-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Goal oriented hypermedia workflow
Hypergoal - goal oriented hypermedia workflow
A system for which enables hypermedia clients to express a goal which the server directs them to achieve. This differs from traditional clients in which the server(s) generally do not have the context of what the client is trying to do.
Sample use cases
- Attending an event
- Purchasing a house
- [Anya Stettler] (https://github.com/anyarms)
- [Daniel Yokomizo] (https://github.com/dyokomizo)
- [Glenn Block] (https://github.com/glennblock)
- [James Snell] (https://github.com/jasnell)
- [Thomas Velthoven] (https://github.com/thovel)
- Misha put your info here :-)
- We need to enable hypermedia clients to participate in complex and distributed business processes across multiple systems and vendors
- Allows clients to focus on the goal rather than the rel
- Additional workflows can be discovered as part of an existing workflow.
- The workflow can change and evolve dynamically.
- Allows work to be highly distributed across many systems
- Does not require third party systems to be coordinated
- Can build on existing standards
-
Context- A JSON object which contains the goal that the client is trying to achieve, and data related to the achievement of that goal. It is a JSON-LD document. -
Activity- A JSON object which contains one or moreStepswhich may be executed in parallel. -
Step- A JSON object which contains two links:- A link to a resource which can be a task or another workflow.
- A link to a completion callback for the
Step.
-
Worklow- A JSON object which contains one or more Activities which are necessary to complete a goal.
-
Client- The client who is trying to achieve a goal -
Context Controller- Manages persistence of theContext -
Workflow Controller- Manages the overall workflow to help the client achieve it's goal. Ensures theContextis always valid. CreatesActivitiesfor the client to navigate the workflow.
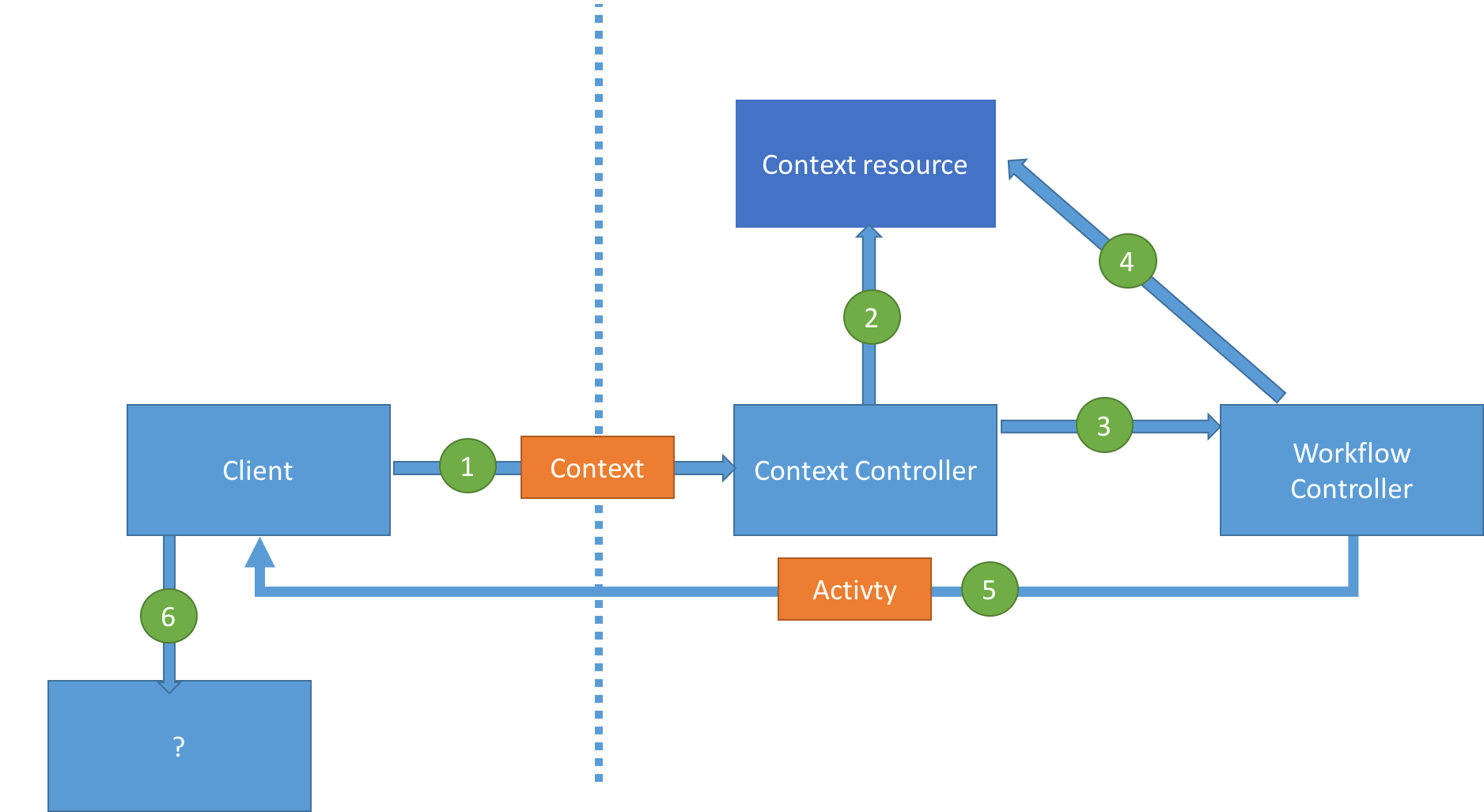
- Client sends a
Contextto aContext Controllerto express the goal it wants to perform. ThisGoal Contextcontains the goal description and related data. -
Context Controllerpersists theContext resource. (add link here) -
Contextis sent to theWorkflow Controller. -
Workflow Controllervalidates that theContextcontains the pre-requisite information. -
Workflow Controllerreturns an activity to the client
- If the
Contextis valid, the controller returns anActivitycontaining a list of possible steps to the client, some of which are required and all off which may be performed in parallel. - If the
Contextis not valid, the controller returns anActivitywhich containsStepsfor making theContextvalid. - Each
Stepwithin theActivityhas a link to aTaskor AWorkflow. TheStepalso contains a callback link to theContext Controllerto say that theStephas completed. - There is a also an
Activitycompleted callback link which points to theWorkflow Controller.
