-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 266
Max Area of Island
- 🔗 Leetcode Link: Max Area of Island
- 💡 Problem Difficulty: Medium
- ⏰ Time to complete: 20 mins
- 🛠️ Topics: Array, 2D-Array, DFS, BFS
- 🗒️ Similar Questions: Surrounded Regions, Number of Islands, Count Sub Islands
Understand what the interviewer is asking for by using test cases and questions about the problem.
- Established a set (2-3) of test cases to verify their own solution later.
- Established a set (1-2) of edge cases to verify their solution handles complexities.
- Have fully understood the problem and have no clarifying questions.
- Have you verified any Time/Space Constraints for this problem?
- Can the input grid be blank?
- Let’s assume the grid is not blank. We don’t need to consider empty inputs.
- Can the islands have lakes?
- Let’s assume the islands do not have lakes
- What is the time and space constraints?
- Time complexity should be O(m*n), m being the rows of the matrix and n being the columns of matrix. Space complexity should be O(1), excluding the recursive stack.
HAPPY CASE
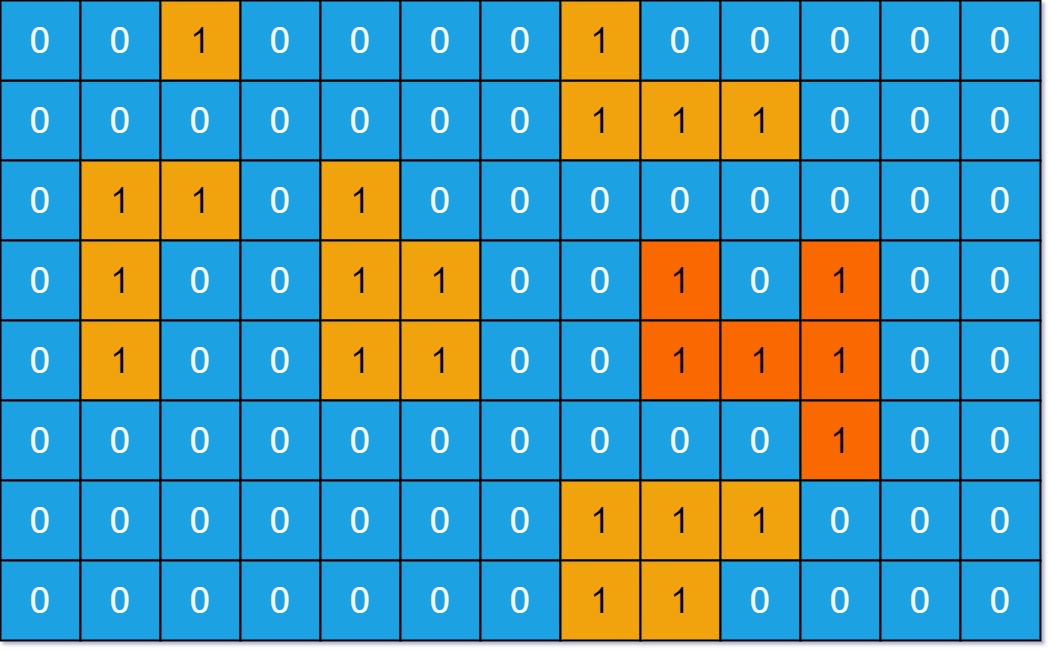
Input: grid = [
[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],
[0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]
]
Output: 6
Explanation: The answer is not 11, because the island must be connected 4-directionally.Input: grid = [[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]]
Output: 0
EDGE CASE
Input: grid = [[1]]
Output: 1
Match what this problem looks like to known categories of problems, e.g. Linked List or Dynamic Programming, and strategies or patterns in those categories.
For 2D-Array, common solution patterns include:
- Perform a BFS/DFS Search through the 2D Array
- A search through the 2D Array (either BFS or DFS) can help us find and measure the area of each islands. Which of these two traversals will better help us locate islands?
- Hash the 2D Array in some way to help with the Strings
- Hashing would not directly help us find islands. However, we could hash where certain 1's are in the 2D Array to jumpstart searches (BFS/DFS) faster.
- Create/Utilize a Trie
- A Trie would not help us much in this problem since we are not trying to determine anything about a sequence of characters.
Plan the solution with appropriate visualizations and pseudocode.
General Idea: Perform a DFS for islands in the grid.
main function:
0) Write the helper dfs function
1) Initialize a variable to keep track of the largest islands
2) Iterate over the grid
3) If a '1' is seen: "explore" the island from this '1' using dfs and check size against previously recorded max area
4) Return the largest island size
helper dfs function:
0) Basecase: Out of bound or grid value is 0, return 0
1) Change the grid value to '0' to mark it as visited
2) Recursively check 4 neighbors from the current cell for more island cells (1's) and tack on 1 to account for this square- It can be easy to miss the underlying traversal problem. Make sure to think about how you can optimize traversing the input grid and use the structure to your advantage.
- Some people might forget to use a visited set or some other mechanism to keep track of what coordinates with 1's have already been visited.
Implement the code to solve the algorithm.
class Solution:
def maxAreaOfIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
# Write the helper dfs function
def helper(i: int,j:int) -> int:
# Basecase: Out of bound or grid value is 0, return 0
if i < 0 or i > len(grid) - 1 or j < 0 or j > len(grid[0]) - 1 or grid[i][j] == 0:
return 0
# Change the grid value to '0' to mark it as visited
grid[i][j] = 0
# Recursively check 4 neighbors from the current cell for more island cells (1's) and tack on 1 to account for this square
return helper(i+1, j) + helper(i-1, j) + helper(i, j+1) + helper(i, j-1) + 1
# Initialize a variable to keep track of the largest islands
maxArea = 0
# Iterate over the grid
for i in range(len(grid)):
for j in range(len(grid[0])):
# If a '1' is seen: "explore" the island from this '1' using dfs and check size against previously recorded max area
if grid[i][j] == 1:
maxArea = max(maxArea, helper(i,j))
# Return the largest island size
return maxAreaclass Solution {
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
// Initialize a variable to keep track of the largest islands
int max_area = 0;
// Iterate over the grid
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++)
// If a '1' is seen: "explore" the island from this '1' using dfs and check size against previously recorded max area
if(grid[i][j] == 1)max_area = Math.max(max_area, AreaOfIsland(grid, i, j));
// Return the largest island size
return max_area;
}
// helper dfs function
public int AreaOfIsland(int[][] grid, int i, int j){
// Basecase: Out of bound or grid value is 0, return 0
if( i >= 0 && i < grid.length && j >= 0 && j < grid[0].length && grid[i][j] == 1){
// Change the grid value to '0' to mark it as visited
grid[i][j] = 0;
// Recursively check 4 neighbors from the current cell for more island cells (1's) and tack on 1 to account for this square
return 1 + AreaOfIsland(grid, i+1, j) + AreaOfIsland(grid, i-1, j) + AreaOfIsland(grid, i, j-1) + AreaOfIsland(grid, i, j+1);
}
return 0;
}
}Review the code by running specific example(s) and recording values (watchlist) of your code's variables along the way.
- Trace through your code with an input to check for the expected output
- Catch possible edge cases and off-by-one errors
Evaluate the performance of your algorithm and state any strong/weak or future potential work.
Assume N represents the number of rows in 2D-array.
Assume M represents the number of columns in 2D-array.
-
Time Complexity:
O(N * M)we need to view each item in the 2D-Array -
Space Complexity:
O(1), we only need to store the max area, excluding the recursive call stack. IF we include the recursive call stack, it will costO(N*M)because a dfs call might be the entire matrix.