Group is one of the world’s biggest e-commerce companies, with subsidiaries in more than 20 countries, including Crate & Barrel (USA), Otto.de (Germany) and 3 Suisses (France). For this challenge, you are provided a dataset with 93 features for more than 200,000 products. The objective is to build a predictive model which is able to distinguish between seven main product categories. Originally a Kaggle competition.
Four combined databases compiling heart disease information. This database contains 76 attributes, but all published experiments refer to using a subset of 14 of them. In particular, the Cleveland database is the only one that has been used by ML researchers to this date. The "goal" field refers to the presence of heart disease in the patient. It is integer valued from 0 (no presence) to 4. Also available on Kaggle, data.world and included in the kmed R package
This dataset is originally from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. The objective of the dataset is to diagnostically predict whether or not a patient has diabetes, based on certain diagnostic measurements included in the dataset. Several constraints were placed on the selection of these instances from a larger database. In particular, all patients here are females at least 21 years old of Pima Indian heritage. Interestingly, the objective of the original study by Schulz et al. in 2006 was to determine genetic and environmental determinants for type 2 diabetes and obesity. To this purpose, the effects of different environments on these diseases in Pima Indians in Mexico and Available on Kaggle, data.world and included in the mlbench R package. Note there is a different UCI diabetes dataset
The datasets contains transactions made by credit cards in September 2013 by european cardholders and was compiled by the Machine Learning group of Université Libre de Bruxelles in collaboration with Worldline. This dataset presents transactions that occurred in two days, where we have 492 frauds out of 284,807 transactions. The dataset is highly unbalanced, the positive class (frauds) account for 0.172% of all transactions.
It contains only numerical input variables which are the result of a PCA transformation, as due to confidentiality issues the original features cannot be provided. Features V1, V2, … V28 are the principal components obtained with PCA, the only features which have not been transformed with PCA are 'Time' and 'Amount'. Feature 'Time' contains the seconds elapsed between each transaction and the first transaction in the dataset. The feature 'Amount' is the transaction Amount, this feature can be used for example-dependant cost-senstive learning. Feature 'Class' is the response variable and it takes value 1 in case of fraud and 0 otherwise. Available on Kaggle, data.world and datahub.io.
Data from a semi-conductor manufacturing process. A complex modern semi-conductor manufacturing process is normally under consistent surveillance via the monitoring of signals/variables collected from sensors and or process measurement points. However, not all of these signals are equally valuable in a specific monitoring system. The measured signals contain a combination of useful information, irrelevant information as well as noise. It is often the case that useful information is buried in the latter two. Engineers typically have a much larger number of signals than are actually required. If we consider each type of signal as a feature, then feature selection may be applied to identify the most relevant signals. The Process Engineers may then use these signals to determine key factors contributing to yield excursions downstream in the process. This will enable an increase in process throughput, decreased time to learning and reduce the per unit production costs.
To enhance current business improvement techniques the application of feature selection as an intelligent systems technique is being investigated.
The dataset presented in this case represents a selection of such features where each example represents a single production entity with associated measured features and the labels represent a simple pass/fail yield for in house line testing, figure 2, and associated date time stamp. Where .1 corresponds to a pass and 1 corresponds to a fail and the data time stamp is for that specific test point. Available on Kaggle and the UCI Machine Learning repository.
- Each dataset and its accompanying material is put in a separate folder.
- Copies of articles are included for convenience.
- Non-open-access journals are referenced.
- Notebooks can be opened directly in Google Colab, to make it easier to get started directly without having to install Anaconda etc.
An end-to-end machine learning tutorial following the steps of CRISP-DM is also included, using the California housing prices dataset. This tutorial is based on based chapter 2 from Aurélien Géron's book Hands-On Machine Learning with SCikit-Learn and TensorFlow.
© 2020 by Daniel Kapitan and Joran Lokkerbol. JADS Discover projects.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.