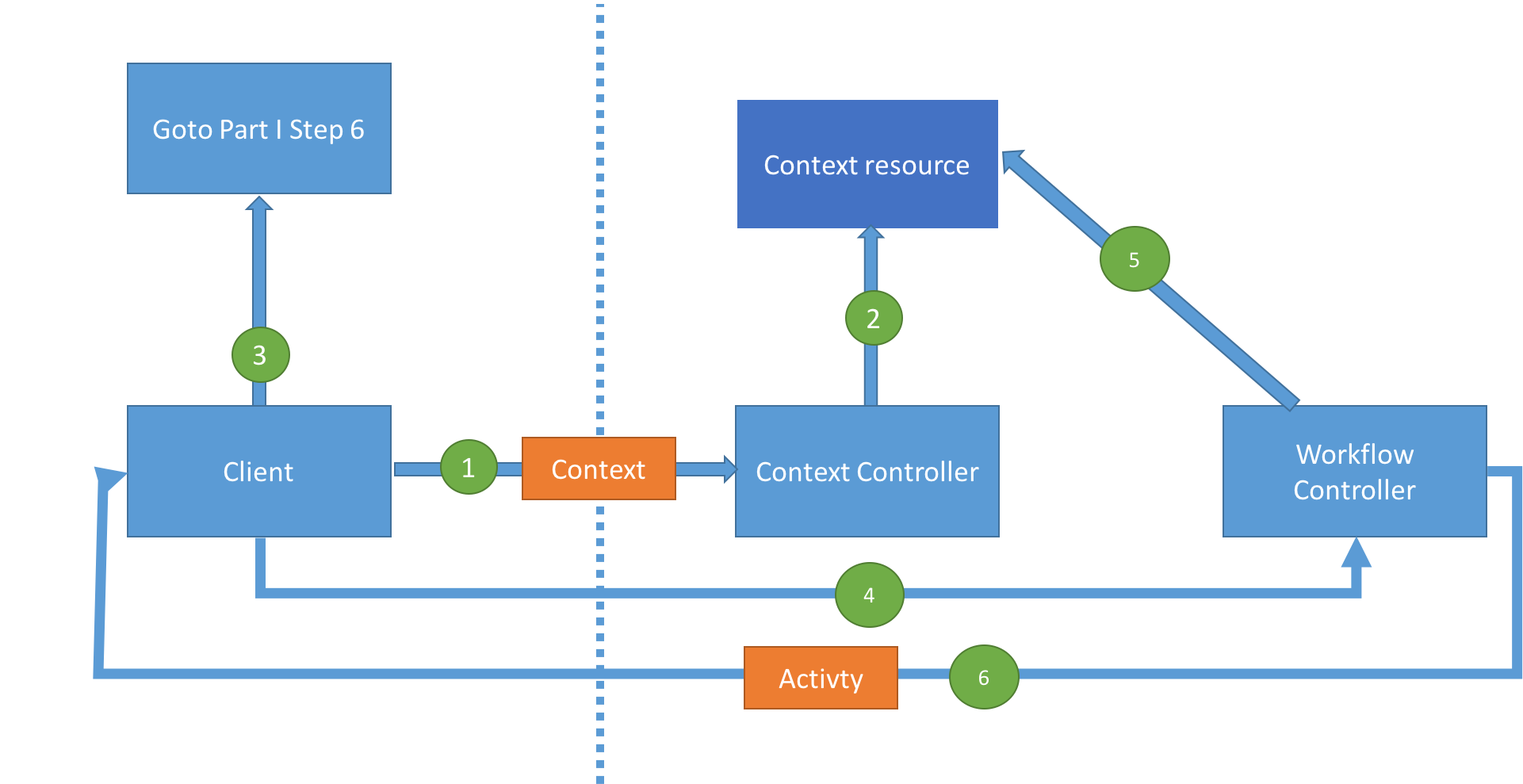
- The client follows a
Stepwithin theActivity. - The client follows the
Stepcompletion callback passing in a newStep Contextwhich contains the data for theStep. - The
Context Controllerpersists theStep Context. It then makes a copy of theGoal Contextwhich contains a link to theStep Context. - If there are more steps to be performed, goto step
6. - The client invokes the
Activitycompleted callback. - The
Workflow Controllervalidates that all requiredActivity Stepswere completed.
- If the
Activityhas not been completed, it will return a newActivitywith the remainingStepsthat need to be completed. - If the
Activityhas been completed, then it will return a newActivitycontaining the next of set ofStepsin theWorkflow. 13 - Goto step6

planning -> bookings reconsiliation -> transitions
-Goal/State
- need
- preference
- policy
- requirement
- preference
planning: Advice potential-transition(state1, state2) option1 option2 option3
rank(risk(needs), fulfill(needs)) = match(option1, needs) rank(risk(needs), fulfill(needs)) = match(option2, needs) rank(risk(needs), fulfill(needs)) = match(option1, needs) rank(risk(needs), fulfill(needs)) = match(option2, needs)
plan booking1(option1) booking2(option2)
reconciliation executed-transition(booking)
advice provider ranker planner reconciler
Home :: Code of Conduct :: People :: Agenda :: Travel :: What Is RestFest?